|
Province Of Grosseto
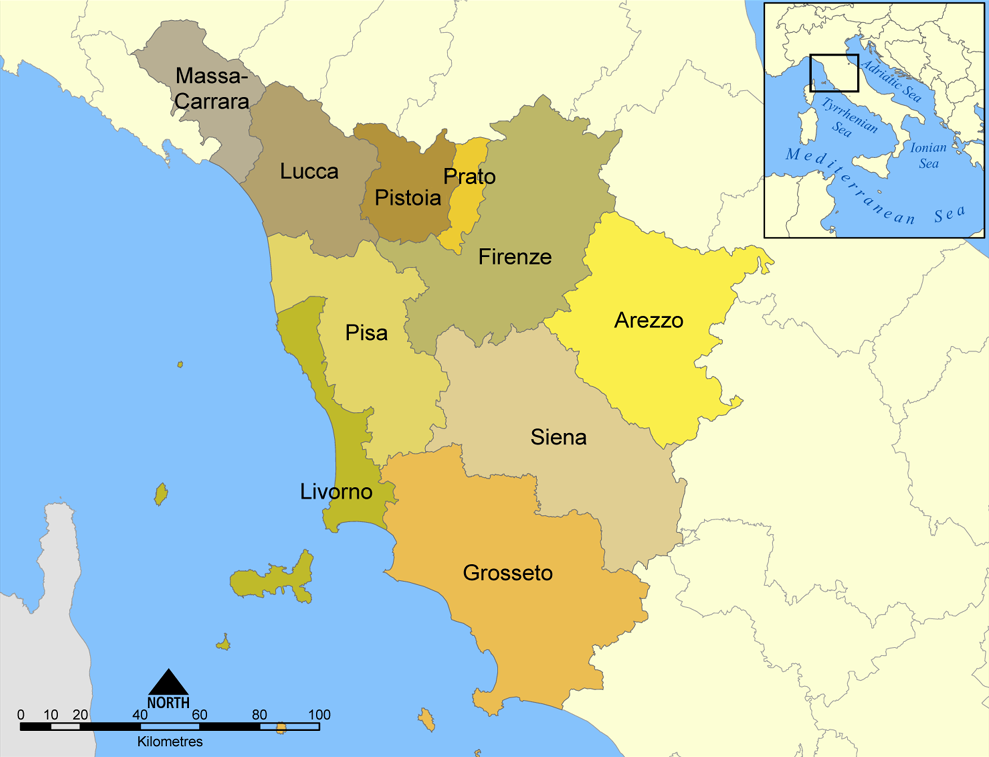
The province of Grosseto ( it, links=no, provincia di Grosseto) is a province in the Tuscany region of Italy. Its capital is the city of Grosseto. As of 2013 the province had a total population of 225,098 people. Geography The Province of Grosseto completely occupies the southern end of Tuscany, and with a territorial area of , it is the most extensive in the region and one of the least dense in population in Italy. The province is bordered to the northwest by the Province of Livorno, to the north by the Province of Pisa, to the northeast by the Province of Siena, and to the southeast by the Province of Viterbo in Lazio. To the south is the Tyrrhenian Sea, which includes the southern islands of the Tuscan archipelago, including Isola del Giglio and the smaller Giannutri islands and Formiche di Grosseto and Formica di Burano. The Arcipelago Toscano National Park spans both the provinces of Grosseto and Livorno, and includes the seven main islands of the Tuscan Archipelago: Elba ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Provinces Of Italy
The provinces of Italy ( it, province d'Italia) are the second-level administrative divisions of the Italy, Italian Republic, on an intermediate level between a municipality () and a regions of Italy, region (). Since 2015, provinces have been classified as "institutional bodies of second level". There are currently 107 institutional bodies of second level in Italy, including 80 ordinary provinces, 2 autonomous provinces, 4 regional decentralization entities, 6 free municipal consortia, and 14 Metropolitan cities of Italy, metropolitan cities, as well as the Aosta Valley region (which also exercises the powers of a province). Italian provinces (with the exception of the current Sardinian provinces) correspond to the NUTS statistical regions of Italy, NUTS 3 regions. Overview A province of the Italian Republic is composed of many municipalities (). Usually several provinces together form a region; the region of Aosta Valley is the sole exception—it is not subdivided into prov ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lazio
it, Laziale , population_note = , population_blank1_title = , population_blank1 = , demographics_type1 = , demographics1_footnotes = , demographics1_title1 = , demographics1_info1 = , demographics1_title2 = , demographics1_info2 = , demographics1_title3 = , demographics1_info3 = , timezone1 = CET , utc_offset1 = +1 , timezone1_DST = CEST , utc_offset1_DST = +2 , postal_code_type = , postal_code = , area_code_type = ISO 3166 code , area_code = IT-62 , blank_name_sec1 = GDP (nominal) , blank_info_sec1 = €201 billion (2019) , blank1_name_sec1 = GDP per capita , blank1_info_sec1 = €34,300 (2019) , blank2_name_sec1 = HDI (2019) , blank2_info_sec1 = 0.914 · 3rd of 21 , blank_name_sec2 = NUTS Region , blank_info_sec2 = ITE , website www. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ombrone
The Ombrone (Latin: ''Umbro'') is a long river in Tuscany, central Italy. The Ombrone's source is at San Gusmè, near Castelnuovo Berardenga, on the south-eastern side of the Monti del Chianti. After a twisting route, it receives the waters of the tributaries Arbia, Merse and Orcia before reaching the plain near Istia d'Ombrone. It subsequently passes near the city of Grosseto, before flowing into the Tyrrhenian Sea. See also *Ombrone (département) Ombrone was a department of the First French Empire in modern-day Italy. It was named after the river Ombrone. It was formed in 1808, when the Kingdom of Etruria (formerly the Grand Duchy of Tuscany) was annexed directly to France. Its capital w .... References External linksOmbrone river: Finding the source by turismo.intoscana.it. Rivers of the Province of Grosseto Rivers of the Province of Siena Drainage basins of the Tyrrhenian Sea Rivers of Italy {{Italy-river-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maremma
The Maremma (, ; from Latin , "maritime and) is a coastal area of western central Italy, bordering the Tyrrhenian Sea. It includes much of south-western Tuscany and part of northern Lazio. It was formerly mostly marshland, often malarial, but was drained by order of Ferdinando I de' Medici. It was traditionally populated by the '' butteri'', mounted cattle herders who rode horses fitted with one of two distinctive styles of saddle, the ''scafarda'' and the ''bardella''. Geography The Maremma has an area of about . The central part corresponds approximately with the province of Grosseto, extending northward to the Colline Metallifere and the slopes of Monte Amiata, but the region extends northward from Piombino to the mouth of the , and southwards into Lazio as far as Civitavecchia. Animal breeds The Maremma has given rise to, or given its name to, several breeds of domestic animal. These include two breeds of working horse, the Maremmano and the Cavallo Romano della Ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Colline Metallifere
The Colline Metallifere (), or the Metalliferous Hills ("Metal-bearing Hills"), are a mountain-hill group in the Tuscan Antiapennine, in central Italy. They occupy the central-western part of Tuscany, divided between the provinces of Livorno, Pisa, Siena and Grosseto. The territory, with the exception of the Poggio di Montieri and Cornate di Gerfalco peaks, both above the 1,000 m, is mostly hilly, with a rich variety of minerary resources, whence the name. It also includes geothermic energy sources, part of which used in ENEL power plants at Larderello and Lago Boracifero. Rivers include the Cecina, the Cornia and the Merse. The metal resources of the Colline Metallifere were exploited since ancient times by the Etruscans. Production reached its peak in the mid-19th century, declining quickly however afterwards. The numerous railways serving the mills are now mostly suppressed. __NOTOC__ Communes Province of Livorno *Sassetta *Campiglia Marittima * Suvereto Province ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mount Capanne
Mount Capanne ( it, Monte Capanne) is the highest mountain on the Italian island of Elba and in the province of Livorno, Tuscany, Italy. It is located in the western part of the island, reaching a height of in elevation above the Mediterranean Sea. Features The mountain is part of the Arcipelago Toscano National Park. The Monte Capanne summit can be reached in 14 minutes via cable car, which departs from Marciana.The mountain has Matorral shrublands and woodlands vegetation habitats, of the Mediterranean forests, woodlands, and scrub biome A biome () is a biogeographical unit consisting of a biological community that has formed in response to the physical environment in which they are found and a shared regional climate. Biomes may span more than one continent. Biome is a broader .... See also * Tuscan Archipelago References External links Elba Capanne Arcipelago Toscano National Park {{Livorno-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gorgona, Italy
Gorgona () is the northernmost island in the Tuscan Archipelago, a group of islands off the west coast of Italy. Between Corsica and Livorno, this diminutive island has been valued most for its wildlife, especially marine birds, and its isolation. The latter quality resulted in the foundation of Gorgona Abbey in the Middle Ages. After its closure the monastery grounds and buildings were appropriated in 1869, at the foundation of an agricultural penal colony, which is currently in use. Geography Gorgona is located about 19 nautical miles (about ) straight out from Livorno. It is a ferry ride of about 1.5 hours; however, access to the island is forbidden without permission from the Italian Ministry of Justice. It grants a standing concession exclusively to one group for supervised tours. Photographic equipment is not allowed. Private boats may approach the island no closer than except in emergencies. Capraia is away; Corsica, . The only landing place is "Cala dello Scalo", ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pianosa
Pianosa () is an island in the Tuscan Archipelago in the Tyrrhenian Sea, Italy. It is about in area, with a coastal perimeter of . Geography In Roman times the island was named ''Planasia'' (plain) because of its flatness – its highest point stands at above sea level. It is a triangular-shaped land mass south west of Elba, and is a frazione of the municipality of Campo nell'Elba. Pianosa is the fifth biggest island of the Tuscan Archipelago and the only one to be formed out of sedimentary rock of the Neogene and Quaternary; such fossils as echinoderms, mollusca and bryozoa of the Pliocene are frequently found. Flora The vegetation consists mainly of Mediterranean species as lentisco, fennel, juniper, rosemary and ''Pinus halepensis'', which was introduced on the island in the 1900s. Fauna The animals living on the island are largely small mammals, such as hedgehog and hare, introduced in the 1800s, as well as the pheasant and the red-legged partridge; the magpie and t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Montecristo
Montecristo, also Monte Cristo (, ) and formerly Oglasa ( grc, Ὠγλάσσα, Ōglássa), is an island in the Tyrrhenian Sea and part of the Tuscan Archipelago. Administratively it belongs to the municipality of Portoferraio in the province of Livorno, Italy. The island has an area of , is approximately wide at its widest point, and is long; the coasts are steep, and extend for . The island is a state nature reserve and forms part of the Tuscan Archipelago National Park. Much of the island's fame is derived from the fact that it provides the title of 1844 novel ''The Count of Monte Cristo'', by Alexandre Dumas, and is one of the novel's settings. History The history of the island begins with the Iron Age. The Etruscans exploited the forests of oak needed to fuel the bloomeries of the mainland where the iron ore of Elba's mines was melted. The Greeks gave Montecristo its oldest known name, ''Oglasa'' or ''Ocrasia'', after the yellowish colour of the rocks. The Romans, how ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Capraia
Capraia is an Italian island, the northwesternmost of the seven islands of the Tuscan Archipelago, and the third largest after Elba and Giglio. It is also a ''comune'' (Capraia Isola) belonging to the Province of Livorno. The island has a population of about 400. Geography Capraia is from the city of Livorno by sea, and northwest of the island of Elba; it is slightly closer, at , to the island of Corsica. The island is accessible by ferries that depart from the port of Livorno. Capraia is of volcanic origin, has an area of and its highest point is above sea level. It is about long (from Punta della Teglia to Punta dello Zenobio) and about wide. It has a coastline that is about in circumference. The island is part of the Arcipelago Toscano National Park and marine sanctuary. The island's small harbour, Porto di Capraia, is connected to the village by the one and only asphalted road on the island. The village, dominated by the Fortress of St George, preserves its orig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Elba
Elba ( it, isola d'Elba, ; la, Ilva) is a Mediterranean island in Tuscany, Italy, from the coastal town of Piombino on the Italian mainland, and the largest island of the Tuscan Archipelago. It is also part of the Arcipelago Toscano National Park, and the third largest island in Italy, after Sicily and Sardinia. It is located in the Tyrrhenian Sea about east of the French island of Corsica. The island is part of the province of Livorno and is divided into seven municipalities, with a total population of about 30,000 inhabitants which increases considerably during the summer. The municipalities are Portoferraio (which is also the island's principal town), Campo nell'Elba, Capoliveri, Marciana, Marciana Marina, Porto Azzurro, and Rio. Elba was the site of Napoleon's first exile, from 1814 to 1815. Geography Elba is the largest remaining stretch of land from the ancient tract that once connected the Italian peninsula to Corsica. The northern coast faces the Ligurian Sea, t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Formiche Di Grosseto
The Formiche di Grosseto ("Ants of Grosseto") is a group of islets which emerge sharply in the Tuscan Archipelago. They are located in open sea among the coast of the Natural Park of Maremma and Pianosa, approximately from Porto Santo Stefano on Monte Argentario and from Marina di Grosseto; they are part of the ''comune'' of Grosseto and are placed in a nature reserve which makes part of a special protection area. Description The ''Formiche di Grosseto'' are three islets named, according to their dimensions, ''Formichino'', ''Formica Media'' and ''Formica Grande'' which develop a total surface of about 120,000 square metres which extend lined up from north-west to south-east over one mile. ''Formichino'' is the smallest and is formed by two skerries, is the southernmost and has an area of only 20 square metres. ''Formica Media'' is a long narrow strip of rock that continues under water situated on a shoal. ''Formica Grande'' is the largest, has a rhomboidal shape, it is 370 m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



2.jpg)


