|
Reading Span
The reading span task (RST) is a common memory span task widely cited in, and adapted for, investigations of working memory, cognitive processing, and reading comprehension that was first published by Meredyth Daneman and Patricia Carpenter in 1980.Daneman, M., & Carpenter, P. A. (1980). Individual differences in working memory and reading. Journal of Verbal Learning and Verbal Behavior The ''Journal of Memory and Language'' is a peer-reviewed interdisciplinary academic journal of cognitive science, which focuses primarily on the issues of memory and language comprehension. It has been published by Elsevier since 1985. The curren ..., 19(4), 450–466. It is a verbal working memory test. Task Original The original RST required participants to read series of unconnected sentences aloud and to remember the final word of each sentence of a series (grouped according to the total number of sentences). With each sentence presented on a card, participants were cued to recall the me ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Memory Span
In psychology and neuroscience, memory span is the longest list of items that a person can repeat back in correct order immediately after presentation on 50% of all trials. Items may include words, numbers, or letters. The task is known as ''digit span'' when numbers are used. Memory span is a common measure of working memory and short-term memory. It is also a component of cognitive ability tests such as the WAIS. Backward memory span is a more challenging variation which involves recalling items in reverse order. As a functional aspect Functionally, memory span is used to measure the number of discrete units over which the individual can successively distribute his attention and still organize them into a working unit. To generalize, it refers to the ability of an individual to reproduce immediately, after one presentation, a series of discrete stimuli in their original order. Experiments in memory span have found that the more familiar a person is with the type of subject matter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
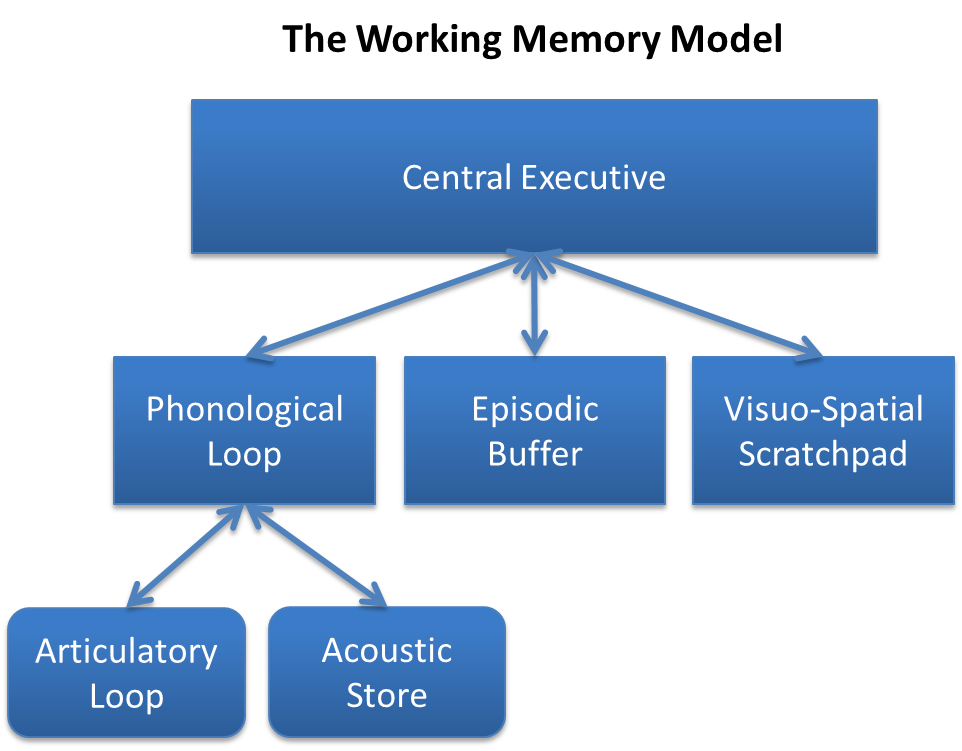
Working Memory
Working memory is a cognitive system with a limited capacity that can hold information temporarily. It is important for reasoning and the guidance of decision-making and behavior. Working memory is often used synonymously with short-term memory, but some theorists consider the two forms of memory distinct, assuming that working memory allows for the manipulation of stored information, whereas short-term memory only refers to the short-term storage of information. Working memory is a theoretical concept central to cognitive psychology, neuropsychology, and neuroscience. History The term "working memory" was coined by Miller, Galanter, and Pribram, and was used in the 1960s in the context of theories that likened the mind to a computer. In 1968, Atkinson and Shiffrin used the term to describe their "short-term store". What we now call working memory was formerly referred to variously as a "short-term store" or short-term memory, primary memory, immediate memory, operant me ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cognitive Processing
Cognition refers to "the mental action or process of acquiring knowledge and understanding through thought, experience, and the senses". It encompasses all aspects of intellectual functions and processes such as: perception, attention, thought, intelligence, the formation of knowledge, memory and working memory, judgment and evaluation, reasoning and computation, problem solving and decision making, comprehension and production of language. Imagination is also a cognitive process, it is considered as such because it involves thinking about possibilities. Cognitive processes use existing knowledge and discover new knowledge. Cognitive processes are analyzed from different perspectives within different contexts, notably in the fields of linguistics, musicology, anesthesia, neuroscience, psychiatry, psychology, education, philosophy, anthropology, biology, systemics, logic, and computer science. These and other approaches to the analysis of cognition (such as embodied cognition) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reading Comprehension
Reading comprehension is the ability to process text, understand its meaning, and to integrate with what the reader already knows. Fundamental skills required in efficient reading comprehension are knowing meaning of words, ability to understand meaning of a word from discourse context, ability to follow organization of passage and to identify antecedents and references in it, ability to draw inferences from a passage about its contents, ability to identify the main thought of a passage, ability to answer questions answered in a passage, ability to recognize the literary devices or propositional structures used in a passage and determine its tone, to understand the situational mood (agents, objects, temporal and spatial reference points, casual and intentional inflections, etc.) conveyed for assertions, questioning, commanding, refraining etc. and finally ability to determine writer's purpose, intent and point of view, and draw inferences about the writer (discourse-semantics). ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Patricia Carpenter (psychologist)
Patricia A. Carpenter is a psychologist who, as of 1997, held the Lee and Marge Gregg Professorship of Psychology at Carnegie Mellon University. Carpenter has studied individual variability in working memory, comprehension rates in speed reading, and how brain function during complex cognitive tasks appears in functional magnetic resonance imaging. With Marcel Just Marcel Just is D. O. Hebb Professor of Psychology at Carnegie Mellon University. His research uses brain imaging (fMRI) in high-level cognitive tasks to study the neuroarchitecture of cognition. Just's areas of expertise include psycholinguistic ..., she coauthored ''The Psychology of Reading and Language Comprehension'' (1987). Education and career Carpenter earned her Ph.D. in 1972 from Stanford University, and on earning her doctorate joined the Carnegie Mellon University faculty. Selected publications * * * References External linksPatricia Carpenter's Biography - CMU Department of Psychology [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Journal Of Verbal Learning And Verbal Behavior
The ''Journal of Memory and Language'' is a peer-reviewed interdisciplinary academic journal of cognitive science, which focuses primarily on the issues of memory and language comprehension. It has been published by Elsevier since 1985. The current editor-in-chief is Kathleen Rastle (Royal Holloway, University of London). The Institute for Scientific Information's ''Journal Citation Reports'' ranked the journal first in the field of linguistics, with a 2010 impact factor of 4.014. Abstracting and indexing The journal is indexed in Abstracts in Anthropology, Current Contents, Current Index to Journals in Education, Neuroscience Citation Index, PsycINFO, Research Alert, Scopus, and the Social Sciences Citation Index The Social Sciences Citation Index (SSCI) is a commercial citation index product of Clarivate Analytics. It was originally developed by the Institute for Scientific Information from the Science Citation Index. The Social Sciences Citation Inde .... External l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Memory Tests
Memory is the faculty of the mind by which data or information is encoded, stored, and retrieved when needed. It is the retention of information over time for the purpose of influencing future action. If past events could not be remembered, it would be impossible for language, relationships, or personal identity to develop. Memory loss is usually described as forgetfulness or amnesia. Memory is often understood as an informational processing system with explicit and implicit functioning that is made up of a sensory processor, short-term (or working) memory, and long-term memory. This can be related to the neuron. The sensory processor allows information from the outside world to be sensed in the form of chemical and physical stimuli and attended to various levels of focus and intent. Working memory serves as an encoding and retrieval processor. Information in the form of stimuli is encoded in accordance with explicit or implicit functions by the working memory processor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |