|
Radio Latino
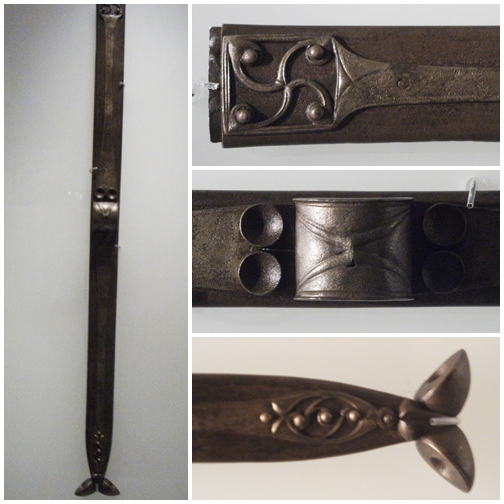
A radio latino is a measuring instrument used in surveying and military engineering starting in the 16th century. It gets its name from the inventor, Latino Orsini. The radio latino can be considered a kind of geometric square.Daumas, Maurice, ''Scientific Instruments of the Seventeenth and Eighteenth Centuries and Their Makers'', Portman Books, London 1989 It was a general purpose instrument that could be used for a variety of angular measurements as well as depth and inside dimension measures. Usage The slider (blue in the adjacent diagram) could move along the central rod, causing the deltoid formed by four other rods to change shape symmetrically. The end points of the rods had sights on them, allowing various sight lines to be defined. The central rod was graduated with various scales. These scales allowed the angles between the end rods (represented by the red lines in the diagram) to be determined as well as the angle with its vertex at one end of the main rod and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Latino Di Camillo Orsini
Latino Orsini (c. 1530 – c. 1580) was an Italian politician. Born in Rome, Latino Orsini was the son of Camillo Orsini, one of the most famous ''condottieri'' of the 16th century. Latino himself had a military career: he supervised the earthwork fortifications designed by his father for Castel Sant'Angelo and built a section of the walls of Civitavecchia. During the Cyprus war, the Venetians appointed him governor of Candia (the present-day island of Crete), where he lived for more than a decade. He was also ambassador of Gregory XIII (1502–1585, Pope from 1572) to the Senate of the Venetian Republic.Cantile, Andrea. Leonardo: the genius and the cartographer: the representation of land in science and art. Ist. Geografico Militare, 2003. p130 One of his military inventions, the "trestles" (''cavalletti'', literally "little horses" in Italian) to protect infantry from cavalry attacks, was published by Vespasiano Romani in ''Trattato e modo di difendere la fanteria dalla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geometric Square
Geometry (; ) is, with arithmetic, one of the oldest branches of mathematics. It is concerned with properties of space such as the distance, shape, size, and relative position of figures. A mathematician who works in the field of geometry is called a '' geometer''. Until the 19th century, geometry was almost exclusively devoted to Euclidean geometry, which includes the notions of point, line, plane, distance, angle, surface, and curve, as fundamental concepts. During the 19th century several discoveries enlarged dramatically the scope of geometry. One of the oldest such discoveries is Carl Friedrich Gauss' ("remarkable theorem") that asserts roughly that the Gaussian curvature of a surface is independent from any specific embedding in a Euclidean space. This implies that surfaces can be studied ''intrinsically'', that is, as stand-alone spaces, and has been expanded into the theory of manifolds and Riemannian geometry. Later in the 19th century, it appeared that geome ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radio Latino
A radio latino is a measuring instrument used in surveying and military engineering starting in the 16th century. It gets its name from the inventor, Latino Orsini. The radio latino can be considered a kind of geometric square.Daumas, Maurice, ''Scientific Instruments of the Seventeenth and Eighteenth Centuries and Their Makers'', Portman Books, London 1989 It was a general purpose instrument that could be used for a variety of angular measurements as well as depth and inside dimension measures. Usage The slider (blue in the adjacent diagram) could move along the central rod, causing the deltoid formed by four other rods to change shape symmetrically. The end points of the rods had sights on them, allowing various sight lines to be defined. The central rod was graduated with various scales. These scales allowed the angles between the end rods (represented by the red lines in the diagram) to be determined as well as the angle with its vertex at one end of the main rod and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kite (geometry)
In Euclidean geometry, a kite is a quadrilateral with reflection symmetry across a diagonal. Because of this symmetry, a kite has two equal angles and two pairs of adjacent equal-length sides. Kites are also known as deltoids, but the word ''deltoid'' may also refer to a deltoid curve, an unrelated geometric object sometimes studied in connection with quadrilaterals.See H. S. M. Coxeter's review of in : "It is unfortunate that the author uses, instead of 'kite', the name 'deltoid', which belongs more properly to a curve, the three-cusped hypocycloid." A kite may also be called a dart, particularly if it is not convex. Every kite is an orthodiagonal quadrilateral (its diagonals are at right angles) and, when convex, a tangential quadrilateral (its sides are tangent to an inscribed circle). The convex kites are exactly the quadrilaterals that are both orthodiagonal and tangential. They include as special cases the right kites, with two opposite right angles; the rhombi, with two ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Graduation (instrument)
A graduation is a marking used to indicate points on a visual scale, which can be present on a container, a measuring device, or the axes of a line plot, usually one of many along a line or curve, each in the form of short line segments perpendicular to the line or curve. Often, some of these line segments are longer and marked with a numeral, such as every fifth or tenth graduation. The scale itself can be linear (the graduations are spaced at a constant distance apart) or nonlinear. Linear graduation of a scale occurs mainly (but not exclusively) on straight measuring devices, such as a rule or measuring tape, using units such as inches or millimetres. Graduations can also be spaced at varying spatial intervals, such as when using a logarithmic, for instance on a measuring cup, can vary in scale due to the container's non- cylindrical shape. Graduations along a curve Circular graduations of a scale occur on a circular arc or limb of an instrument. In some cases, non-circ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vertex (geometry)
In geometry, a vertex (in plural form: vertices or vertexes) is a point (geometry), point where two or more curves, line (geometry), lines, or edge (geometry), edges meet. As a consequence of this definition, the point where two lines meet to form an angle and the corners of polygons and polyhedron, polyhedra are vertices. Definition Of an angle The ''vertex'' of an angle is the point where two Line (mathematics)#Ray, rays begin or meet, where two line segments join or meet, where two lines intersect (cross), or any appropriate combination of rays, segments, and lines that result in two straight "sides" meeting at one place. :(3 vols.): (vol. 1), (vol. 2), (vol. 3). Of a polytope A vertex is a corner point of a polygon, polyhedron, or other higher-dimensional polytope, formed by the intersection (Euclidean geometry), intersection of Edge (geometry), edges, face (geometry), faces or facets of the object. In a polygon, a vertex is called "convex set, convex" if the internal an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Regular Polygon
In Euclidean geometry, a regular polygon is a polygon that is Equiangular polygon, direct equiangular (all angles are equal in measure) and Equilateral polygon, equilateral (all sides have the same length). Regular polygons may be either convex polygon, convex, star polygon, star or Skew polygon, skew. In the limit (mathematics), limit, a sequence of regular polygons with an increasing number of sides approximates a circle, if the perimeter or area is fixed, or a regular apeirogon (effectively a Line (geometry), straight line), if the edge length is fixed. General properties ''These properties apply to all regular polygons, whether convex or star polygon, star.'' A regular ''n''-sided polygon has rotational symmetry of order ''n''. All vertices of a regular polygon lie on a common circle (the circumscribed circle); i.e., they are concyclic points. That is, a regular polygon is a cyclic polygon. Together with the property of equal-length sides, this implies that every regular p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shadow Square
The shadow square, also known as an altitude scale, was an instrument used to determine the linear height of an object, in conjunction with the alidade, for angular observations. An early example was described in an Arabic treatise likely dating to 9th or 10th-century Baghdad. Shadow squares are often found on the backs of astrolabes. Uses The main use of a shadow square is to measure the linear height of an object using its shadow. It does so by simulating the ratio between an object, generally a gnomon, and its shadow. If the sun's ray is between 0 degrees and 45 degrees the umbra versa (Vertical axis) is used, between 45 degrees and 90 degrees the umbra recta (Horizontal axis) is used and when the sun's ray is at 45 degrees its shadow falls exactly on the umbra media (y=x) It was used during the time of medieval astronomy to determine the height of, and to track the movement of celestial bodies such as the sun when more advanced measurement methods were not available. These met ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scabbard
A scabbard is a sheath for holding a sword, knife, or other large blade. As well, rifles may be stored in a scabbard by horse riders. Military cavalry and cowboys had scabbards for their saddle ring carbine rifles and Lever action, lever-action rifles on their horses for storage and protection. Scabbards have been made of many materials over the millennia, including leather, wood, and metals such as brass or steel. Most commonly, sword scabbards were worn suspended from a sword belt or shoulder belt called a baldric. Antiquity Wooden scabbards were typically covered in fabric or leather; the leather versions also usually bore metal fittings for added protection and carrying ease. Japanese blades typically have their sharp cutting edge protected by a wooden scabbard called a Japanese sword mountings#Saya, saya. Many scabbards, such as ones the Greeks and Romans used, were small and light. It was designed for holding the sword rather than protecting it. All-metal scabbards were ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brass
Brass is an alloy of copper (Cu) and zinc (Zn), in proportions which can be varied to achieve different mechanical, electrical, and chemical properties. It is a substitutional alloy: atoms of the two constituents may replace each other within the same crystal structure. Brass is similar to bronze, another copper alloy, that uses tin instead of zinc. Both bronze and brass may include small proportions of a range of other elements including arsenic (As), lead (Pb), phosphorus (P), aluminium (Al), manganese (Mn), and silicon (Si). Historically, the distinction between the two alloys has been less consistent and clear, and modern practice in museums and archaeology increasingly avoids both terms for historical objects in favor of the more general "copper alloy". Brass has long been a popular material for decoration due to its bright, gold-like appearance; being used for drawer pulls and doorknobs. It has also been widely used to make utensils because of its low melting ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Military Engineering
Military engineering is loosely defined as the art, science, and practice of designing and building military works and maintaining lines of military transport and military communications. Military engineers are also responsible for logistics behind military tactics. Modern military engineering differs from civil engineering. In the 20th and 21st centuries, military engineering also includes other engineering disciplines such as mechanical and electrical engineering techniques. According to NATO, "military engineering is that engineer activity undertaken, regardless of component or service, to shape the physical operating environment. Military engineering incorporates support to maneuver and to the force as a whole, including military engineering functions such as engineer support to force protection, counter-improvised explosive devices, environmental protection, engineer intelligence and military search. Military engineering does not encompass the activities undertaken by those ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Surveying
Surveying or land surveying is the technique, profession, art, and science of determining the terrestrial two-dimensional or three-dimensional positions of points and the distances and angles between them. A land surveying professional is called a land surveyor. These points are usually on the surface of the Earth, and they are often used to establish maps and boundaries for ownership, locations, such as the designed positions of structural components for construction or the surface location of subsurface features, or other purposes required by government or civil law, such as property sales. Surveyors work with elements of geodesy, geometry, trigonometry, regression analysis, physics, engineering, metrology, programming languages, and the law. They use equipment, such as total stations, robotic total stations, theodolites, GNSS receivers, retroreflectors, 3D scanners, LiDAR sensors, radios, inclinometer, handheld tablets, optical and digital levels, subsurface locators, d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)



_crop.jpg)