|
Pydiflumetofen
Pydiflumetofen is a broad spectrum fungicide used in agriculture to protect crops from fungal diseases. It was first marketed by Syngenta in 2016 using their brand name Miravis. The compound is an amide which combines a pyrazole acid with a substituted phenethylamine to give an inhibitor of succinate dehydrogenase, an enzyme that inhibits cellular respiration in almost all living organisms. History Inhibition of succinate dehydrogenase, the complex II in the mitochondrial respiration chain, has been known as a fungicidal mechanism of action since the first examples were marketed in the 1960s. The first compound in this class was carboxin, which had a narrow spectrum of useful biological activity, mainly on basidiomycetes and was used as a seed treatment. By 2016, at least 17 further examples of this mechanism of action were developed by crop protection companies, with the market leader being boscalid, owing to its broader spectrum of fungal species controlled. However, it lacked f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pydiflumetofen Synthesis
Pydiflumetofen is a broad spectrum fungicide used in agriculture to protect crops from fungal diseases. It was first marketed by Syngenta in 2016 using their brand name Miravis. The compound is an amide which combines a pyrazole acid with a substituted phenethylamine to give an inhibitor of succinate dehydrogenase, an enzyme that inhibits cellular respiration in almost all living organisms. History Inhibition of succinate dehydrogenase, the complex II in the mitochondrial respiration chain, has been known as a fungicidal mechanism of action since the first examples were marketed in the 1960s. The first compound in this class was carboxin, which had a narrow spectrum of useful biological activity, mainly on basidiomycetes and was used as a seed treatment. By 2016, at least 17 further examples of this mechanism of action were developed by crop protection companies, with the market leader being boscalid, owing to its broader spectrum of fungal species controlled. However, it lacked f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
3-(Difluoromethyl)-1-methyl-1H-pyrazole-4-carboxylic Acid
3-(Difluoromethyl)-1-methyl-1''H''-pyrazole-4-carboxylic acid is a chemical compound which is used commercially as an intermediate to seven fungicides which act by inhibition of succinate dehydrogenase (SDHI). It consists of a pyrazole ring with difluoromethyl, methyl and carboxylic acid groups attached in specific positions. Background Inhibition of succinate dehydrogenase, the complex II in the mitochondrial respiration chain, has been known as a fungicidal mechanism of action since the first examples were marketed in the 1960s. By 2016, at least 18 examples were developed by crop protection companies, with the market leader being boscalid, owing to its broad spectrum of fungal species controlled. However, it lacked full control of important cereal diseases, especially septoria leaf blotch ''Zymoseptoria tritici''. A group of compounds which did control septoria were 3-(difluoromethyl)-1-methyl-1H-pyrazole-4-carboxylic amides, as shown below, ordered by year of their first re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sedaxane
Sedaxane is a broad spectrum fungicide used as a seed treatment in agriculture to protect crops from fungal diseases. It was first marketed by Syngenta in 2011 using their brand name Vibrance. The compound is an amide which combines a pyrazole acid with an aryl amine to give an inhibitor of succinate dehydrogenase. The compound is widely registered for use, including in Australia, the EU, UK and US. History Inhibition of succinate dehydrogenase, the complex II in the mitochondrial respiration chain, has been known as a fungicidal mechanism of action since the first examples were marketed in the 1960s. The first compound in this class was carboxin, which had a narrow spectrum of useful biological activity, mainly on basidiomycetes and was used as a seed treatment. By 2016, at least 17 further examples of this mechanism of action were developed by crop protection companies, with the market leader being boscalid, owing to its broader spectrum of fungal species controlled. How ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Syngenta
Syngenta AG is a provider of agricultural science and technology, in particular seeds and pesticides with its management headquarters in Basel, Switzerland. It is owned by ChemChina, a Chinese state-owned enterprise. Syngenta was founded in 2000 by the merger of the agrichemical businesses of Novartis and AstraZeneca, and acquired by China National Chemical Corporation (ChemChina) in 2017. Its business units are Syngenta Crop Protection, Syngenta Seeds, Adama, and Syngenta Group China. In 2020, the Syngenta Group was formed, bringing together Syngenta, Adama, and the agricultural business of Sinochem under a single entity. Syngenta's primary products include pesticides, selective herbicides, non-selective herbicides, fungicides, insecticides, as well as corn, soya, and biofuel. Syngenta brands include Actara (Thiamethoxam), Agrisure (corn with Viptera trait), Alto (Cyproconazole), Amistar (azoxystrobin), Avicta, Axial, Bicep II, Bravo, Callisto, Celest, Cruiser (TMX, Thiamet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British Crop Production Council
The British Crop Production Council (BCPC) is an organisation that promotes the use of good science and technology in the understanding and application of effective and sustainable crop production. BCPC is a Registered Charity and a Company limited by Guarantee. Function The key objectives of BPCP are to: *Identify developing issues in the science and practice of crop protection and production, and provide informed, independent analysis and views on these to opinion formers, government and the public *Publish definitive information for growers, advisors and other stakeholders in the food, fuel and fibre production chain, in the form of reference works, manuals and handbooks *Organise and co-host conferences and symposia to provide platforms for the reporting and debate of scientific relevant results and opinion *Contribute to the future of UK (bio) science by providing publications for schools which stimulate interest and learning. History BCPC was formed in 1967 by the amalga ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sodium Cyanoborohydride
Sodium cyanoborohydride is the chemical compound with the formula Sodium, NaBoron, BHydrogen, H3cyanide, CN. It is a colourless salt, but commercial samples can appear tan. It is widely used in organic synthesis for the reduction of imines. The salt tolerates aqueous conditions. Use Owing to the presence of the electron-withdrawing cyanide substituent, [B(CN)H3]− is less reducing than is sodium borohydride, [BH4]−. As a mild reducing agent, it is used to convert imines to amines. It is especially favored for reductive aminations, wherein aldehydes or ketones are treated with an amine in the presence of this reagent: : R2CO + R'NH2 + NaBH3CN + CH3OH → R2CH-NHR' + "NaCH3OBH2CN" The reagent is typically used in excess. Selectivity is achieved at mildly basic solutions (pH 7–10). The reagent is ideal for reductive aminations ("Borch Reaction"). In conjunction with tosylhydrazine, sodium cyanoborohydride is used in the reductive deoxygenation of ketones. Structure and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Methoxyamine
Methoxyamine is the organic compound with the formula CH3ONH2. Also called ''O''-methylhydroxylamine, it a colourless volatile liquid that is soluble in polar organic solvent and in water. It is a derivative of hydroxylamine with the hydroxyl hydrogen replaced by a methyl group. Alternatively, it can be viewed as a derivative of methanol with the hydroxyl hydrogen replaced by an amino group. It is an isomer of N-methylhydroxylamine and aminomethanol. It decomposes in an exothermic reaction (-56 kJ/mol) to methane and azanone unless stored as a hydrochloride salt. Synthesis Methoxyamine is prepared via ''O''-alkylation of hydroxylamine derivatives. For example, it is obtained by ''O''-methylation of acetone oxime followed by hydrolysis of the ''O''-methylated oxime: :(CH3)2CNOCH3 + H2O → (CH3)2CO + H2NOCH3 The other broad method involves methanolysis of hydroxylamine sulfonates: :H2NOSO3− + CH3OH → H2NOCH3 + HSO4− Reactions Analogous to the behavior o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reduction (chemistry)
Redox (reduction–oxidation, , ) is a type of chemical reaction in which the oxidation states of substrate (chemistry), substrate change. Oxidation is the loss of Electron, electrons or an increase in the oxidation state, while reduction is the gain of electrons or a decrease in the oxidation state. There are two classes of redox reactions: * ''Electron-transfer'' – Only one (usually) electron flows from the reducing agent to the oxidant. This type of redox reaction is often discussed in terms of redox couples and electrode potentials. * ''Atom transfer'' – An atom transfers from one substrate to another. For example, in the rusting of iron, the oxidation state of iron atoms increases as the iron converts to an oxide, and simultaneously the oxidation state of oxygen decreases as it accepts electrons released by the iron. Although oxidation reactions are commonly associated with the formation of oxides, other chemical species can serve the same function. In hydrogen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nitroethane
Nitroethane is an organic compound having the chemical formula C2H5NO2. Similar in many regards to nitromethane, nitroethane is an oily liquid at standard temperature and pressure. Pure nitroethane is colorless and has a fruity odor. Preparation Nitroethane is produced industrially by treating propane with nitric acid at 350–450 °C. This exothermic reaction produces four industrially significant nitroalkanes: nitromethane, nitroethane, 1-nitropropane, and 2-nitropropane. The reaction involves free radicals, such as CH3CH2CH2O., which arise via homolysis of the corresponding nitrite ester. These alkoxy radicals are susceptible to C—C fragmentation reactions, which explains the formation of a mixture of products.Sheldon B. Markofsky “Nitro Compounds, Aliphatic” in ''Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry'', Wiley-VCH, Weinheim, 2002. . Alternatively, nitroethane can be produced by the Victor Meyer reaction of haloethanes such as chloroethane, bromo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
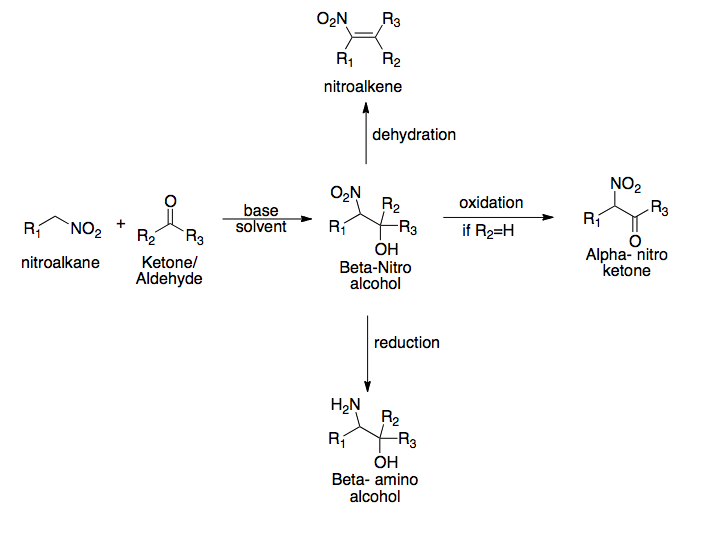
Henry Reaction
The Henry reaction is a classic carbon–carbon bond formation reaction in organic chemistry. Discovered in 1895 by the Belgian chemist Louis Henry (1834–1913), it is the combination of a nitroalkane and an aldehyde or ketone in the presence of a base to form β-nitro alcohols. This type of reaction is also referred to as a nitroaldol reaction (nitroalkane, aldehyde, and alcohol). It is nearly analogous to the aldol reaction that had been discovered 23 years prior that couples two carbonyl compounds to form β-hydroxy carbonyl compounds known as "aldols" (aldehyde and alcohol). The Henry reaction is a useful technique in the area of organic chemistry due to the synthetic utility of its corresponding products, as they can be easily converted to other useful synthetic intermediates. These conversions include subsequent dehydration to yield nitroalkenes, oxidation of the secondary alcohol to yield α-nitro ketones, or reduction of the nitro group to yield β-amino alcohols. Many ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beta-Nitrostyrene
β-Nitrostyrene is an aromatic compound and a nitroalkene used in the synthesis of indigo dye and the slimicide bromo-nitrostyrene. Applications β-Nitrostyrene is a chemical precursor for slimicides and dyes. Specifically bromo-nitrostyrene is obtained upon treatment with bromine followed by partial dehydrohalogenation while 2-nitrobenzaldehyde is obtained by treatment with ozone respectively. Many of the syntheses of psychedelic substituted phenethylamines and substituted amphetamines described by Alexander Shulgin in his book PiHKAL use substituted nitrostyrenes as precursors. They are the final precursor, reduced with lithium aluminium hydride to the final product (an amine). Chemical synthesis The chemical is produced by either the Henry reaction of benzaldehyde and nitromethane or by direct nitration of styrene using nitric oxide Nitric oxide (nitrogen oxide or nitrogen monoxide) is a colorless gas with the formula . It is one of the principal oxides of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amine
In chemistry, amines (, ) are compounds and functional groups that contain a basic nitrogen atom with a lone pair. Amines are formally derivatives of ammonia (), wherein one or more hydrogen atoms have been replaced by a substituent such as an alkyl or aryl group (these may respectively be called alkylamines and arylamines; amines in which both types of substituent are attached to one nitrogen atom may be called alkylarylamines). Important amines include amino acids, biogenic amines, trimethylamine, and aniline; Inorganic derivatives of ammonia are also called amines, such as monochloramine (). The substituent is called an amino group. Compounds with a nitrogen atom attached to a carbonyl group, thus having the structure , are called amides and have different chemical properties from amines. Classification of amines Amines can be classified according to the nature and number of substituents on nitrogen. Aliphatic amines contain only H and alkyl substituents. A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |