|
Radiculopathy
Radiculopathy, also commonly referred to as pinched nerve, refers to a set of conditions in which one or more nerves are affected and do not work properly (a neuropathy). Radiculopathy can result in pain ( radicular pain), weakness, altered sensation (paresthesia) or difficulty controlling specific muscles. Pinched nerves arise when surrounding bone or tissue, such as cartilage, muscles or tendons, put pressure on the nerve and disrupt its function. In a radiculopathy, the problem occurs at or near the root of the nerve, shortly after its exit from the spinal cord. However, the pain or other symptoms often radiate to the part of the body served by that nerve. For example, a nerve root impingement in the neck can produce pain and weakness in the forearm. Likewise, an impingement in the lower back or lumbar- sacral spine can be manifested with symptoms in the foot. The radicular pain that results from a radiculopathy should not be confused with referred pain, which is differen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
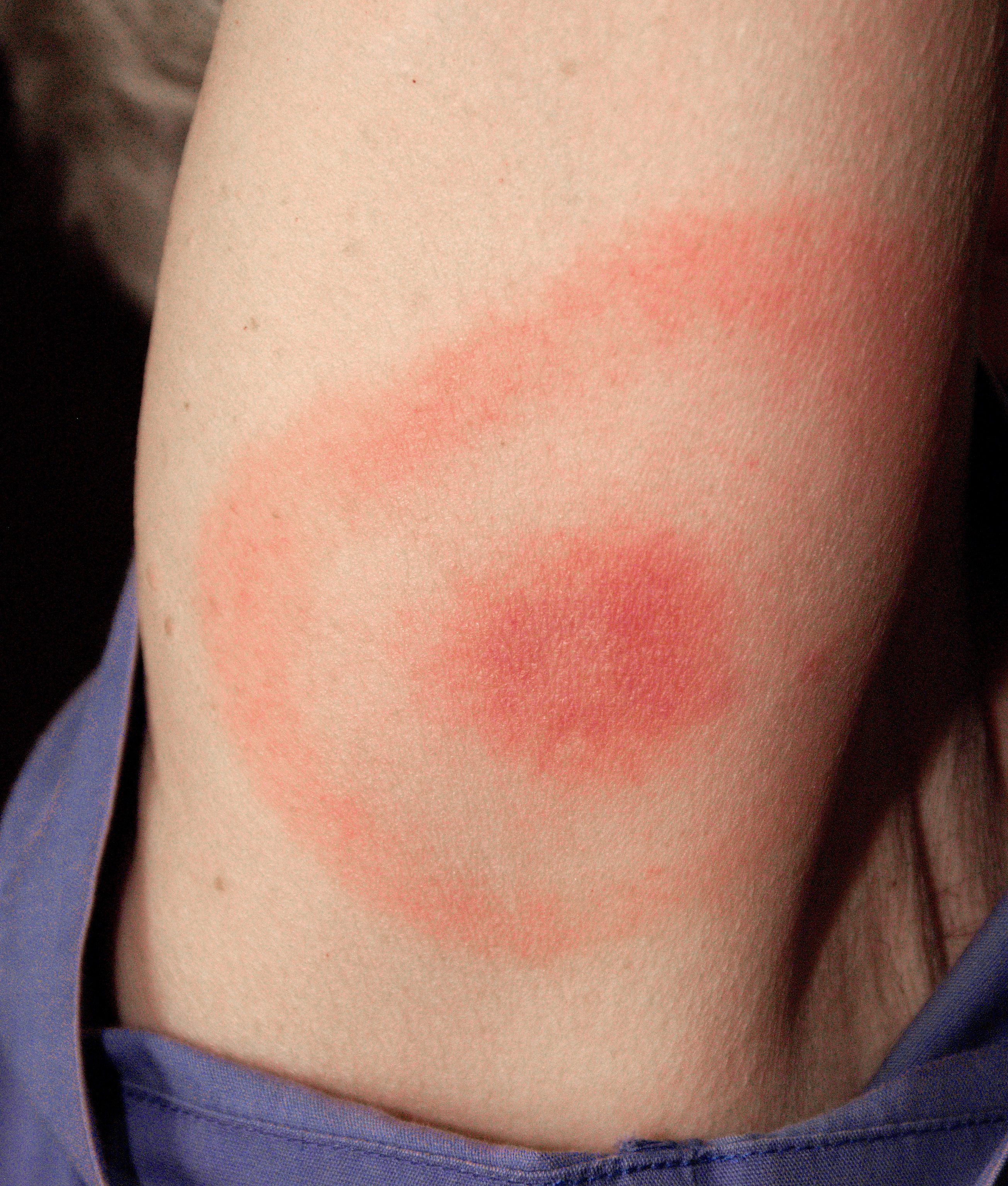
Lyme Disease
Lyme disease, also known as Lyme borreliosis, is a vector-borne disease caused by the '' Borrelia'' bacterium, which is spread by ticks in the genus '' Ixodes''. The most common sign of infection is an expanding red rash, known as erythema migrans (EM), which appears at the site of the tick bite about a week afterwards. The rash is typically neither itchy nor painful. Approximately 70–80% of infected people develop a rash. Early diagnosis can be difficult. Other early symptoms may include fever, headaches and tiredness. If untreated, symptoms may include loss of the ability to move one or both sides of the face, joint pains, severe headaches with neck stiffness or heart palpitations. Months to years later repeated episodes of joint pain and swelling may occur. Occasionally shooting pains or tingling in the arms and legs may develop. Despite appropriate treatment about 10 to 20% of those affected develop joint pains, memory problems and tiredness for at least six months. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nerve Root
A nerve root (Latin: ''radix nervi'') is the initial segment of a nerve leaving the central nervous system. Nerve roots can be classified as: *Cranial nerve roots: the initial or proximal segment of one of the twelve pairs of cranial nerves leaving the central nervous system from the brain stem or the highest levels of the spinal cord. * Spinal nerve roots: the initial or proximal segment of one of the thirty-one pairs of spinal nerves leaving the central nervous system from the spinal cord. Each spinal nerve is formed by the union of a sensory dorsal root and a motor ventral root, meaning that there are sixty-two dorsal/ventral root pairs, and therefore one hundred and twenty-four nerve roots in total, each of which stems from a bundle of nerve rootlets (or root filaments). Cranial nerve roots Cranial nerves originate directly from the brain's surface: two from the cerebrum and the ten others from the brain stem. Cranial roots differ from spinal roots: some of these roots do not ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radicular Pain
Radicular pain, or radiculitis, is pain "radiated" along the dermatome (sensory distribution) of a nerve due to inflammation or other irritation of the nerve root (radiculopathy) at its connection to the spinal column. A common form of radiculitis is sciatica – radicular pain that radiates along the sciatic nerve from the lower spine to the lower back, gluteal muscles, back of the upper thigh, calf, and foot as often secondary to nerve root irritation from a spinal disc herniation or from osteophytes in the lumbar region of the spine. Friday, 20 January 2017 Radiculitis indicates inflammation of the spinal nerve root, which may lead to pain in that nerve's distribution without weakness as opposed to radiculopathy. When the radiating pain is associated with numbness or weakness, the diagnosis is radiculopathy if the lesion is at the nerve root and myelopathy if at the spinal cord itself. See also * Intervertebral disc * Sciatica * Spinal disc herniation * Arachnoiditis Arac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tarlov Cysts
Tarlov cysts, are type II innervated meningeal cysts, cerebrospinal-fluid-filled (CSF) sacs most frequently located in the spinal canal of the sacral region of the spinal cord ( S1– S5) and much less often in the cervical, thoracic or lumbar spine. They can be distinguished from other meningeal cysts by their nerve-fiber-filled walls. Tarlov cysts are defined as cysts formed within the nerve-root sheath at the dorsal root ganglion. The etiology of these cysts is not well understood; some current theories explaining this phenomenon have not yet been tested or challenged but include increased pressure in CSF, filling of congenital cysts with one-way valves, inflammation in response to trauma and disease. They are named for American neurosurgeon Isadore Tarlov, who described them in 1938. Tarlov cysts are relatively uncommon when compared to other neurological cysts. Initially, Isadore Tarlov believed them to be asymptomatic, however as his research progressed, Tarlov found th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Degenerative Disc Disease
Degenerative disc disease (DDD) is a medical condition typically brought on by the normal aging process in which there are anatomic changes and possibly a loss of function of one or more intervertebral discs of the spine. DDD can take place with or without symptoms, but is typically identified once symptoms arise. The root cause is thought to be loss of soluble proteins within the fluid contained in the disc with resultant reduction of the oncotic pressure, which in turn causes loss of fluid volume. Normal downward forces cause the affected disc to lose height, and the distance between vertebrae is reduced. The anulus fibrosus, the tough outer layers of a disc, also weakens. This loss of height causes laxity of the longitudinal ligaments, which may allow anterior, posterior, or lateral shifting of the vertebral bodies, causing facet joint malalignment and arthritis; scoliosis; cervical hyperlordosis; thoracic hyperkyphosis; lumbar hyperlordosis; narrowing of the space availabl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spondylolisthesis
Spondylolisthesis is the displacement of one spinal vertebra compared to another. While some medical dictionaries define spondylolisthesis specifically as the forward or anterior displacement of a vertebra over the vertebra inferior to it (or the sacrum), it is often defined in medical textbooks as displacement in any direction.Introduction to chapter 17 in: Page 250 in: Spondylolisthesis is graded based upon the degree of slippage of one vertebral body relative to the subsequent adjacent vertebral body. Spondylolisthesis is classified as one of the six major etiologies: degenerative, traumatic, dysplastic, [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neurosurgery
Neurosurgery or neurological surgery, known in common parlance as brain surgery, is the medical specialty concerned with the surgical treatment of disorders which affect any portion of the nervous system including the brain, spinal cord and peripheral nervous system. Education and context In different countries, there are different requirements for an individual to legally practice neurosurgery, and there are varying methods through which they must be educated. In most countries, neurosurgeon training requires a minimum period of seven years after graduating from medical school. United States In the United States, a neurosurgeon must generally complete four years of undergraduate education, four years of medical school, and seven years of residency (PGY-1-7). Most, but not all, residency programs have some component of basic science or clinical research. Neurosurgeons may pursue additional training in the form of a fellowship after residency, or, in some cases, as a senior ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proximal Diabetic Neuropathy
Proximal diabetic neuropathy, also known as diabetic amyotrophy, is a complication of diabetes mellitus that affects the nerves that supply the thighs, hips, buttocks and/or lower legs. Proximal diabetic neuropathy is a type of diabetic neuropathy characterized by muscle wasting, weakness, pain, or changes in sensation/numbness of the leg. It is caused by damage to the nerves of the lumbosacral plexus. Proximal diabetic neuropathy is most commonly seen people with type 2 diabetics.National Diabetes Information Clearinghouse (NDIC). (2009, February). ''Diabetic neuropathies: the nerve damage of diabetes''. Retrieved March 20, 2012, from http://diabetes.niddk.nih.gov/dm/pubs/neuropathies/#proximalneuropathy It is less common than distal polyneuropathy that often occurs in diabetes. Signs and symptoms Signs and symptoms of proximal diabetic neuropathy depend on the nerves affected. The first symptom is usually pain in the buttocks, hips, thighs or legs. This pain often starts sudde ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spinal Epidural Hematoma
Spinal extradural haematoma or spinal epidural hematoma (SEH) is bleeding into the epidural space in the spine. These may arise spontaneously (e.g. during childbirth), or as a rare complication of epidural anaesthesia or of surgery (such as laminectomy). Symptoms usually include back pain which radiates to the arms or the legs. They may cause pressure on the spinal cord or cauda equina, which may present as pain, muscle weakness, or dysfunction of the bladder and bowel. Pathophysiology The anatomy of the epidural space is such that spinal epidural hematoma has a different presentation from intracranial epidural hematoma. In the spine, the epidural space contains loose fatty tissue and a network of large, thin-walled veins, referred to as the epidural venous plexus. The source of bleeding in spinal epidural hematoma is likely to be this venous plexus. Diagnosis The best way to confirm the diagnosis is MRI. Risk factors include anatomical abnormalities and bleeding disorders Coagu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spinal Epidural Abscess
An epidural abscess refers to a collection of pus and infectious material located in the epidural space superficial to the dura mater which surrounds the central nervous system. Due to its location adjacent to brain or spinal cord, epidural abscesses have the potential to cause weakness, pain, and paralysis. Types Spinal epidural abscess A spinal epidural abscess (SEA) is a collection of pus or inflammatory granulation between the dura mater and the vertebral column. Currently the annual incidence rate of SEAs is estimated to be 2.5-3 per 10,000 hospital admissions. Incidence of SEA is on the rise, due to factors such as an aging population, increase in use of invasive spinal instrumentation, growing number of patients with risk factors such as diabetes and intravenous drug use. SEAs are more common in posterior than anterior areas, and the most common location is the thoracolumbar area, where epidural space is larger and contains more fat tissue. SEAs are more common in males, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shingles
Shingles, also known as zoster or herpes zoster, is a viral disease characterized by a painful skin rash with blisters in a localized area. Typically the rash occurs in a single, wide mark either on the left or right side of the body or face. Two to four days before the rash occurs there may be tingling or local pain in the area. Otherwise, there are typically few symptoms though some people may have fever or headache, or feel tired. The rash usually heals within two to four weeks; however, some people develop ongoing nerve pain which can last for months or years, a condition called postherpetic neuralgia (PHN). In those with poor immune function the rash may occur widely. If the rash involves the eye, vision loss may occur. Shingles is caused by the varicella zoster virus (VZV) that also causes chickenpox. In the case of chickenpox, also called varicella, the initial infection with the virus typically occurs during childhood or adolescence. Once the chickenpox has resolv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neoplastic Disease
A neoplasm () is a type of abnormal and excessive growth of tissue. The process that occurs to form or produce a neoplasm is called neoplasia. The growth of a neoplasm is uncoordinated with that of the normal surrounding tissue, and persists in growing abnormally, even if the original trigger is removed. This abnormal growth usually forms a mass, when it may be called a tumor. ICD-10 classifies neoplasms into four main groups: benign neoplasms, in situ neoplasms, malignant neoplasms, and neoplasms of uncertain or unknown behavior. Malignant neoplasms are also simply known as cancers and are the focus of oncology. Prior to the abnormal growth of tissue, as neoplasia, cells often undergo an abnormal pattern of growth, such as metaplasia or dysplasia. However, metaplasia or dysplasia does not always progress to neoplasia and can occur in other conditions as well. The word is from Ancient Greek 'new' and 'formation, creation'. Types A neoplasm can be benign, potentially m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |