|
Quadrilateral Mesh
A mesh is a representation of a larger geometric domain by smaller discrete cells. Meshes are commonly used to compute solutions of partial differential equations and render computer graphics, and to analyze geographical and cartographic data. A mesh partitions space into ''elements'' (or ''cells'' or ''zones'') over which the equations can be solved, which then approximates the solution over the larger domain. Element boundaries may be constrained to lie on internal or external boundaries within a model. Higher-quality (better-shaped) elements have better numerical properties, where what constitutes a "better" element depends on the general governing equations and the particular solution to the model instance. Common cell shapes Two-dimensional There are two types of two-dimensional cell shapes that are commonly used. These are the triangle and the quadrilateral. Computationally poor elements will have sharp internal angles or short edges or both. Triangle This cell shape consis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polygon Mesh
In 3D computer graphics and solid modeling, a polygon mesh is a collection of , s and s that defines the shape of a polyhedral object. The faces usually consist of triangles ( triangle mesh), quadrilaterals (quads), or other simple convex polygons (n-gons), since this simplifies rendering, but may also be more generally composed of concave polygons, or even polygons with holes. The study of polygon meshes is a large sub-field of computer graphics (specifically 3D computer graphics) and geometric modeling. Different representations of polygon meshes are used for different applications and goals. The variety of operations performed on meshes may include: Boolean logic (Constructive solid geometry), smoothing, simplification, and many others. Algorithms also exist for ray tracing, collision detection, and rigid-body dynamics with polygon meshes. If the mesh's edges are rendered instead of the faces, then the model becomes a wireframe model. Volumetric meshes are dis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Example Of 2D Mesh
Example may refer to: * '' exempli gratia'' (e.g.), usually read out in English as "for example" * .example, reserved as a domain name that may not be installed as a top-level domain of the Internet ** example.com, example.net, example.org, example.edu, second-level domain names reserved for use in documentation as examples * HMS ''Example'' (P165), an Archer-class patrol and training vessel of the Royal Navy Arts * ''The Example'', a 1634 play by James Shirley * ''The Example'' (comics), a 2009 graphic novel by Tom Taylor and Colin Wilson * Example (musician), the British dance musician Elliot John Gleave (born 1982) * ''Example'' (album), a 1995 album by American rock band For Squirrels See also * * Exemplar (other), a prototype or model which others can use to understand a topic better * Exemplum, medieval collections of short stories to be told in sermons * Eixample The Eixample (; ) is a district of Barcelona between the old city ( Ciutat Vella) an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Laplacian Smoothing
Laplacian smoothing is an algorithm to smooth a polygonal mesh In 3D computer graphics and solid modeling, a polygon mesh is a collection of , s and s that defines the shape of a polyhedral object. The faces usually consist of triangles (triangle mesh), quadrilaterals (quads), or other simple convex polyg .... For each vertex in a mesh, a new position is chosen based on local information (such as the position of neighbours) and the vertex is moved there. In the case that a mesh is topologically a rectangular grid (that is, each internal vertex is connected to four neighbours) then this operation produces the Laplacian of the mesh. More formally, the smoothing operation may be described per-vertex as: :\bar_= \frac \sum_^\bar_j Where N is the number of adjacent vertices to node i, \bar_ is the position of the j-th adjacent vertex and \bar_ is the new position for node i. See also * Tutte embedding, an embedding of a planar mesh in which each vertex is already at the aver ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
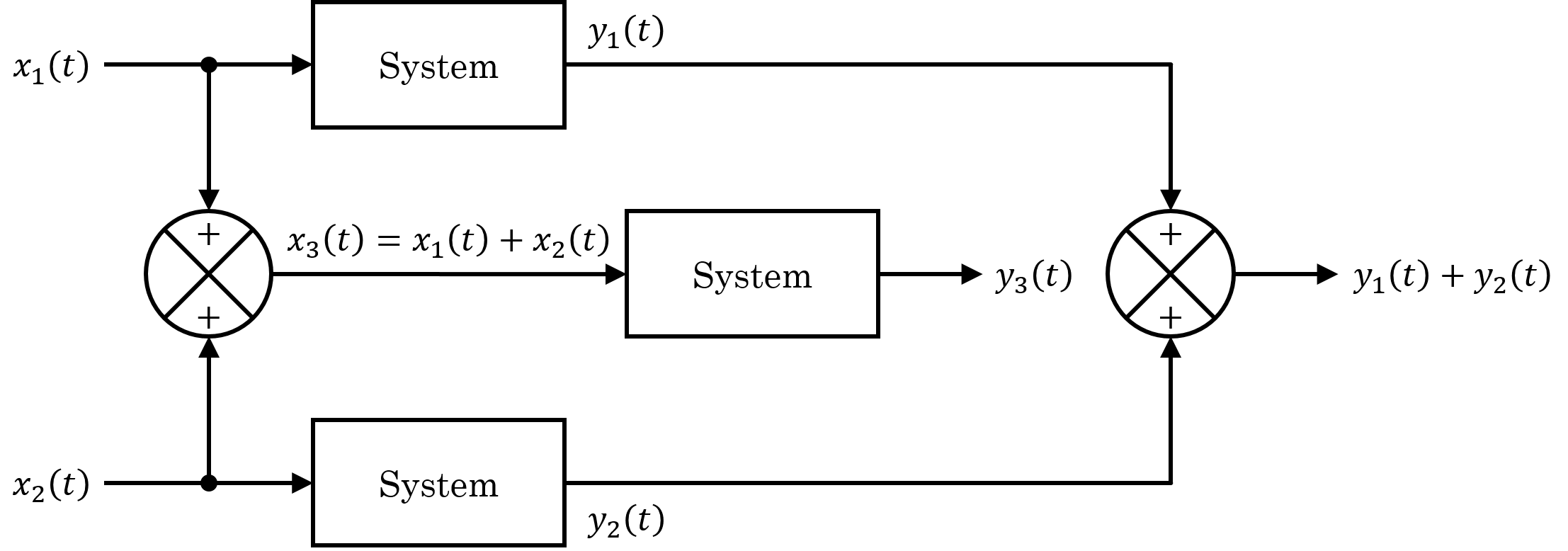
Linear System
In systems theory, a linear system is a mathematical model of a system based on the use of a linear operator. Linear systems typically exhibit features and properties that are much simpler than the nonlinear case. As a mathematical abstraction or idealization, linear systems find important applications in automatic control theory, signal processing, and telecommunications. For example, the propagation medium for wireless communication systems can often be modeled by linear systems. Definition A general deterministic system can be described by an operator, that maps an input, as a function of to an output, a type of black box description. A system is linear if and only if it satisfies the superposition principle, or equivalently both the additivity and homogeneity properties, without restrictions (that is, for all inputs, all scaling constants and all time.) The superposition principle means that a linear combination of inputs to the system produces a linear combinat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Principles Of Grid Generation
Mesh generation is the practice of creating a mesh, a subdivision of a continuous geometric space into discrete geometric and topological cells. Often these cells form a simplicial complex. Usually the cells partition the geometric input domain. Mesh cells are used as discrete local approximations of the larger domain. Meshes are created by computer algorithms, often with human guidance through a GUI , depending on the complexity of the domain and the type of mesh desired. A typical goal is to create a mesh that accurately captures the input domain geometry, with high-quality (well-shaped) cells, and without so many cells as to make subsequent calculations intractable. The mesh should also be fine (have small elements) in areas that are important for the subsequent calculations. Meshes are used for rendering to a computer screen and for physical simulation such as finite element analysis or computational fluid dynamics. Meshes are composed of simple cells like triangles becaus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mesh Generation
Mesh generation is the practice of creating a mesh, a subdivision of a continuous geometric space into discrete geometric and topological cells. Often these cells form a simplicial complex. Usually the cells partition the geometric input domain. Mesh cells are used as discrete local approximations of the larger domain. Meshes are created by computer algorithms, often with human guidance through a GUI , depending on the complexity of the domain and the type of mesh desired. A typical goal is to create a mesh that accurately captures the input domain geometry, with high-quality (well-shaped) cells, and without so many cells as to make subsequent calculations intractable. The mesh should also be fine (have small elements) in areas that are important for the subsequent calculations. Meshes are used for rendering to a computer screen and for physical simulation such as finite element analysis or computational fluid dynamics. Meshes are composed of simple cells like triangles because, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aspect Ratio Grid
Aspect or Aspects may refer to: Entertainment * ''Aspect magazine'', a biannual DVD magazine showcasing new media art * Aspect Co., a Japanese video game company * Aspects (band), a hip hop group from Bristol, England * ''Aspects'' (Benny Carter album), a 1959 album by Benny Carter * ''Aspects'' (The Eleventh House album), a 1976 album by Larry Coryell and The Eleventh House * ''Aspects'' (novel), a posthumous novel by John M. Ford Persons * Alain Aspect, a French physicist and Nobel prize recipient (1947–) Other * Aspect (computer programming), a feature linked to many parts of a program but not necessarily the primary function of the program * Aspect (geography), the compass direction that a slope faces * Aspect (religion), a particular manifestation of a deity * Aspect (trade union), a trade union in the United Kingdom * Aspect Software, an American call center technology and customer experience company * Astrological aspect, an angle the planets have to each other * Gra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Smooth And Large Jump
Smooth may refer to: Mathematics * Smooth function, a function that is infinitely differentiable; used in calculus and topology * Smooth manifold, a differentiable manifold for which all the transition maps are smooth functions * Smooth algebraic variety, an algebraic variety with no singular points * Smooth number, a number whose prime factors are all less than a certain value; used in applications of number theory * Smoothsort, a sorting algorithm Arts and entertainment Music * Smooth (singer), Juanita Stokes, American singer, rapper and actress * ''Smooth'' (album), by Smooth, 1995 * ''Smooth'', an album by Gerald Albright, 1994 * "Smooth" (Florida Georgia Line song), 2017 * "Smooth" (iiO song), 2004 * "Smooth" (Santana song), featuring Rob Thomas, 1999 * "Smooth", a mashup by Neil Cicierega from ''Mouth Moods'', 2017 Other media * ''Smooth'' (magazine), an American publication for young black men * Smooth Radio (other), UK radio station networks * smoothfm, an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |