|
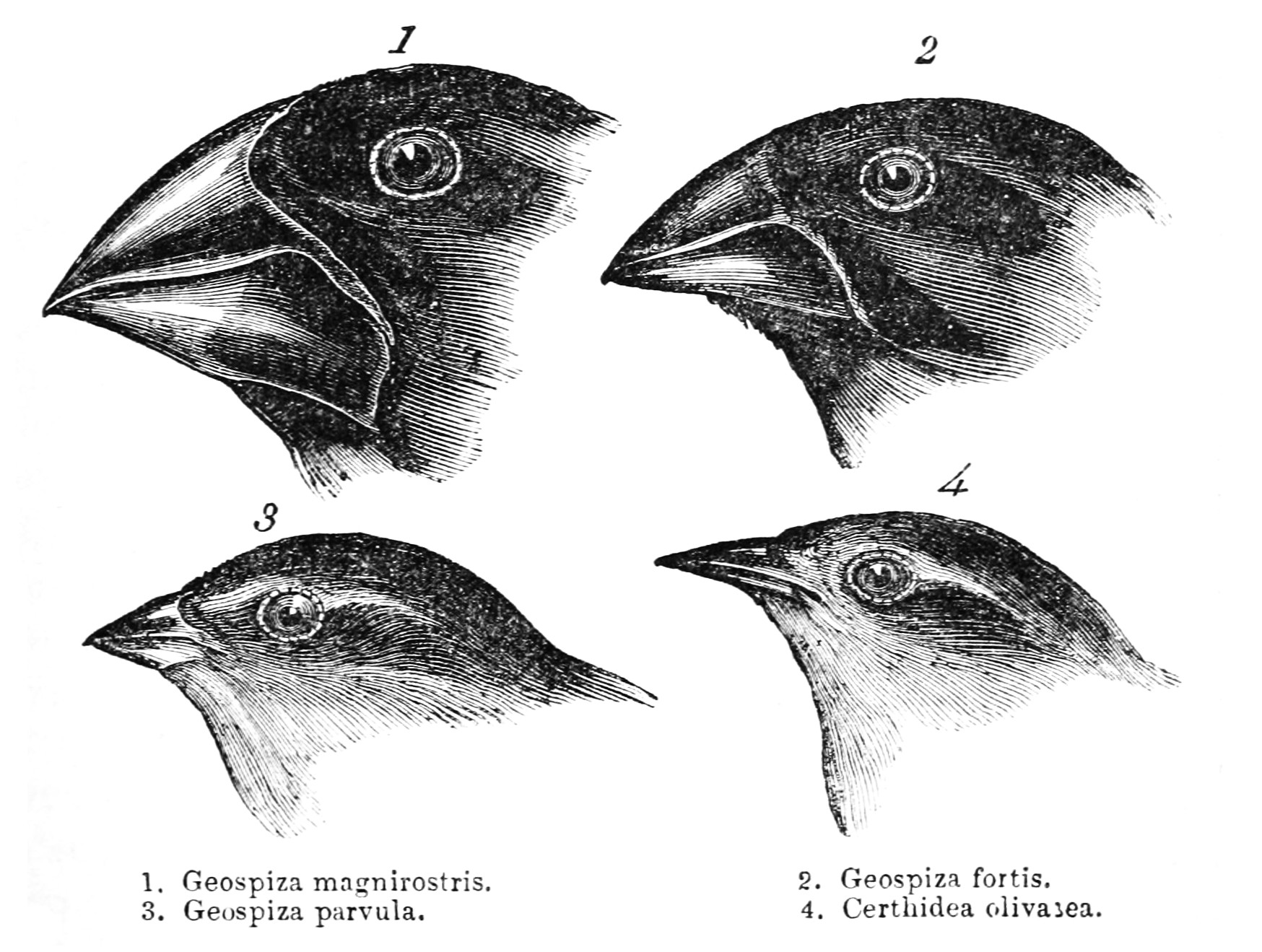
Rate Of Evolution
The rate of evolution is quantified as the speed of genetic or morphological change in a lineage over a period of time. The speed at which a molecular entity (such as a protein, gene, etc.) evolves is of considerable interest in evolutionary biology since determining the evolutionary rate is the first step in characterizing its evolution. Calculating rates of evolutionary change is also useful when studying phenotypic changes in phylogenetic comparative biology. In either case, it can be beneficial to consider and compare both genomic (such as DNA sequence) data and paleontological (such as fossil record) data, especially in regards to estimating the timing of divergence events and establishing geological time scales. At the organism level In his extensive study of evolution and paleontology, George Gaylord Simpson established evolutionary rates by using the fossil record to count the number of successive genera that occurred within a lineage during a given time period. For exampl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Evolutionary Biology
Evolutionary biology is the subfield of biology that studies the evolutionary processes (natural selection, common descent, speciation) that produced the diversity of life on Earth. It is also defined as the study of the history of life forms on Earth. Evolution is based on the theory that all species are related and they gradually change over time. In a population, the genetic variations affect the physical characteristics i.e. phenotypes of an organism. These changes in the phenotypes will be an advantage to some organisms, which will then be passed onto their offspring. Some examples of evolution in species over many generations are the Peppered Moth and Flightless birds. In the 1930s, the discipline of evolutionary biology emerged through what Julian Huxley called the modern synthesis of understanding, from previously unrelated fields of biological research, such as genetics and ecology, systematics, and paleontology. The importance of studying Evolutionary biology is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Niles Eldredge
Niles Eldredge (; born August 25, 1943) is an American biologist and paleontologist, who, along with Stephen Jay Gould, proposed the theory of punctuated equilibrium in 1972. Education Eldredge began his undergraduate studies in Latin at Columbia University. Before completing his degree he switched to the study of geology under Norman D. Newell. It was at this time that his work at the American Museum of Natural History began, under the combined Columbia University-American Museum graduate studies program. Eldredge graduated ''summa cum laude'' from Columbia College of Columbia University in 1965, and enrolled in the university's doctoral program while continuing his research at the museum. He completed his PhD in 1969. Career and research Paleontology In 1969, Eldredge became a curator in the Department of Invertebrates at the American Museum of Natural History, and subsequently a curator in the Invertebrate Paleontology section, a position from which he recently retired. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mass Extinction
An extinction event (also known as a mass extinction or biotic crisis) is a widespread and rapid decrease in the biodiversity on Earth. Such an event is identified by a sharp change in the diversity and abundance of multicellular organisms. It occurs when the rate of extinction increases with respect to the background extinction rate and the rate of speciation. Estimates of the number of major mass extinctions in the last 540 million years range from as few as five to more than twenty. These differences stem from disagreement as to what constitutes a "major" extinction event, and the data chosen to measure past diversity. The "Big Five" mass extinctions In a landmark paper published in 1982, Jack Sepkoski and David M. Raup identified five particular geological intervals with excessive diversity loss. They were originally identified as outliers on a general trend of decreasing extinction rates during the Phanerozoic, but as more stringent statistical tests have been applied to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Small Population Size
Small populations can behave differently from larger populations. They are often the result of population bottlenecks from larger populations, leading to loss of heterozygosity and reduced genetic diversity and loss or fixation of alleles and shifts in allele frequencies. A small population is then more susceptible to demographic and genetic stochastic events, which can impact the long-term survival of the population. Therefore, small populations are often considered at risk of endangerment or extinction, and are often of conservation concern. Demographic effects The influence of stochastic variation in demographic (reproductive and mortality) rates is much higher for small populations than large ones. Stochastic variation in demographic rates causes small populations to fluctuate randomly in size. This variation could be a result of unequal sex ratios, high variance in family size, inbreeding or fluctuating population size.Frankham, R., Briscoe, D. A., & Ballou, J. D. (2002). ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
History Of Molecular Evolution
The history of molecular evolution starts in the early 20th century with "comparative biochemistry", but the field of molecular evolution came into its own in the 1960s and 1970s, following the rise of molecular biology. The advent of protein sequencing allowed molecular biologists to create phylogenies based on sequence comparison, and to use the differences between homologous sequences as a molecular clock to estimate the time since the last common ancestor. In the late 1960s, the neutral theory of molecular evolution provided a theoretical basis for the molecular clock, though both the clock and the neutral theory were controversial, since most evolutionary biologists held strongly to panselectionism, with natural selection as the only important cause of evolutionary change. After the 1970s, nucleic acid sequencing allowed molecular evolution to reach beyond proteins to highly conserved ribosomal RNA sequences, the foundation of a reconceptualization of the early history of life. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neutral Theory Of Molecular Evolution
The neutral theory of molecular evolution holds that most evolutionary changes occur at the molecular level, and most of the variation within and between species are due to random genetic drift of mutant alleles that are selectively neutral. The theory applies only for evolution at the molecular level, and is compatible with phenotypic evolution being shaped by natural selection as postulated by Charles Darwin. The neutral theory allows for the possibility that most mutations are deleterious, but holds that because these are rapidly removed by natural selection, they do not make significant contributions to variation within and between species at the molecular level. A neutral mutation is one that does not affect an organism's ability to survive and reproduce. The neutral theory assumes that most mutations that are not deleterious are neutral rather than beneficial. Because only a fraction of gametes are sampled in each generation of a species, the neutral theory suggests that a mu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
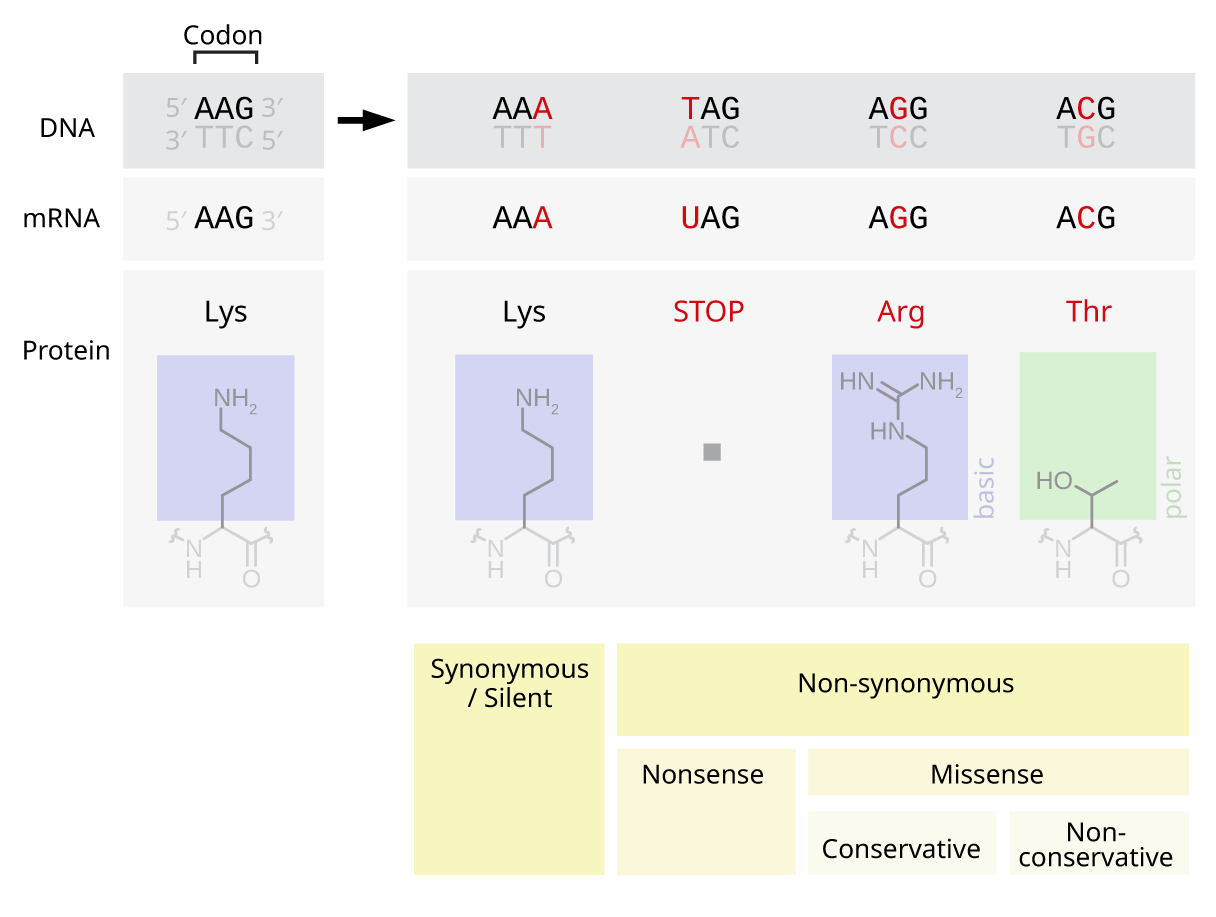
Silent Mutations
Silent mutations are mutations in DNA that do not have an observable effect on the organism's phenotype. They are a specific type of neutral mutation. The phrase ''silent mutation'' is often used interchangeably with the phrase ''synonymous mutation''; however, synonymous mutations are not always silent, nor vice versa. Synonymous mutations can affect transcription, splicing, mRNA transport, and translation, any of which could alter phenotype, rendering the synonymous mutation non-silent. The substrate specificity of the tRNA to the rare codon can affect the timing of translation, and in turn the co-translational folding of the protein. This is reflected in the codon usage bias that is observed in many species. Mutations that cause the altered codon to produce an amino acid with similar functionality (''e.g.'' a mutation producing leucine instead of isoleucine) are often classified as silent; if the properties of the amino acid are conserved, this mutation does not usually signifi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Koinophilia
Koinophilia is an evolutionary hypothesis proposing that during sexual selection, animals preferentially seek mates with a minimum of unusual or mutant features, including functionality, appearance and behavior. Koinophilia intends to explain the clustering of sexual organisms into species and other issues described by Darwin's Dilemma. The term derives from the Greek word ''koinos'' meaning "common" or "that which is shared", and ''philia'', meaning "fondness". Natural selection causes beneficial inherited features to become more common at the expense of their disadvantageous counterparts. The koinophilia hypothesis proposes that a sexually-reproducing animal would therefore be expected to avoid individuals with rare or unusual features, and to prefer to mate with individuals displaying a predominance of common or average features. Mutants with strange, odd or peculiar features would be avoided because most mutations that manifest themselves as changes in appearance, functiona ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Group Selection
Group selection is a proposed mechanism of evolution in which natural selection acts at the level of the group, instead of at the level of the individual or gene. Early authors such as V. C. Wynne-Edwards and Konrad Lorenz argued that the behavior of animals could affect their survival and reproduction as groups, speaking for instance of actions for the good of the species. In the 1930s, R.A. Fisher and J.B.S. Haldane proposed the concept of kin selection, a form of altruism from the gene-centered view of evolution, arguing that animals should sacrifice for their relatives, and thereby implying that they should not sacrifice for non-relatives. From the mid 1960s, evolutionary biologists such as John Maynard Smith, W. D. Hamilton, George C. Williams, and Richard Dawkins argued that natural selection acted primarily at the level of the gene. They argued on the basis of mathematical models that individuals would not altruistically sacrifice fitness for the sake of a group unless ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nature (journal)
''Nature'' is a British weekly scientific journal founded and based in London, England. As a multidisciplinary publication, ''Nature'' features peer-reviewed research from a variety of academic disciplines, mainly in science and technology. It has core editorial offices across the United States, continental Europe, and Asia under the international scientific publishing company Springer Nature. ''Nature'' was one of the world's most cited scientific journals by the Science Edition of the 2019 ''Journal Citation Reports'' (with an ascribed impact factor of 42.778), making it one of the world's most-read and most prestigious academic journals. , it claimed an online readership of about three million unique readers per month. Founded in autumn 1869, ''Nature'' was first circulated by Norman Lockyer and Alexander Macmillan as a public forum for scientific innovations. The mid-20th century facilitated an editorial expansion for the journal; ''Nature'' redoubled its efforts in exp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Silent Mutation
Silent mutations are mutations in DNA that do not have an observable effect on the organism's phenotype. They are a specific type of neutral mutation. The phrase ''silent mutation'' is often used interchangeably with the phrase '' synonymous mutation''; however, synonymous mutations are not always silent, nor vice versa. Synonymous mutations can affect transcription, splicing, mRNA transport, and translation, any of which could alter phenotype, rendering the synonymous mutation non-silent. The substrate specificity of the tRNA to the rare codon can affect the timing of translation, and in turn the co-translational folding of the protein. This is reflected in the codon usage bias that is observed in many species. Mutations that cause the altered codon to produce an amino acid with similar functionality (''e.g.'' a mutation producing leucine instead of isoleucine) are often classified as silent; if the properties of the amino acid are conserved, this mutation does not usually signif ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mutation
In biology, a mutation is an alteration in the nucleic acid sequence of the genome of an organism, virus, or extrachromosomal DNA. Viral genomes contain either DNA or RNA. Mutations result from errors during DNA or viral replication, mitosis, or meiosis or other types of damage to DNA (such as pyrimidine dimers caused by exposure to ultraviolet radiation), which then may undergo error-prone repair (especially microhomology-mediated end joining), cause an error during other forms of repair, or cause an error during replication (translesion synthesis). Mutations may also result from insertion or deletion of segments of DNA due to mobile genetic elements. Mutations may or may not produce detectable changes in the observable characteristics (phenotype) of an organism. Mutations play a part in both normal and abnormal biological processes including: evolution, cancer, and the development of the immune system, including junctional diversity. Mutation is the ultimate source o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |