|
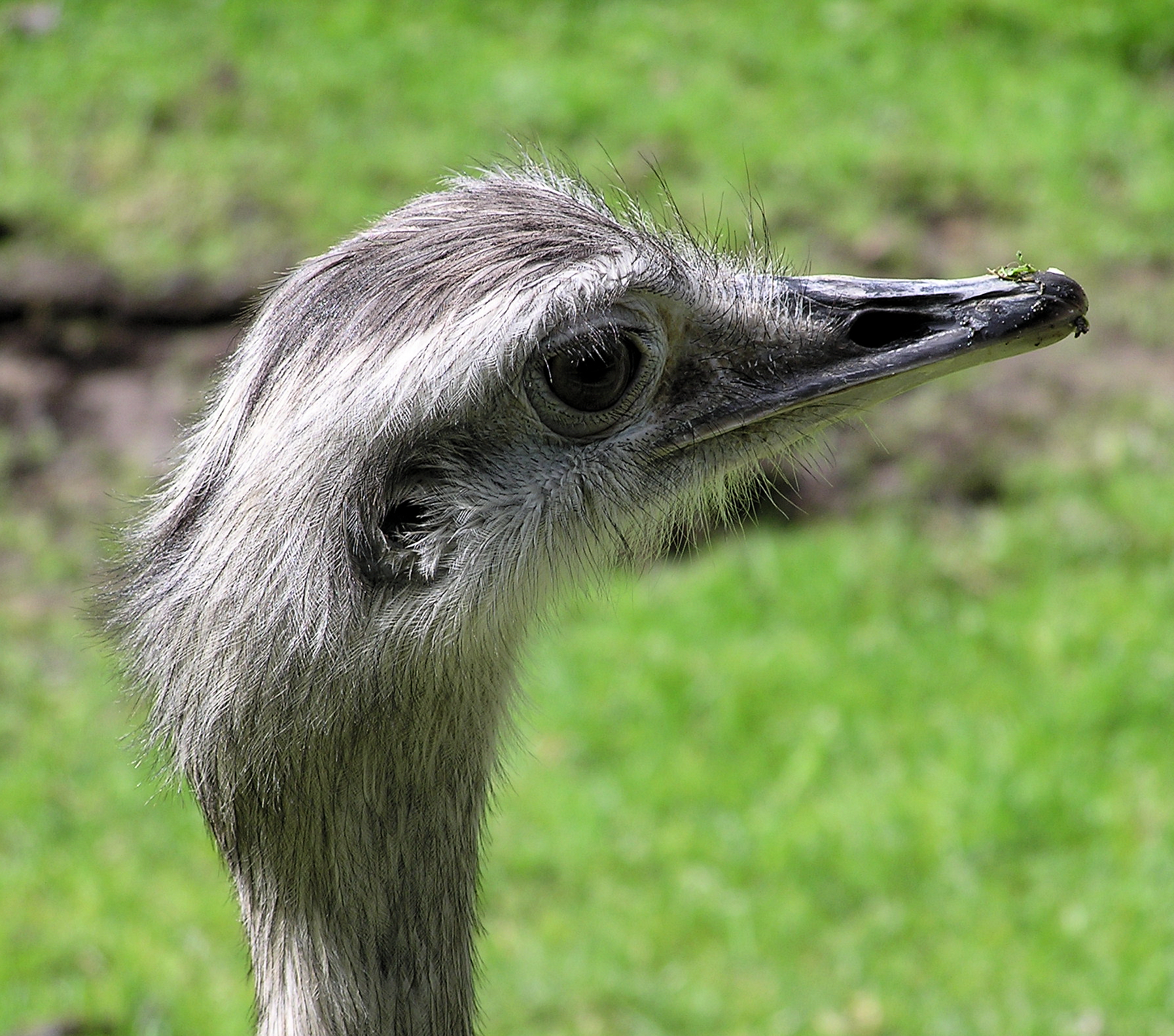
Ratites
A ratite () is any of a diverse group of flightless, large, long-necked, and long-legged birds of the infraclass Palaeognathae. Kiwi, the exception, are much smaller and shorter-legged and are the only nocturnal extant ratites. The systematics of and relationships within the paleognath clade have been in flux. Previously, all the flightless members had been assigned to the order Struthioniformes, which is more recently regarded as containing only the ostrich. The modern bird superorder Palaeognathae consists of ratites and the flighted Neotropic tinamous (compare to Neognathae). Unlike other flightless birds, the ratites have no keel on their sternum — hence the name, from the Latin ''ratis'' (raft, a vessel which has no keel - in contradistinction to extant flighted birds with a keel). Without this to anchor their wing muscles, they could not have flown even if they developed suitable wings. Ratites are a paraphyletic group; tinamous fall within them, and are the sister gro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Palaeognathae
Palaeognathae (; ) is a infraclass of birds, called paleognaths, within the class Aves of the clade Archosauria. It is one of the two extant infraclasses of birds, the other being Neognathae, both of which form Neornithes. Palaeognathae contains five extant branches of flightless lineages (plus two extinct clades), termed ratites, and one flying lineage, the Neotropic tinamous.Wetmore, A. (1960) A Classification for Birds of the World. Smithsonian Miscellaneous Collection (Washington D.C.: Smithsonian Institution) 139: 1–37. There are 47 species of tinamous, five of kiwis (''Apteryx''), three of cassowaries (''Casuarius''), one of emus (''Dromaius'') (another became extinct in historic times), two of rheas (''Rhea'') and two of ostrich ('' Struthio'').Clements, J. C. ''et al''. (2010) Recent research has indicated that paleognaths are monophyletic but the traditional taxonomic split between flightless and flighted forms is incorrect; tinamous are within the ratite r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flightless Bird
Flightless birds are birds that through evolution lost the ability to fly. There are over 60 extant species, including the well known ratites (ostriches, emu, cassowaries, rheas, and kiwi) and penguins. The smallest flightless bird is the Inaccessible Island rail (length 12.5 cm, weight 34.7 g). The largest (both heaviest and tallest) flightless bird, which is also the largest living bird, is the ostrich (2.7 m, 156 kg). Many domesticated birds, such as the domestic chicken and domestic duck, have lost the ability to fly for extended periods, although their ancestral species, the red junglefowl and mallard, respectively, are capable of extended flight. A few particularly bred birds, such as the Broad Breasted White turkey, have become totally flightless as a result of selective breeding; the birds were bred to grow massive breast meat that weighs too much for the bird's wings to support in flight. Flightlessness has evolved in many different birds independe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Common Ostrich
The common ostrich (''Struthio camelus''), or simply ostrich, is a species of flightless bird native to certain large areas of Africa and is the largest living bird species. It is one of two extant species of ostriches, the only living members of the genus '' Struthio'' in the ratite order of birds. The other is the Somali ostrich (''Struthio molybdophanes''), which was recognized as a distinct species by BirdLife International in 2014 having been previously considered a distinctive subspecies of ostrich. The common ostrich belongs to the order Struthioniformes. Struthioniformes previously contained all the ratites, such as the kiwis, emus, rheas, and cassowaries. However, recent genetic analysis has found that the group is not monophyletic, as it is paraphyletic with respect to the tinamous, so the ostriches are now classified as the only members of the order. Phylogenetic studies have shown that it is the sister group to all other members of Palaeognathae and thus the flig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kiwi (bird)
Kiwi ( ) are flightless birds endemic to New Zealand of the order Apterygiformes. The five extant species fall into the family Apterygidae () and genus ''Apteryx'' (). Approximately the size of a domestic chicken, kiwi are by far the smallest living ratites (which also include ostriches, emus, rheas and cassowaries). However, the ratite group is polyphyletic, and cladistically also includes tinamous, which can also be of moderate size. Members of this expanded group are known as paleognaths. DNA sequence comparisons have yielded the conclusion that kiwi are much more closely related to the extinct Malagasy elephant birds than to the moa with which they shared New Zealand. There are five recognised species, four of which are currently listed as Vulnerable species, vulnerable, and Little spotted kiwi, one of which is Near-threatened species, near-threatened. All species have been negatively affected by historic Deforestation in New Zealand, deforestation, but their remainin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apterygiformes
Kiwi ( ) are flightless birds endemic to New Zealand of the order Apterygiformes. The five extant species fall into the family Apterygidae () and genus ''Apteryx'' (). Approximately the size of a domestic chicken, kiwi are by far the smallest living ratites (which also include ostriches, emus, rheas and cassowaries). However, the ratite group is polyphyletic, and cladistically also includes tinamous, which can also be of moderate size. Members of this expanded group are known as paleognaths. DNA sequence comparisons have yielded the conclusion that kiwi are much more closely related to the extinct Malagasy elephant birds than to the moa with which they shared New Zealand. There are five recognised species, four of which are currently listed as vulnerable, and one of which is near-threatened. All species have been negatively affected by historic deforestation, but their remaining habitat is well-protected in large forest reserves and national parks. At present, the greates ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rheiformes
Rheiformes is an order that contains the family Rheidae (rheas). It is in the infraclass Paleognathae, which contains all ratites. Extant members are found in South America. While the IOC World Bird List and the Clements Checklist categorise Rheiformes as its own order, the BirdLife Data Zone includes rheas, along with ostriches, tinamous, cassowaries, emu, and kiwis, in the order Struthioniformes. Of the two extant species of rheas recognized by the IUCN Red List, , '' Rhea americana'' is listed as near threatened, while ''Rhea pennata Darwin's rhea or the lesser rhea (''Rhea pennata'') is a large flightless bird, the smaller of the two extant species of rheas. It is found in the Altiplano and Patagonia in South America. Description The lesser rhea stands at tall. Length ...'' is listed as least concern. From 2014 to 2022, the IUCN recognised '' Rhea tarapacensis'' as a separate species, and listed it as near threatened in its last assessment in 2020; in 2022, it w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Casuariiformes
The Casuariiformes is an order of large flightless birds that has four surviving members: the three species of cassowary, and the only remaining species of emu. They are divided into either a single family, Casuariidae, or more typically two, with the emu splitting off into its own family, Dromaiidae. All four living members are native to Australia-New Guinea,Clements, J (2007) but some possible extinct taxa occurred in other landmasses. Systematics and evolution The emus form a distinct family, characterized by legs adapted for running. The total number of cassowary species described, based on minor differences in casque shape and color variations, formerly reached nine. Now, however, only three species are recognized, and most authorities only acknowledge few subspecies or none at all. The fossil record of casuariforms is interesting, but not very extensive. Regarding fossil species of ''Dromaius'' and ''Casuarius'', see their genus pages. As with all ratites, there are se ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Greater Rhea
The greater rhea (''Rhea americana'') is a species of flightless bird native to eastern South America. Other names for the greater rhea include the grey, common, or American rhea; ema ( Portuguese); or ñandú ( Guaraní and Spanish). One of two species in the genus '' Rhea'', in the family Rheidae, the greater rhea is native to Brazil, Bolivia, Argentina, Paraguay and Uruguay. It inhabits a variety of open areas, such as grasslands, savanna or grassy wetlands. Weighing , the greater rhea is the largest bird in South America and the largest native, extant bird anywhere in the Americas. In the wild, the greater rhea has a life expectancy of 10.5 years. It is also notable for its reproductive habits, and for the fact that a population has established itself in Northern Germany in recent years. The species is listed as Near Threatened by the IUCN. Taxonomy and systematics The greater rhea derives its scientific name from Rhea, a Greek goddess, and the Latinized form of America. It ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bl(Ornithologist)
BL (or similar) may refer to: Arts and entertainment * BL Publishing, a division of the wargames manufacturing company, Games Workshop * ''Boston Legal'', a US legal comedy drama * Boys' love, Japanese term for female-oriented fiction featuring idealized romantic relationships between two males Businesses and organizations * Bell Labs, an audio-technology research and design enterprise * Boys' Latin School of Maryland, a US private school * Brisbane Lions, an Australian rules football team in the Australian Football League * British Library, the UK's national library * British Leyland, a former UK vehicle manufacturing company * Pacific Airlines (IATA code BL), a low-cost airline * Lytvyn Bloc, a Ukrainian political party Food and drink * Bitter lemon, a carbonated soft drink * Bud Light, an American lager beer In law * Bachelor of Laws (B.L.), an undergraduate degree in law * Barrister-at-Law, a degree and professional qualification in Ireland, Northern Ireland and Nigeri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sunder
Sunder may refer to: *Sunder (actor) or Sunder Singh (1908-1992), an actor in Punjabi and Hindi films *Sunder (comics) Sabra Sabreclaw Sabreclaw is a character in the MC2 universe who first appeared in '' J2'' #8 (May 1999). He is the half-brother of Wild Thing and the son of Wolverine. The character has claws (similar to Sabretooth), a healing factor, enhan ..., a fictional character in the Marvel Universe * Sunder (''Transformers''), a character from the ''Transformers'' franchise * Sundar or Sunder, an Indian given name (including a list of persons with the name) See also * Sunder Nagar, a region in Mumbai, Maharashtra, India * Sundre (other) {{disambiguation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Johann Karl Wilhelm Illiger
Johann Karl Wilhelm Illiger (19 November 1775 – 10 May 1813) was a German entomologist and zoologist. Illiger was the son of a merchant in Braunschweig. He studied under the entomologist Johann Hellwig, and later worked on the zoological collections of Johann Centurius Hoffmannsegg. Illiger was professor and director of the "zoological museum" (which is the Natural History Museum of Berlin in the present day) from its formation in 1810 until his death. He was the author of ''Prodromus systematis mammalium et avium'' (1811), which was an overhaul of the Linnaean system. It was a major influence on the adoption of the concept of the family. He also edited the ''Magazin für Insektenkunde'', widely known as "Illiger's Magazine". In 1811 he introduced the taxonomic order Proboscidea for elephants, the American mastodon and the woolly mammoth. He also described the subspecies ''Odobenus rosmarus divergens'', commonly known as the Pacific walrus. Illiger's macaw (''Promolius m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alexander Keyserling
Alexander Friedrich Michael Lebrecht Nikolaus Arthur Graf von Keyserling (15 August 1815 – 8 May 1891) was a Baltic German geologist and paleontologist from the Keyserlingk family of Baltic German nobility. Career Alexander von Keyserling was born on at the Kabillen Manor, , Courland Governorate (in present-day Kabile, Kuldīga Municipality, Latvia), then part of the Russian Empire. His father was Count Heinrich Diedrich Wilhelm von Keyserling, 3rd Count of Rautenburg, was a spokesman, and in Courland, his mother was Baroness Anna Amalie Benigna . His family was of Westphalian origin and was originated in Herford, they were considered part of the ''Uradel'', or old nobility. The first ever mentioned member was Albert Keserlink (1443-1467 or 1468), the mayor of Herford. Alexander belonged to the ''House of Rautenburg- Telsen-Paddern'', which was a subdivided branch of the Prussian comital branch. The branch's founder Dietrich II von Keyserling, Herr auf und , was e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |