|
Rapier Loom
A rapier loom is a shuttleless weaving loom in which the filling yarn is carried through the shed of warp yarns to the other side of the loom by finger-like carriers called rapiers. A stationary package of yarn is used to supply the weft yarns in the rapier machine. One end of a rapier, a rod or steel tape, carries the weft yarn. The other end of the rapier is connected to the control system. The rapier moves across the width of the fabric, carrying the weft yarn across through the shed to the opposite side. The rapier is then retracted, leaving the new pick in place. In some versions of the loom, two rapiers are used, each half the width of the fabric in size. One rapier carries the yarn to the centre of the shed, where the opposing rapier picks up the yarn and carries it the remainder of the way across the shed. The double rapier is used more frequently than the single rapier due to its increased pick insertion speed and ability to weave wider widths of fabric. The housing f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
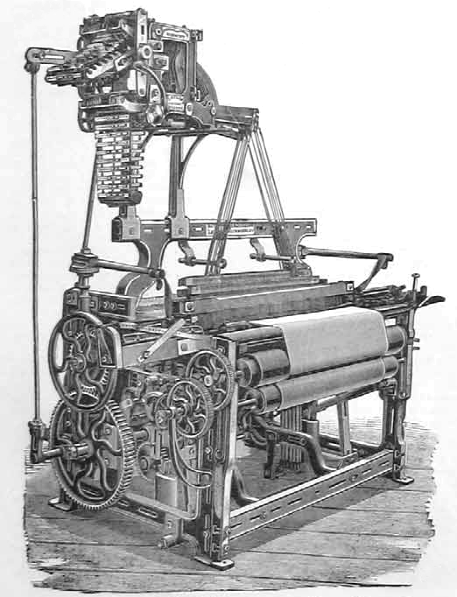
Ruti Rapier Loom
Ruti may refer to: As a given name * Ruti Olajugbagbe, winner of series seven of ''The Voice UK'' * Ruti Sela, Israeli video artist * Ruti Zisser, Israeli American lifestyle designer, fashion designer, wardrobe stylist, and businesswoman As a surname * Mari Ruti, Distinguished Professor of critical theory and of gender and sexuality studies at the University of Toronto Other uses * Aker (god), the Egyptian god of the horizon * Ruti (crater), a crater on Ganymede * Rüti (other), a number of places in Switzerland * Ruti, an alternative spelling of roti Roti (also known as chapati) is a round flatbread native to the Indian subcontinent. It is popular in India, Sri Lanka, Pakistan, Nepal, Bangladesh, Maldives, Myanmar, Malaysia, Indonesia, Singapore, Thailand, Guyana, Suriname, Jamaica, Trini ..., an unleavened flatbread * Ruti, a 1998 Bangladesh film {{Disambig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dobby Loom
A dobby loom, or dobbie loom, is a type of floor loom that controls all the warp threads using a device called a dobby. Dobbies can produce more complex fabric designs than tappet looms but are limited in comparison to Jacquard looms. Dobby looms first appeared around 1843, roughly 40 years after Joseph Marie Jacquard invented the Jacquard device that can be mounted atop a loom to lift the individual heddles and warp threads. The word ''dobby'' is a corruption of "draw boy," which refers to the weaver's helpers who used to control the warp thread by pulling on draw threads. A dobby loom is an alternative to a treadle loom. Both are floor looms in which every warp thread on the loom is attached to a single shaft using a device called a heddle. A shaft is sometimes known as a harness. Each shaft controls a set of threads. Raising or lowering several shafts at the same time gives a huge variety of possible sheds (gaps) through which the shuttle containing the weft thread can b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
English Inventions
English inventions and discoveries are objects, processes or techniques invented, innovated or discovered, partially or entirely, in England by a person from England. Often, things discovered for the first time are also called inventions and in many cases, there is no clear line between the two. Nonetheless, science and technology in England continued to develop rapidly in absolute terms. Furthermore, according to a Japanese research firm, over 40% of the world's inventions and discoveries were made in the UK, followed by France with 24% of the world's inventions and discoveries made in France and followed by the US with 20%. The following is a list of inventions, innovations or discoveries known or generally recognised to be English. Agriculture * 1627: Publication of first experiments in Water desalination and filtration by Sir Francis Bacon (1561–1626). * 1701: Seed drill improved by Jethro Tull (1674–1741). *18th century: of the horse-drawn hoe and scarifier by Je ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Industrial Revolution
The Industrial Revolution was the transition to new manufacturing processes in Great Britain, continental Europe, and the United States, that occurred during the period from around 1760 to about 1820–1840. This transition included going from hand production methods to machines, new chemical manufacturing and iron production processes, the increasing use of steam power and water power, the development of machine tools and the rise of the mechanized factory system. Output greatly increased, and a result was an unprecedented rise in population and in the rate of population growth. Textiles were the dominant industry of the Industrial Revolution in terms of employment, value of output and capital invested. The textile industry was also the first to use modern production methods. The Industrial Revolution began in Great Britain, and many of the technological and architectural innovations were of British origin. By the mid-18th century, Britain was the world's leadi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Weaving Equipment
Weaving is a method of textile production in which two distinct sets of yarns or threads are interlaced at right angles to form a fabric or cloth. Other methods are knitting, crocheting, felting, and braiding or plaiting. The longitudinal threads are called the warp and the lateral threads are the weft, woof, or filling. (''Weft'' is an Old English word meaning "that which is woven"; compare ''leave'' and ''left''.) The method in which these threads are interwoven affects the characteristics of the cloth. Cloth is usually woven on a loom, a device that holds the warp threads in place while filling threads are woven through them. A fabric band that meets this definition of cloth (warp threads with a weft thread winding between) can also be made using other methods, including tablet weaving, back strap loom, or other techniques that can be done without looms. The way the warp and filling threads interlace with each other is called the weave. The majority of woven products ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Textile Manufacture During The Industrial Revolution
Textile manufacture during the British Industrial Revolution was centred in south Lancashire and the towns on both sides of the Pennines in the United Kingdom. The main drivers of the Industrial Revolution were textile manufacturing, iron founding, steam power, oil drilling, the discovery of electricity and its many industrial applications, the telegraph and many others. Railroads, steam boats, the telegraph and other innovations massively increased worker productivity and raised standards of living by greatly reducing time spent during travel, transportation and communications.. Before the 18th century, the manufacture of cloth was performed by individual workers, in the premises in which they lived and goods were transported around the country by packhorses or by river navigations and contour-following canals that had been constructed in the early 18th century. In the mid-18th century, artisans were inventing ways to become more productive. Silk, wool, and linen fabrics wer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Northrop Loom
The Northrop Loom was a fully automatic power loom marketed by George Draper and Sons, Hopedale, Massachusetts beginning in 1895. It was named after James Henry Northrop who invented the shuttle-charging mechanism. Background James Henry Northrop, (8 May 1856 - 12 December 1940) was born in Keighley, West Yorkshire in the United Kingdom, where he worked in the textile industry. He emigrated to Boston, Massachusetts in 1881. Northrop worked as a mechanic and foreman, for George Draper and Sons. There he invented a spooler guide. He left and tried to be a chicken farmer, but was unsuccessful. It was at that time that he invented a shuttle-charger. Otis Draper saw a model of the device on March 5, 1889. Draper was also developing the Rhoades shuttle-charger. Northrop was given a loom to test his idea. By May 20 he concluded that his first idea was not practical, and thought of another idea. On July 5, the completed loom was running, and as it seemed to have more advantages t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paul Moody (inventor)
Paul Moody (May 23, 1779 – July 5, 1831) was a U.S. textile machinery inventor born in Byfield, Massachusetts (Town of Newbury). He is often credited with developing and perfecting the first power loom in America, which launched the first successful integrated cotton mill at Waltham, Massachusetts in 1814, under the leadership of Francis Cabot Lowell and his associates. Early life Paul Moody was born May 24, 1779 at Byfield, Massachusetts, the son of Paul Moody and one of nine children. Although Moody's academic education was limited, at age sixteen he learned the weaver's craft, and soon became an expert. He later went to work at a nail factory of Jacob Perkins, first in Byfield and later in Amesbury, Massachusetts when the company moved. In 1812 he worked for Kendrick and Worthen, makers of carding machinery. On July 13, 1800 (one source says September 1798), he married Susan Morrill of Amesbury. The couple went on to have three sons. Soon after his marriage, he partne ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
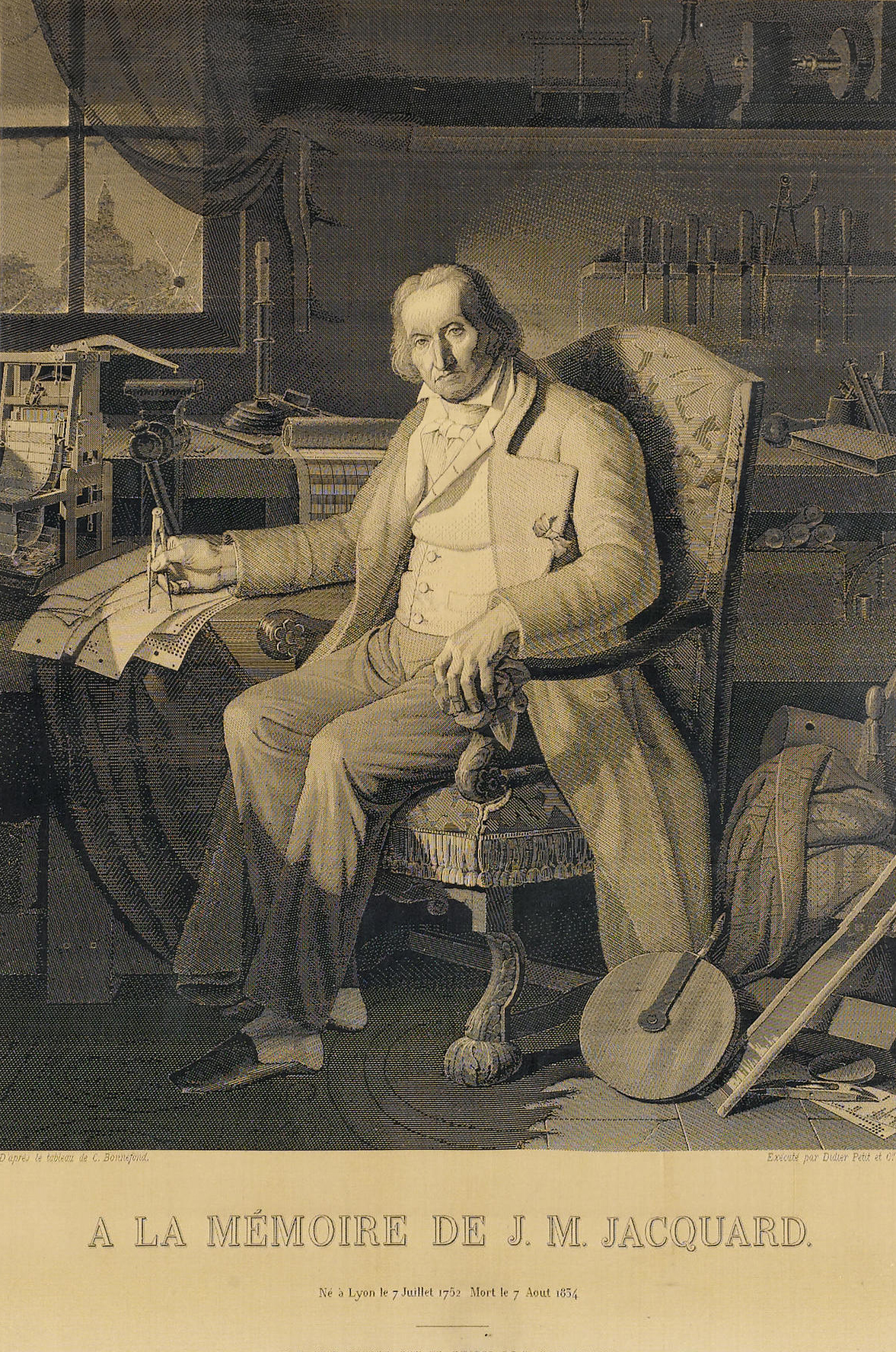
Jacquard Loom
The Jacquard machine () is a device fitted to a loom that simplifies the process of manufacturing textiles with such complex patterns as brocade, damask and matelassé. The resulting ensemble of the loom and Jacquard machine is then called a Jacquard loom. The machine was patented by Joseph Marie Jacquard in 1804, based on earlier inventions by the Frenchmen Basile Bouchon (1725), Jean Baptiste Falcon (1728), and Jacques Vaucanson (1740). The machine was controlled by a "chain of cards"; a number of punched cards laced together into a continuous sequence. Multiple rows of holes were punched on each card, with one complete card corresponding to one row of the design. Both the Jacquard process and the necessary loom attachment are named after their inventor. This mechanism is probably one of the most important weaving innovations as Jacquard shedding made possible the automatic production of unlimited varieties of complex pattern weaving. The term "Jacquard" is not spec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Salford
Salford () is a city and the largest settlement in the City of Salford metropolitan borough in Greater Manchester, England. In 2011, Salford had a population of 103,886. It is also the second and only other city in the metropolitan county after neighbouring Manchester. Salford is located in a meander of the River Irwell which forms part of its boundary with Manchester. The former County Borough of Salford, which also included Broughton, Pendleton and Kersal, was granted city status in 1926. In 1974 the wider Metropolitan Borough of the City of Salford was established with responsibility for a significantly larger region. Historically in Lancashire, Salford was the judicial seat of the ancient hundred of Salfordshire. It was granted a charter by Ranulf de Blondeville, 6th Earl of Chester, in about 1230, making Salford a free borough of greater cultural and commercial importance than its neighbour Manchester.. The Industrial Revolution of the late 18th and early 19th centuries ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Loom
A loom is a device used to weave cloth and tapestry. The basic purpose of any loom is to hold the warp threads under tension to facilitate the interweaving of the weft threads. The precise shape of the loom and its mechanics may vary, but the basic function is the same. Etymology and usage The word "loom" derives from the Old English ''geloma'', formed from ''ge-'' (perfective prefix) and ''loma'', a root of unknown origin; the whole word ''geloma'' meant a utensil, tool, or machine of any kind. In 1404 "lome" was used to mean a machine to enable weaving thread into cloth. By 1838 "loom" had gained the additional meaning of a machine for interlacing thread. Weaving Weaving is done by intersecting the longitudinal threads, the warp, i.e. "that which is thrown across", with the transverse threads, the weft, i.e. "that which is woven". The major components of the loom are the warp beam, heddles, harnesses or shafts (as few as two, four is common, sixteen not unheard of), ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shuttle (weaving)
A shuttle is a tool designed to neatly and compactly store a holder that carries the thread of the weft yarn while weaving with a loom. Shuttles are thrown or passed back and forth through the shed, between the yarn threads of the warp Warp, warped or warping may refer to: Arts and entertainment Books and comics * WaRP Graphics, an alternative comics publisher * ''Warp'' (First Comics), comic book series published by First Comics based on the play ''Warp!'' * Warp (comics), a ... in order to weave in the weft. The simplest shuttles, known as "stick shuttles", are made from a flat, narrow piece of wood with notches on the ends to hold the weft yarn. More complicated shuttles incorporate bobbins or pirns. In the United States, shuttles are often made of wood from the flowering dogwood, because it is hard, resists splintering, and can be polished to a very smooth finish. In the United Kingdom shuttles were usually made of boxwood, cornel, or persimmon. Flying shuttle Shu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)


.jpg)



