|
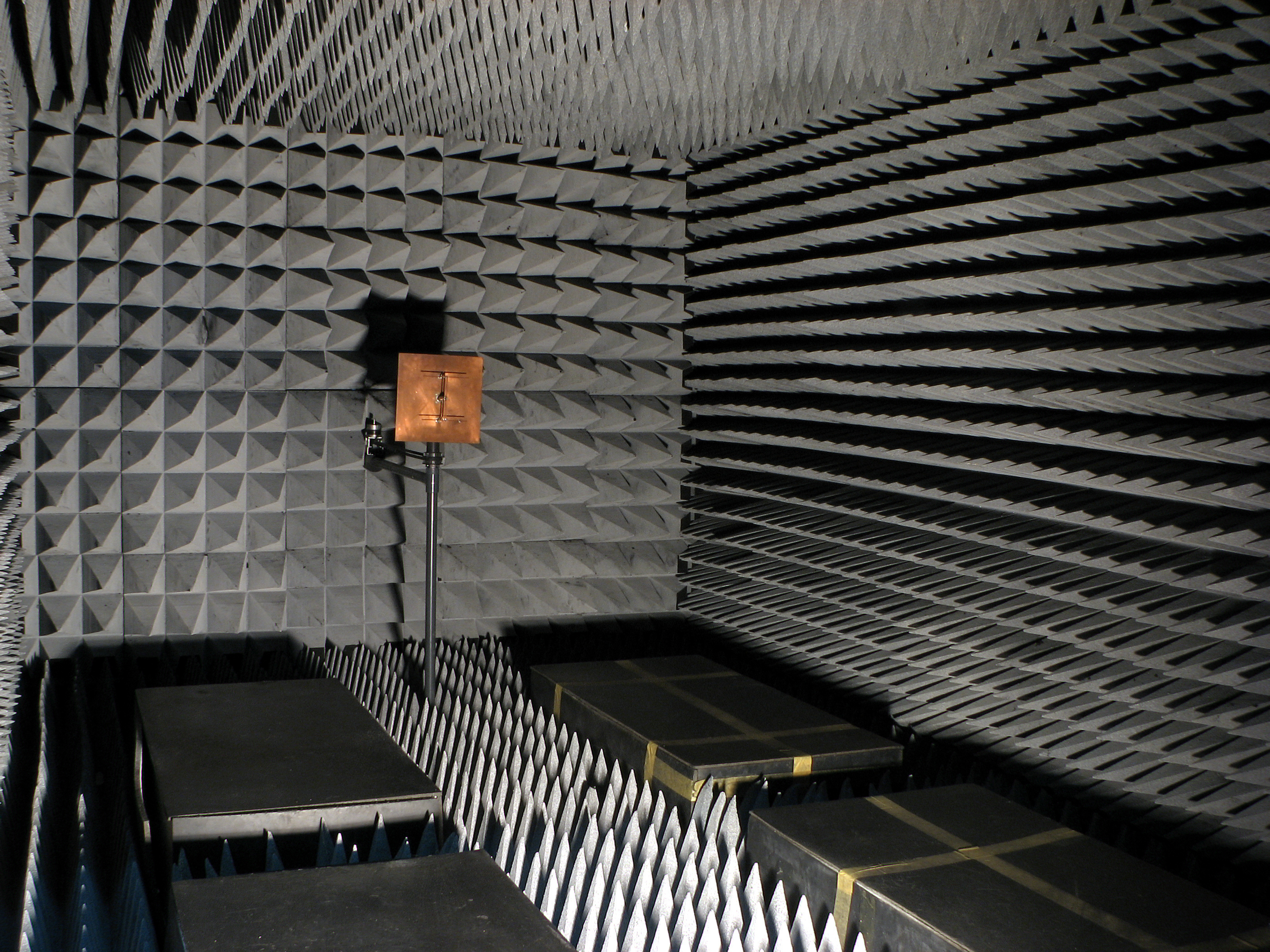
Radiation-absorbent Material
In materials science, radiation-absorbent material, usually known as RAM, is a material which has been specially designed and shaped to absorb incident RF radiation (also known as non-ionising radiation), as effectively as possible, from as many incident directions as possible. The more effective the RAM, the lower the resulting level of reflected RF radiation. Many measurements in electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) and antenna radiation patterns require that spurious signals arising from the test setup, including reflections, are negligible to avoid the risk of causing measurement errors and ambiguities. Introduction One of the most effective types of RAM comprises arrays of pyramid shaped pieces, each of which is constructed from a suitably lossy material. To work effectively, all internal surfaces of the anechoic chamber must be entirely covered with RAM. Sections of RAM may be temporarily removed to install equipment but they must be replaced before performing any tes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
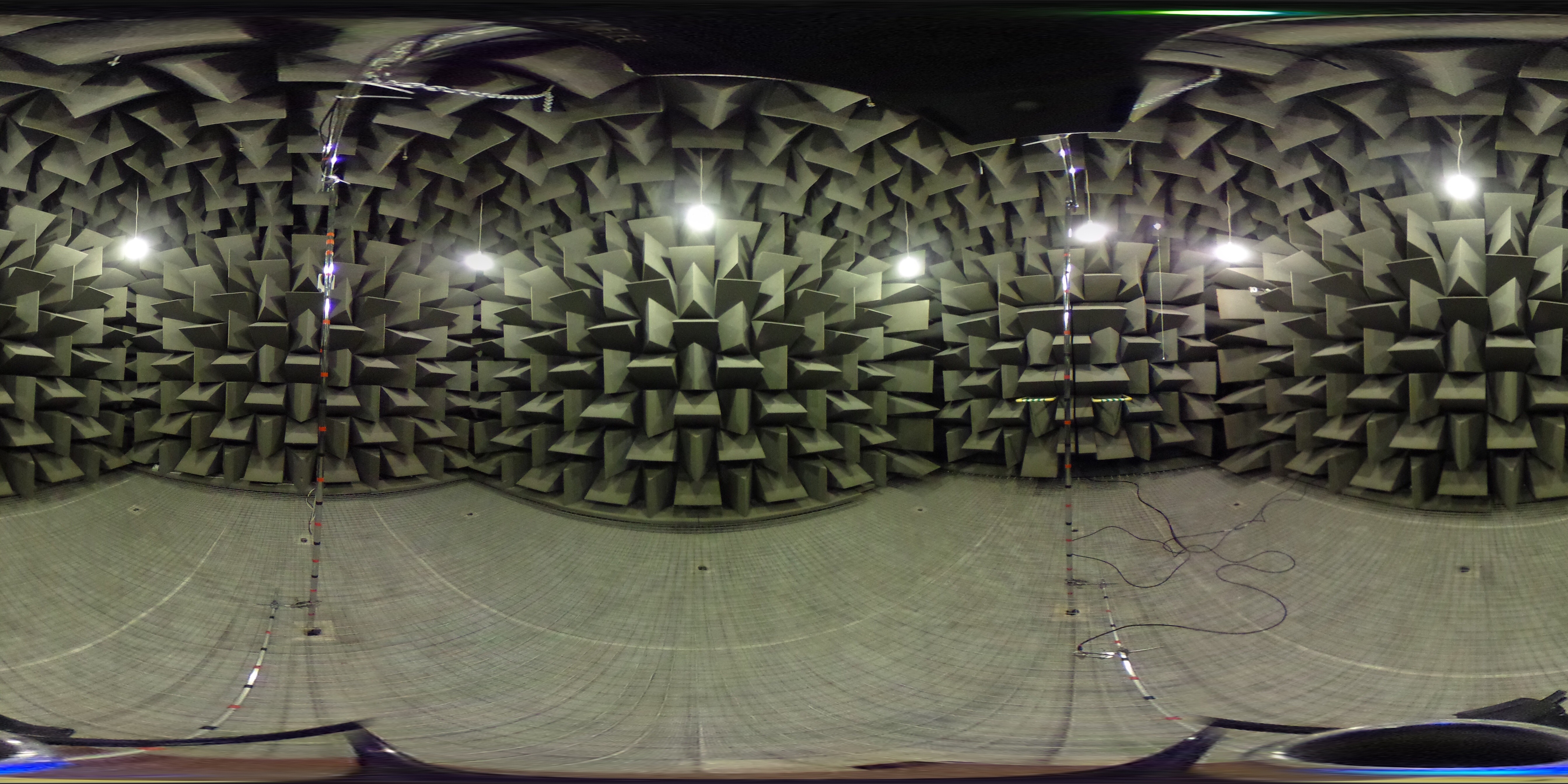
Anechoic Chamber
An anechoic chamber (''an-echoic'' meaning "non-reflective") is a room designed to stop reflections of either sound or electromagnetic waves. They are also often isolated from energy entering from their surroundings. This combination means that a person or detector exclusively hears direct sounds (no reflected sounds), in effect simulating being outside in a free field. Anechoic chambers, a term coined by American acoustics expert Leo Beranek, were initially exclusively used to refer to acoustic anechoic chambers. Recently, the term has been extended to other RF and Sonar anechoic chambers, which eliminate reflection and external noise caused by electromagnetic waves. Anechoic chambers range from small compartments the size of household microwave ovens to ones as large as aircraft hangars. The size of the chamber depends on the size of the objects and frequency ranges being tested. Acoustic anechoic chambers The requirement for what was subsequently called an anechoic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
F-117 Nighthawk Front
The Lockheed F-117 Nighthawk is a retired American single-seat, twin-engine stealth attack aircraft developed by Lockheed's secretive Skunk Works division and operated by the United States Air Force (USAF). It was the first operational aircraft to be designed with stealth technology. The F-117 was based on the ''Have Blue'' technology demonstrator. The Nighthawk's maiden flight took place in 1981 at Groom Lake, Nevada, and the aircraft achieved initial operating capability status in 1983. The aircraft was shrouded in secrecy until it was revealed to the public in 1988. Of the 64 F-117s built, 59 were production versions, with the other five being prototypes. The F-117 was widely publicized for its role in the Gulf War of 1991. Although it was commonly referred to as the "Stealth Fighter", it was strictly an attack aircraft. F-117s took part in the conflict in Yugoslavia, where one was shot down by a surface-to-air missile (SAM) in 1999. The U.S. Air Force retired the F ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Horten Ho 229
The Horten H.IX, RLM designation Ho 229 (or Gotha Go 229 for extensive re-design work done by Gotha to prepare the aircraft for mass production) was a German prototype fighter/bomber initially designed by Reimar and Walter Horten to be built by Gothaer Waggonfabrik. Developed at a late stage of the Second World War, it was the first flying wing to be powered by jet engines.Green 1970, p. 247. The Ho 229 had been designed in response to a call by Hermann Göring, the head of the Luftwaffe, in 1943 for light bomber designs capable of meeting the "3×1000" requirement; namely, to carry of bombs a distance of with a speed of . Only jet propulsion was capable of achieving the required speed, but such engines were relatively primitive and extremely fuel-hungry, necessitating considerable effort across the rest of the design in order to satisfy the range requirement as well. The flying wing configuration was favoured by the Horten brothers due to its high aerodynamic efficiency, as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Semiconductive
A semiconductor is a material which has an electrical conductivity value falling between that of a conductor, such as copper, and an insulator, such as glass. Its resistivity falls as its temperature rises; metals behave in the opposite way. Its conducting properties may be altered in useful ways by introducing impurities (" doping") into the crystal structure. When two differently doped regions exist in the same crystal, a semiconductor junction is created. The behavior of charge carriers, which include electrons, ions, and electron holes, at these junctions is the basis of diodes, transistors, and most modern electronics. Some examples of semiconductors are silicon, germanium, gallium arsenide, and elements near the so-called " metalloid staircase" on the periodic table. After silicon, gallium arsenide is the second-most common semiconductor and is used in laser diodes, solar cells, microwave-frequency integrated circuits, and others. Silicon is a critical element for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Graphite
Graphite () is a crystalline form of the element carbon. It consists of stacked layers of graphene. Graphite occurs naturally and is the most stable form of carbon under standard conditions. Synthetic and natural graphite are consumed on large scale (300 kton/year, in 1989) for uses in pencils, lubricants, and electrodes. Under high pressures and temperatures it converts to diamond. It is a weak conductor of heat and electricity. Types and varieties Natural graphite The principal types of natural graphite, each occurring in different types of ore deposits, are * Crystalline small flakes of graphite (or flake graphite) occurs as isolated, flat, plate-like particles with hexagonal edges if unbroken. When broken the edges can be irregular or angular; * Amorphous graphite: very fine flake graphite is sometimes called amorphous; * Lump graphite (or vein graphite) occurs in fissure veins or fractures and appears as massive platy intergrowths of fibrous or acicular crystalline ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Submarine
A submarine (or sub) is a watercraft capable of independent operation underwater. It differs from a submersible, which has more limited underwater capability. The term is also sometimes used historically or colloquially to refer to remotely operated vehicles and Autonomous underwater vehicle, robots, as well as medium-sized or smaller vessels, such as the midget submarine and the wet sub. Submarines are referred to as ''boats'' rather than ''ships'' irrespective of their size. Although experimental submarines had been built earlier, submarine design took off during the 19th century, and they were adopted by several navies. They were first widely used during World War I (1914–1918), and are now used in many navy, navies, large and small. Military uses include attacking enemy surface ships (merchant and military) or other submarines, and for aircraft carrier protection, Blockade runner, blockade running, Ballistic missile submarine, nuclear deterrence, reconnaissance, conventio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Periscopes
A periscope is an instrument for observation over, around or through an object, obstacle or condition that prevents direct line-of-sight observation from an observer's current position. In its simplest form, it consists of an outer case with mirrors at each end set parallel to each other at a 45° angle. This form of periscope, with the addition of two simple lenses, served for observation purposes in the trenches during World War I. Military personnel also use periscopes in some gun turrets and in armoured vehicles. More complex periscopes using prisms or advanced fiber optics instead of mirrors and providing magnification operate on submarines and in various fields of science. The overall design of the classical submarine periscope is very simple: two telescopes pointed into each other. If the two telescopes have different individual magnification, the difference between them causes an overall magnification or reduction. Early examples Johannes Hevelius described an early ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Submarine Snorkel
A submarine snorkel is a device which allows a submarine to operate submerged while still taking in air from above the surface. British Royal Navy personnel often refer to it as the snort. A concept devised by Dutch engineers, it was widely used on German U-boats during the last year of World War II and known to them as a ''Schnorchel''. History Until the advent of nuclear power, submarines were designed to operate on the surface most of the time and submerge only for evasion or for daylight attacks. Until the widespread use of radar after 1940, at night a submarine was safer on the surface than submerged, because sonar could detect boats underwater but was almost useless against a surface vessel. However, with continued radar improvement as the war progressed, submarines (notably, the German U-boats in the Battle of the Atlantic) were forced to spend more time underwater, running on electric motors that gave speeds of only a few knots and very limited range. An early submar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposing military alliances: the Allies and the Axis powers. World War II was a total war that directly involved more than 100 million personnel from more than 30 countries. The major participants in the war threw their entire economic, industrial, and scientific capabilities behind the war effort, blurring the distinction between civilian and military resources. Aircraft played a major role in the conflict, enabling the strategic bombing of population centres and deploying the only two nuclear weapons ever used in war. World War II was by far the deadliest conflict in human history; it resulted in 70 to 85 million fatalities, mostly among civilians. Tens of millions died due to genocides (including the Holocaust), starvation, ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radar Cross-section
Radar cross-section (RCS), also called radar signature, is a measure of how detectable an object is by radar. A larger RCS indicates that an object is more easily detected. An object reflects a limited amount of radar energy back to the source. The factors that influence this include: *the material with which the target is made; *the size of the target relative to the wavelength of the illuminating radar signal; *the absolute size of the target; *the incident angle (angle at which the radar beam hits a particular portion of the target, which depends upon the shape of the target and its orientation to the radar source); *the reflected angle (angle at which the reflected beam leaves the part of the target hit; it depends upon incident angle); *the polarization of the transmitted and the received radiation with respect to the orientation of the target. While important in detecting targets, strength of emitter and distance are not factors that affect the calculation of an RCS becaus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radar
Radar is a detection system that uses radio waves to determine the distance (''ranging''), angle, and radial velocity of objects relative to the site. It can be used to detect aircraft, ships, spacecraft, guided missiles, motor vehicles, weather formations, and terrain. A radar system consists of a transmitter producing electromagnetic waves in the radio or microwaves domain, a transmitting antenna, a receiving antenna (often the same antenna is used for transmitting and receiving) and a receiver and processor to determine properties of the objects. Radio waves (pulsed or continuous) from the transmitter reflect off the objects and return to the receiver, giving information about the objects' locations and speeds. Radar was developed secretly for military use by several countries in the period before and during World War II. A key development was the cavity magnetron in the United Kingdom, which allowed the creation of relatively small systems with sub-meter resolution. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |