|
Pseudohypoaldosteronism
Pseudohypoaldosteronism (PHA) is a condition that mimics hypoaldosteronism. However, the condition is due to a failure of ''response'' to aldosterone, and levels of aldosterone are actually elevated, due to a lack of feedback inhibition. Types Presentation PHA2 is clinically characterised by hypertension, hyperkalaemia, metabolic acidosis and normal renal function. Mechanism PHA2 is also known as familial hyperkalaemic hypertension, or Gordon syndrome. The underlying genetic defect leads to increased sodium chloride reabsorption in the distal tubule in the kidney, leading to volume expansion, hypertension and lowered renin levels. The hyperkalemia found in PHA2 is proposed to be a function of diminished sodium delivery to the cortical collecting tubule (potassium excretion is mediated by the renal outer medullary potassium channel ROMK in which sodium reabsorption plays a role). Alternatively, WNK4 mutations that result in a gain of function of the Na-Cl co-transporter may inhib ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SCNN1A
The SCNN1A gene encodes for the α subunit of the epithelial sodium channel ENaC in vertebrates. ENaC is assembled as a heterotrimer composed of three homologous subunits α, β, and γ or δ, β, and γ. The other ENAC subunits are encoded by SCNN1B, SCNN1G, and SCNN1D. ENaC is expressed in epithelial cells and is different from the voltage-gated sodium channel that is involved in the generation of action potentials in neurons. The abbreviation for the genes encoding for voltage-gated sodium channel starts with three letters: SCN. In contrast to these sodium channels, ENaC is constitutively active and is not voltage-dependent. The second N in the abbreviation (SCNN1A) represents that these are NON-voltage-gated channels. In most vertebrates, sodium ions are the major determinant of the osmolarity of the extracellular fluid. ENaC allows transfer of sodium ions across the epithelial cell membrane in so-called "tight-epithelia" that have low permeability. The flow of sodium ions acr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SCNN1G
The SCNN1G gene encodes for the γ subunit of the epithelial sodium channel ENaC in vertebrates. ENaC is assembled as a heterotrimer composed of three homologous subunits α, β, and γ or δ, β, and γ. The other ENAC subunits are encoded by SCNN1A, SCNN1B, and SCNN1D. ENaC is expressed in epithelial cells and is different from the voltage-gated sodium channel that is involved in the generation of action potentials in neurons. The abbreviation for the genes encoding for voltage-gated sodium channel starts with three letters: SCN. In contrast to these sodium channels, ENaC is constitutively active and is not voltage-dependent. The second N in the abbreviation (SCNN1) represents that these are NON-voltage-gated channels. In most vertebrates, sodium ions are the major determinant of the osmolarity of the extracellular fluid. ENaC allows transfer of sodium ions across the epithelial cell membrane in so-called "tight-epithelia" that have low permeability. The flow of sodium ions ac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SCNN1B
The SCNN1B gene encodes for the β subunit of the epithelial sodium channel ENaC in vertebrates. ENaC is assembled as a heterotrimer composed of three homologous subunits α, β, and γ or δ, β, and γ. The other ENAC subunits are encoded by SCNN1A, SCNN1G, and SCNN1D. ENaC is expressed in epithelial cells and is different from the voltage-gated sodium channel that is involved in the generation of action potentials in neurons. The abbreviation for the genes encoding for voltage-gated sodium channel starts with three letters: SCN. In contrast to these sodium channels, ENaC is constitutively active and is not voltage-dependent. The second N in the abbreviation (SCNN1A) represents that these are NON-voltage-gated channels. In most vertebrates, sodium ions are the major determinant of the osmolarity of the extracellular fluid. ENaC allows transfer of sodium ions across the epithelial cell membrane in so-called "tight-epithelia" that have low permeability. The flow of sodium ions acr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
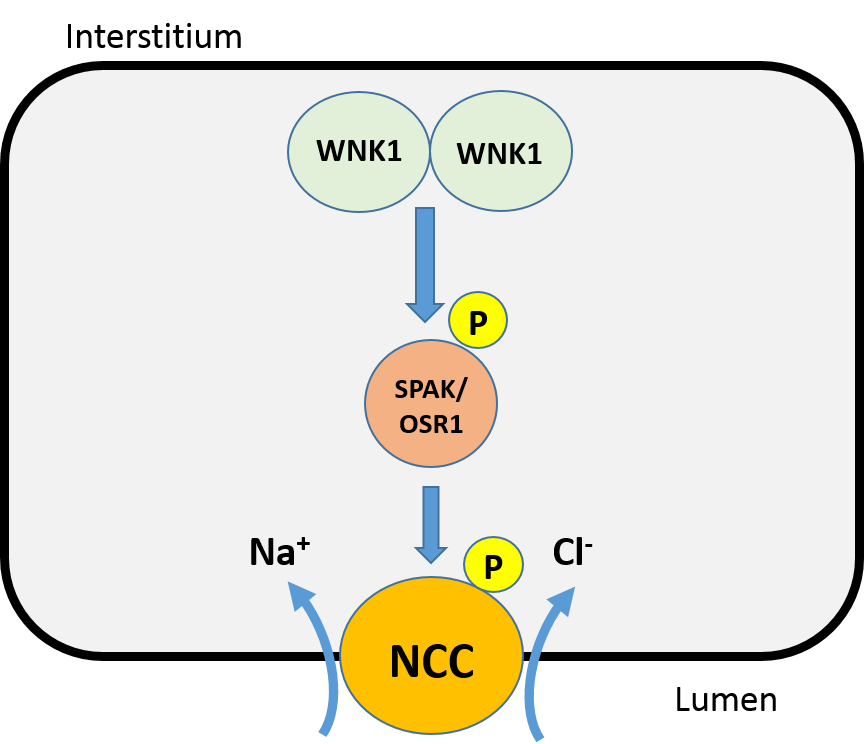
WNK4
Serine/threonine protein kinase WNK4 also known as WNK lysine deficient protein kinase 4 or WNK4, is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ''WNK4'' gene. Missense mutations cause a genetic form of pseudohypoaldosteronism type 2, also called Gordon syndrome. WNK4 is a member of a serine/threonine kinase family that comprises four members. The family is so named because unlike other serine/threonine kinases, WNKs are characterized by the lack of the lysine in the subdomain II of the catalytic domain. Instead, a lysine in the β2 strand of subdomain I of the catalytic domain is responsible for the kinase activity. The ''WNK4'' gene is located on chromosome 17q21-q22. It produces a 1,243-amino acid protein encoded by a 3,732-nucleotide open reading frame within a 4 kb cDNA transcript. WNK4 protein is highly expressed in the distal convoluted tubule (DCT) and the cortical collecting duct (CDD) of the kidney. WNK4 is also present in the brain, lungs, liver, heart, and colon of vari ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hyperkalemia
Hyperkalemia is an elevated level of potassium (K+) in the blood. Normal potassium levels are between 3.5 and 5.0mmol/L (3.5 and 5.0mEq/L) with levels above 5.5mmol/L defined as hyperkalemia. Typically hyperkalemia does not cause symptoms. Occasionally when severe it can cause palpitations, muscle pain, muscle weakness, or numbness. Hyperkalemia can cause an abnormal heart rhythm which can result in cardiac arrest and death. Common causes of hyperkalemia include kidney failure, hypoaldosteronism, and rhabdomyolysis. A number of medications can also cause high blood potassium including spironolactone, NSAIDs, and angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitors. The severity is divided into mild (5.5–5.9mmol/L), moderate (6.0–6.4mmol/L), and severe (>6.5mmol/L). High levels can be detected on an electrocardiogram (ECG). Pseudohyperkalemia, due to breakdown of cells during or after taking the blood sample, should be ruled out. Initial treatment in those with ECG changes is salts ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mineralocorticoid Receptor
The mineralocorticoid receptor (or MR, MLR, MCR), also known as the aldosterone receptor or nuclear receptor subfamily 3, group C, member 2, (NR3C2) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''NR3C2'' gene that is located on chromosome 4q31.1-31.2. MR is a receptor with equal affinity for mineralocorticoids and glucocorticoids. It belongs to the nuclear receptor family where the ligand diffuses into cells, interacts with the receptor and results in a signal transduction affecting specific gene expression in the nucleus. The selective responsive of some tissues and organs to mineralocorticoids over glucocorticoids occurs because mineralocorticoid-responsive cells express Corticosteroid 11-beta-dehydrogenase isozyme 2, an enzyme which selectively inactivates glucocorticoids more readily than mineralocorticoids. Function MR is expressed in many tissues, such as the kidney, colon, heart, central nervous system (hippocampus), brown adipose tissue and sweat glands. In epith ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Epithelial Sodium Channel
The epithelial sodium channel (ENaC), (also known as amiloride-sensitive sodium channel) is a membrane-bound ion channel that is selectively permeable to sodium ions (). It is assembled as a heterotrimer composed of three homologous subunits α or δ, β, and γ, These subunits are encoded by four genes: SCNN1A, SCNN1B, SCNN1G, and SCNN1D. The ENaC is involved primarily in the reabsorption of sodium ions at the collecting ducts of the kidney's nephrons. In addition to being implicated in diseases where fluid balance across epithelial membranes is perturbed, including pulmonary edema, cystic fibrosis, COPD and COVID-19, proteolyzed forms of ENaC function as the human salt taste receptor. The apical membranes of many tight epithelia contain sodium channels that are characterized primarily by their high affinity for the diuretic blocker amiloride. These channels mediate the first step of active sodium reabsorption essential for the maintenance of body salt and water homeostasis. In ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
WNK1
WNK (lysine deficient protein kinase 1), also known as WNK1, is an enzyme that is encoded by the ''WNK1'' gene. WNK1 is serine-threonine protein kinase and part of the "with no lysine/K" kinase WNK family. The predominant role of WNK1 is the regulation of cation-Cl− cotransporters (CCCs) such as the sodium chloride cotransporter ( NCC), basolateral Na-K-Cl symporter (NKCC1), and potassium chloride cotransporter (KCC1) located within the kidney. CCCs mediate ion homeostasis and modulate blood pressure by transporting ions in and out of the cell. ''WNK1'' mutations as a result have been implicated in blood pressure disorders/diseases; a prime example being familial hyperkalemic hypertension (FHHt). Structure The WNK1 protein is composed of 2382 amino acids (molecular weight 230 kDa). The protein contains a kinase domain located within its short N-terminal domain and a long C-terminal tail. The kinase domain has some similarity to the MEKK protein kinase family. As a member ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hyperkalemia
Hyperkalemia is an elevated level of potassium (K+) in the blood. Normal potassium levels are between 3.5 and 5.0mmol/L (3.5 and 5.0mEq/L) with levels above 5.5mmol/L defined as hyperkalemia. Typically hyperkalemia does not cause symptoms. Occasionally when severe it can cause palpitations, muscle pain, muscle weakness, or numbness. Hyperkalemia can cause an abnormal heart rhythm which can result in cardiac arrest and death. Common causes of hyperkalemia include kidney failure, hypoaldosteronism, and rhabdomyolysis. A number of medications can also cause high blood potassium including spironolactone, NSAIDs, and angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitors. The severity is divided into mild (5.5–5.9mmol/L), moderate (6.0–6.4mmol/L), and severe (>6.5mmol/L). High levels can be detected on an electrocardiogram (ECG). Pseudohyperkalemia, due to breakdown of cells during or after taking the blood sample, should be ruled out. Initial treatment in those with ECG changes is salts ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aldosterone
Aldosterone is the main mineralocorticoid steroid hormone produced by the zona glomerulosa of the adrenal cortex in the adrenal gland. It is essential for sodium conservation in the kidney, salivary glands, sweat glands, and colon. It plays a central role in the homeostatic regulation of blood pressure, plasma sodium (Na+), and potassium (K+) levels. It does so primarily by acting on the mineralocorticoid receptors in the distal tubules and collecting ducts of the nephron. It influences the reabsorption of sodium and excretion of potassium (from and into the tubular fluids, respectively) of the kidney, thereby indirectly influencing water retention or loss, blood pressure, and blood volume.Marieb Human Anatomy & Physiology 9th edition, chapter:16, page:629, question number:14 When dysregulated, aldosterone is pathogenic and contributes to the development and progression of cardiovascular and kidney disease. Aldosterone has exactly the opposite function of the atrial natriure ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pediatrics
Pediatrics ( also spelled ''paediatrics'' or ''pædiatrics'') is the branch of medicine that involves the medical care of infants, children, adolescents, and young adults. In the United Kingdom, paediatrics covers many of their youth until the age of 18. The American Academy of Pediatrics recommends people seek pediatric care through the age of 21, but some pediatric subspecialists continue to care for adults up to 25. Worldwide age limits of pediatrics have been trending upward year after year. A medical doctor who specializes in this area is known as a pediatrician, or paediatrician. The word ''pediatrics'' and its cognates mean "healer of children," derived from the two Greek words: (''pais'' "child") and (''iatros'' "doctor, healer"). Pediatricians work in clinics, research centers, universities, general hospitals and children's hospitals, including those who practice pediatric subspecialties (e.g. neonatology requires resources available in a NICU). History The ear ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nephrology
Nephrology (from Greek'' nephros'' "kidney", combined with the suffix ''-logy'', "the study of") is a specialty of adult internal medicine and pediatric medicine that concerns the study of the kidneys, specifically normal kidney function (renal physiology) and kidney disease (renal pathophysiology), the preservation of kidney health, and the treatment of kidney disease, from diet and medication to renal replacement therapy ( dialysis and kidney transplantation). The word “renal” is an adjective meaning “relating to the kidneys”, and its roots are French or late Latin. Whereas according to some opinions, "renal" and "nephro" should be replaced with "kidney" in scientific writings such as "kidney medicine" (instead of nephrology) or "kidney replacement therapy", other experts have advocated preserving the use of renal and nephro as appropriate including in "nephrology" and "renal replacement therapy", respectively. Nephrology also studies systemic conditions that aff ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |