|
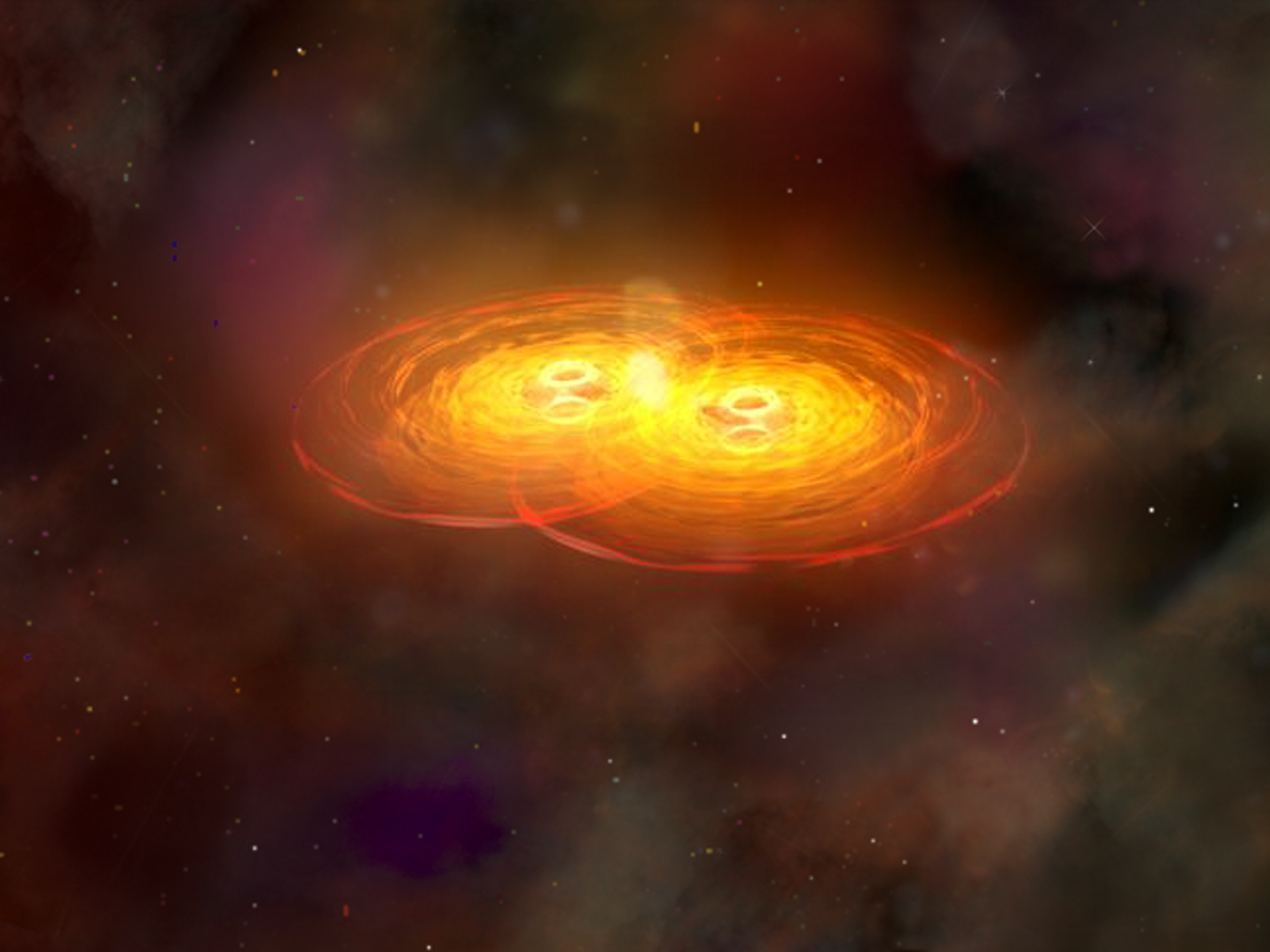
Quasinormal Mode
Quasinormal modes (QNM) are the modes of energy dissipation of a perturbed object or field, ''i.e.'' they describe perturbations of a field that decay in time. Example A familiar example is the perturbation (gentle tap) of a wine glass with a knife: the glass begins to ring, it rings with a set, or superposition, of its natural frequencies — its modes of sonic energy dissipation. One could call these modes ''normal'' if the glass went on ringing forever. Here the amplitude of oscillation decays in time, so we call its modes ''quasi-normal''. To a high degree of accuracy, quasinormal ringing can be approximated by :\psi(t) \approx e^\cos\omega^t where \psi\left(t\right) is the amplitude of oscillation, \omega^ is the frequency, and \omega^ is the decay rate. The quasinormal frequency is described by two numbers, :\omega = \left(\omega^ , \omega^\right) or, more compactly :\psi\left(t\right) \approx \operatorname(e^) :\omega =\omega^ + i\omega^ Here, \mathbf is what is comm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Energy
In physics, energy (from Ancient Greek: ἐνέργεια, ''enérgeia'', “activity”) is the quantitative property that is transferred to a body or to a physical system, recognizable in the performance of work and in the form of heat and light. Energy is a conserved quantity—the law of conservation of energy states that energy can be converted in form, but not created or destroyed. The unit of measurement for energy in the International System of Units (SI) is the joule (J). Common forms of energy include the kinetic energy of a moving object, the potential energy stored by an object (for instance due to its position in a field), the elastic energy stored in a solid object, chemical energy associated with chemical reactions, the radiant energy carried by electromagnetic radiation, and the internal energy contained within a thermodynamic system. All living organisms constantly take in and release energy. Due to mass–energy equivalence, any object that has mass whe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Theoretical Physics
Theoretical physics is a branch of physics that employs mathematical models and abstractions of physical objects and systems to rationalize, explain and predict natural phenomena. This is in contrast to experimental physics, which uses experimental tools to probe these phenomena. The advancement of science generally depends on the interplay between experimental studies and theory. In some cases, theoretical physics adheres to standards of mathematical rigour while giving little weight to experiments and observations.There is some debate as to whether or not theoretical physics uses mathematics to build intuition and illustrativeness to extract physical insight (especially when normal experience fails), rather than as a tool in formalizing theories. This links to the question of it using mathematics in a less formally rigorous, and more intuitive or heuristic way than, say, mathematical physics. For example, while developing special relativity, Albert Einstein was concerned wit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Resonance (quantum Field Theory)
In particle physics, a resonance is the peak located around a certain energy found in differential cross sections of scattering experiments. These peaks are associated with subatomic particles, which include a variety of bosons, quarks and hadrons (such as nucleons, delta baryons or upsilon mesons) and their excitations. In common usage, "resonance" only describes particles with very short lifetimes, mostly high-energy hadrons existing for or less. The width of the resonance (''Γ'') is related to the mean lifetime (''τ'') of the particle (or its excited state) by the relation :\Gamma=\frac where ''h'' is the Planck constant and =\frac. Thus, the lifetime of a particle is the direct inverse of the particle's resonance width. For example, the charged pion has the second-longest lifetime of any meson, at . Therefore, its resonance width is very small, about or about 6.11 MHz. Pions are generally not considered as "resonances". The charged rho meson has a very short lifetime, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Superradiance
In physics, superradiance is the radiation enhancement effects in several contexts including quantum mechanics, astrophysics and relativity. Quantum optics In quantum optics, superradiance is a phenomenon that occurs when a group of ''N'' emitters, such as excited atoms, interact with a common light field. If the wavelength of the light is much greater than the separation of the emitters, then the emitters interact with the light in a collective and coherent fashion. This causes the group to emit light as a high intensity pulse (with rate proportional to ''N''2). This is a surprising result, drastically different from the expected exponential decay (with rate proportional to ''N'') of a group of independent atoms (see spontaneous emission). Superradiance has since been demonstrated in a wide variety of physical and chemical systems, such as quantum dot arrays and J-aggregates. This effect has been used to produce a superradiant laser. Rotational superradiance Rotational supe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Strong Interaction
The strong interaction or strong force is a fundamental interaction that confines quarks into proton, neutron, and other hadron particles. The strong interaction also binds neutrons and protons to create atomic nuclei, where it is called the nuclear force. Most of the mass of a common proton or neutron is the result of the strong interaction energy; the individual quarks provide only about 1% of the mass of a proton. At the range of 10−15 m (slightly more than the radius of a nucleon), the strong force is approximately 100 times as strong as electromagnetism, 106 times as strong as the weak interaction, and 1038 times as strong as gravitation. The strong interaction is observable at two ranges and mediated by two force carriers. On a larger scale (of about 1 to 3 femtometre, fm), it is the force (carried by mesons) that binds protons and neutrons (nucleons) together to form the atomic nucleus, nucleus of an atom. On the smaller scale (less than about 0.8 fm, t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cavity Perturbation Theory
In mathematics and electronics, Cavity perturbation theory describes methods for derivation of perturbation formulae for performance changes of a cavity resonator. These performance changes are assumed to be caused by either introduction of a small foreign object into the cavity, or a small deformation of its boundary. Various mathematical methods can be used to study the characteristics of cavities, which are important in the field of microwave systems, and more generally in the field of electro magnetism. There are many industrial applications for cavity resonators, including microwave ovens, microwave communication systems, and remote imaging systems using electro magnetic waves. How a resonant cavity performs can affect the amount of energy that is required to make it resonate, or the relative stability or instability of the system. Introduction When a resonant cavity is perturbed, e.g. by introducing a foreign object with distinct material properties into the cavity or when ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Purcell Effect
Henry Purcell (, rare: September 1659 – 21 November 1695) was an English composer. Purcell's style of Baroque music was uniquely English, although it incorporated Italian and French elements. Generally considered among the greatest English opera composers, Purcell is often linked with John Dunstaple and William Byrd as England's most important early music composers. No later native-born English composer approached his fame until Edward Elgar, Ralph Vaughan Williams, Gustav Holst, William Walton and Benjamin Britten in the 20th century. Life and work Early life Purcell was born in St Ann's Lane, Old Pye Street, Westminster – the area of London later known as Devil's Acre, a notorious slum – in 1659. Henry Purcell Senior, whose older brother Thomas Purcell was a musician, was a gentleman of the Chapel Royal and sang at the coronation of King Charles II of England. Henry the elder had three sons: Edward, Henry and Daniel. Daniel Purcell, the youngest of the brother ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
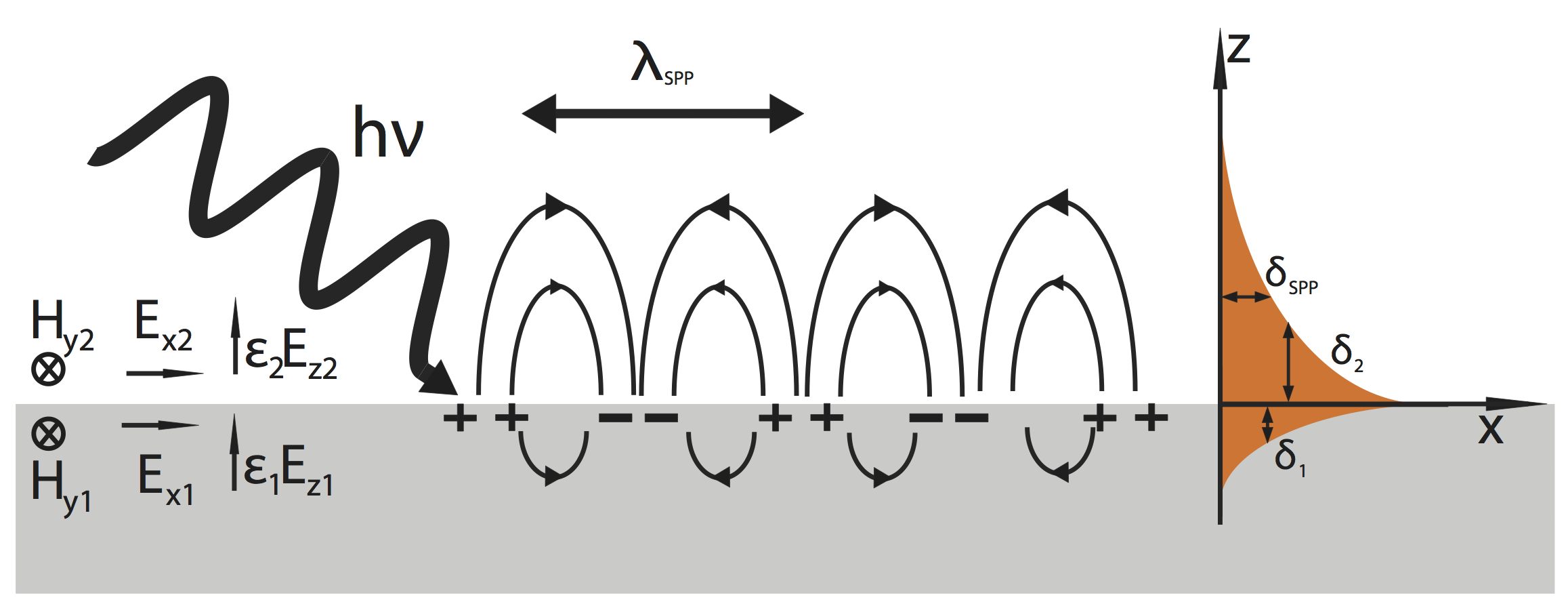
Surface Plasmon
Surface plasmons (SPs) are coherent delocalized electron oscillations that exist at the interface between any two materials where the real part of the dielectric function changes sign across the interface (e.g. a metal-dielectric interface, such as a metal sheet in air). SPs have lower energy than bulk (or volume) plasmons which quantise the longitudinal electron oscillations about positive ion cores within the bulk of an electron gas (or plasma). The charge motion in a surface plasmon always creates electromagnetic fields outside (as well as inside) the metal. The ''total'' excitation, including both the charge motion and associated electromagnetic field, is called either a surface plasmon polariton at a planar interface, or a localized surface plasmon for the closed surface of a small particle. The existence of surface plasmons was first predicted in 1957 by Rufus Ritchie. In the following two decades, surface plasmons were extensively studied by many scientists, the foremost o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Optical Microcavity
An optical microcavity or microresonator is a structure formed by reflecting faces on the two sides of a spacer layer or optical medium, or by wrapping a waveguide in a circular fashion to form a ring. The former type is a standing wave cavity, and the latter is a traveling wave cavity. The name ''micro''cavity stems from the fact that it is often only a few micrometers thick, the spacer layer sometimes even in the nanometer range. As with common lasers, this forms an optical cavity or ''optical resonator'', allowing a standing wave to form inside the spacer layer or a traveling wave that goes around in the ring. Applications and effects The fundamental difference between a conventional optical cavity and microcavities is the effects that arise from the small dimensions of the system, but their operational principle can often be understood in the same way as for larger optical resonators. Quantum effects of the light's electromagnetic field can be observed. For example, the spon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Q Factor
In physics and engineering, the quality factor or ''Q'' factor is a dimensionless parameter that describes how underdamped an oscillator or resonator is. It is defined as the ratio of the initial energy stored in the resonator to the energy lost in one radian of the cycle of oscillation. Q factor is alternatively defined as the ratio of a resonator's centre frequency to its bandwidth when subject to an oscillating driving force. These two definitions give numerically similar, but not identical, results. Higher ''Q'' indicates a lower rate of energy loss and the oscillations die out more slowly. A pendulum suspended from a high-quality bearing, oscillating in air, has a high ''Q'', while a pendulum immersed in oil has a low one. Resonators with high quality factors have low damping, so that they ring or vibrate longer. Explanation The Q factor is a parameter that describes the resonance behavior of an underdamped harmonic oscillator (resonator). Sinusoidally driven resonators ha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Loop Quantum Gravity
Loop quantum gravity (LQG) is a theory of quantum gravity, which aims to merge quantum mechanics and general relativity, incorporating matter of the Standard Model into the framework established for the pure quantum gravity case. It is an attempt to develop a quantum theory of gravity based directly on Einstein's geometric formulation rather than the treatment of gravity as a force. As a theory LQG postulates that the structure of Spacetime, space and time is composed of finite loops woven into an extremely fine fabric or network. These networks of loops are called spin networks. The evolution of a spin network, or spin foam, has a scale above the order of a Planck length, approximately 10−35 meters, and smaller scales are meaningless. Consequently, not just matter, but space itself, prefers an atomic hypothesis, atomic structure. The areas of research, which involves about 30 research groups worldwide, share the basic physical assumptions and the mathematical description of q ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |