|
Prostate Biopsy
Prostate biopsy is a procedure in which small hollow needle-core samples are removed from a man's prostate gland to be examined for the presence of prostate cancer. It is typically performed when the result from a PSA blood test is high. It may also be considered advisable after a digital rectal exam (DRE) finds possible abnormality. PSA screening is controversial as PSA may become elevated due to non-cancerous conditions such as benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH), by infection, or by manipulation of the prostate during surgery or catheterization. Additionally many prostate cancers detected by screening develop so slowly that they would not cause problems during a man's lifetime, making the complications due to treatment unnecessary. The most frequent side effect of the procedure is blood in the urine (31%). Other side effects may include infection (0.9%) and death (0.2%). Ultrasound-guided prostate biopsy The procedure may be performed transrectally, through the urethra or t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prostate Gland
The prostate is both an accessory gland of the male reproductive system and a muscle-driven mechanical switch between urination and ejaculation. It is found only in some mammals. It differs between species anatomically, chemically, and physiologically. Anatomically, the prostate is found below the bladder, with the urethra passing through it. It is described in gross anatomy as consisting of lobes and in microanatomy by zone. It is surrounded by an elastic, fibromuscular capsule and contains glandular tissue as well as connective tissue. The prostate glands produce and contain fluid that forms part of semen, the substance emitted during ejaculation as part of the male sexual response. This prostatic fluid is slightly alkaline, milky or white in appearance. The alkalinity of semen helps neutralize the acidity of the vaginal tract, prolonging the lifespan of sperm. The prostatic fluid is expelled in the first part of ejaculate, together with most of the sperm, because of the a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
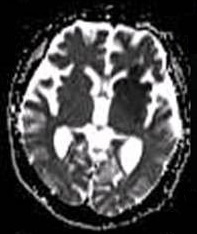
Magnetic Resonance Imaging
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a medical imaging technique used in radiology to form pictures of the anatomy and the physiological processes of the body. MRI scanners use strong magnetic fields, magnetic field gradients, and radio waves to generate images of the organs in the body. MRI does not involve X-rays or the use of ionizing radiation, which distinguishes it from CT and PET scans. MRI is a medical application of nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) which can also be used for imaging in other NMR applications, such as NMR spectroscopy. MRI is widely used in hospitals and clinics for medical diagnosis, staging and follow-up of disease. Compared to CT, MRI provides better contrast in images of soft-tissues, e.g. in the brain or abdomen. However, it may be perceived as less comfortable by patients, due to the usually longer and louder measurements with the subject in a long, confining tube, though "Open" MRI designs mostly relieve this. Additionally, implants and oth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Male Genital Surgery
Male (Mars symbol, symbol: ♂) is the sex of an organism that produces the gamete (sex cell) known as sperm, which fuses with the larger female gamete, or ovum, in the process of fertilization. A male organism cannot sexual reproduction, reproduce sexually without access to at least one ovum from a female, but some organisms can reproduce both sexually and Asexual reproduction, asexually. Most male mammals, including male humans, have a Y chromosome, which codes for the production of larger amounts of testosterone to develop male reproductive organs. Not all species share a common sex-determination system. In most animals, including Homo sapiens, humans, sex is determined genetics, genetically; however, species such as ''Cymothoa exigua'' change sex depending on the number of females present in the vicinity. In humans, the word ''male'' can also be used to refer to gender in the social sense of gender role or gender identity. Overview The existence of separate sexes has evol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
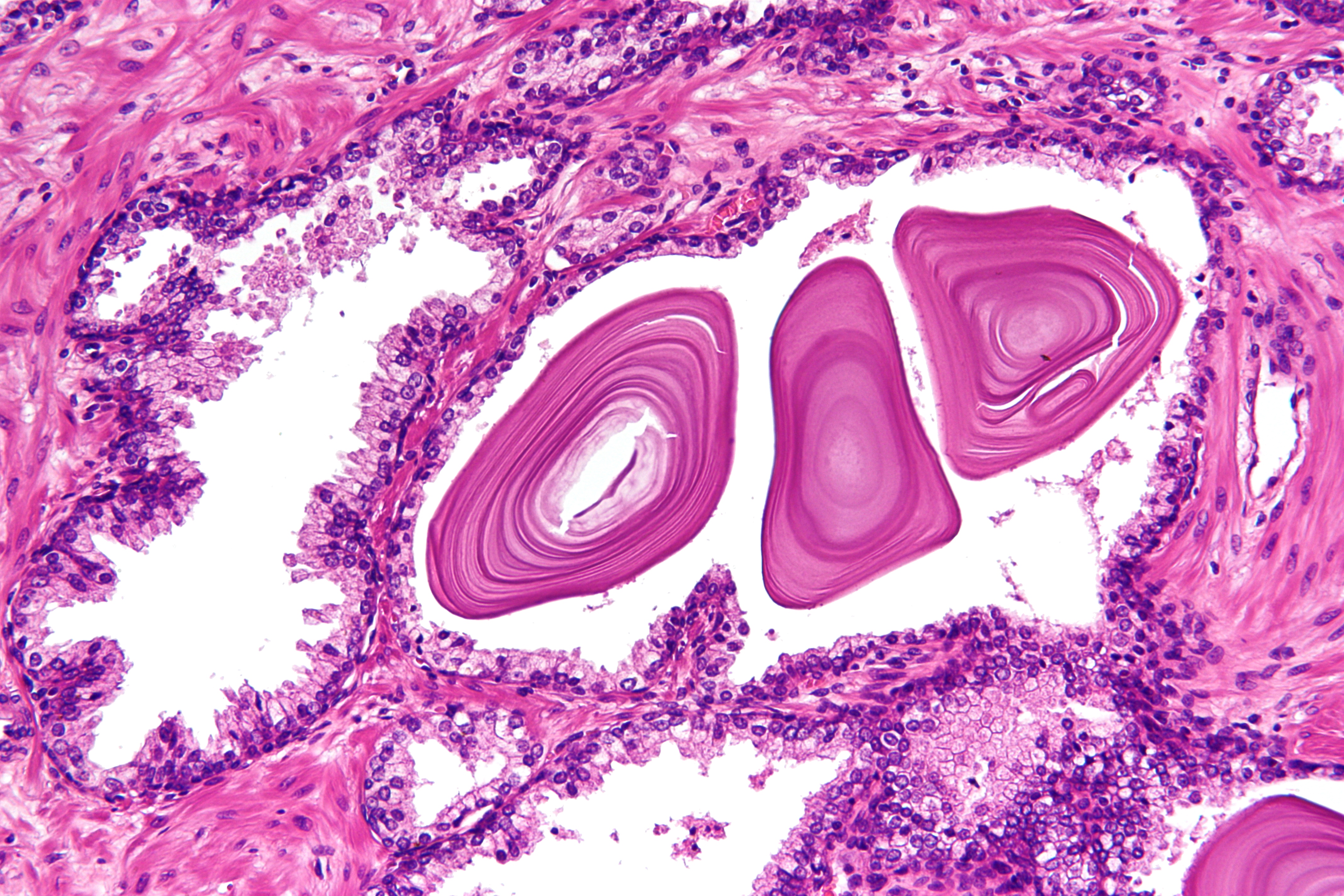
Histopathology
Histopathology (compound of three Greek words: ''histos'' "tissue", πάθος ''pathos'' "suffering", and -λογία '' -logia'' "study of") refers to the microscopic examination of tissue in order to study the manifestations of disease. Specifically, in clinical medicine, histopathology refers to the examination of a biopsy or surgical specimen by a pathologist, after the specimen has been processed and histological sections have been placed onto glass slides. In contrast, cytopathology examines free cells or tissue micro-fragments (as "cell blocks"). Collection of tissues Histopathological examination of tissues starts with surgery, biopsy, or autopsy. The tissue is removed from the body or plant, and then, often following expert dissection in the fresh state, placed in a fixative which stabilizes the tissues to prevent decay. The most common fixative is 10% neutral buffered formalin (corresponding to 3.7% w/v formaldehyde in neutral buffered water, such as phosphate buf ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biopsy
A biopsy is a medical test commonly performed by a surgeon, interventional radiologist, or an interventional cardiologist. The process involves extraction of sample cells or tissues for examination to determine the presence or extent of a disease. The tissue is then fixed, dehydrated, embedded, sectioned, stained and mounted before it is generally examined under a microscope by a pathologist; it may also be analyzed chemically. When an entire lump or suspicious area is removed, the procedure is called an excisional biopsy. An incisional biopsy or core biopsy samples a portion of the abnormal tissue without attempting to remove the entire lesion or tumor. When a sample of tissue or fluid is removed with a needle in such a way that cells are removed without preserving the histological architecture of the tissue cells, the procedure is called a needle aspiration biopsy. Biopsies are most commonly performed for insight into possible cancerous or inflammatory conditions. History T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gleason Score
The Gleason grading system is used to help evaluate the prognosis of men with prostate cancer using samples from a prostate biopsy. Together with other parameters, it is incorporated into a strategy of prostate cancer staging which predicts prognosis and helps guide therapy. A Gleason score is given to prostate cancer based upon its microscopic appearance. Cancers with a higher Gleason score are more aggressive and have a worse prognosis. Pathological scores range from 2 to 10, with higher numbers indicating greater risks and higher mortality. The system is widely accepted and used for clinical decision making even as it is recognised that certain biomarkers, like ACP1 expression, might yield higher predictive value for future disease course. The histopathologic diagnosis of prostate cancer has implications for the possibility and methodology of Gleason scoring. For example, it is not recommended in signet-ring adenocarcinoma or urothelial carcinoma of the prostate, and the sc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Active Surveillance Of Prostate Cancer
Active surveillance is a management option for localized prostate cancer that can be offered to appropriate patients who would also be candidates for aggressive local therapies (surgery and radiotherapy), with the intent to intervene if the disease progresses. Active surveillance should not be confused with watchful waiting, another observational strategy for men that would not be candidates for curative therapy (surgery, radiation) because of a limited life expectancy. Active surveillance offers men with a prostate cancer that is thought to have a low risk of causing harm in the absence of treatment, a chance to delay or avoid aggressive treatment and its associated side effects.While prostate cancer is the most common non cutaneous cancer and second leading cause of cancer-related death in American men, it is conservatively estimated that approximately 100,000 men per year in the United States who would be eligible for conservative treatment through active surveillance, undergo unn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
PI-RADS
PI-RADS is an acronym for Prostate Imaging Reporting and Data System, defining standards of high quality clinical service for multi-parametric Magnetic Resonance Imaging (mpMRI), including image creation and reporting. History In 2007, the AdMeTech Foundation's International Prostate MRI Working Group convened the key global experts, including members of thEuropean Society of Urogenital Radiology(ESUR) and the American College of Radiology (ACR). In March 2009 in Vienna an ESUR Prostate MRI Committee was formed, with the aim to produce minimal and maximal standards for acquisition and reporting of prostate MRI. This standardization was endorsed by the results of a consensus meeting in London in December 2009 Dr. Jelle Barentsz published with the ESUR Prostate MRI Committee the first PI-RADS (v.1) version in December 2011. Following this initiative the ACR, ESUR, and the AdMeTech Foundation formed a Joint Steering Committee, and by 2016 published a second version of PI-RADS (v.2 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jocelyne Troccaz
Jocelyne Troccaz (born 1959) is a French roboticist and researcher in medical imaging and image-guided robotics. She is a director of research for the French National Centre for Scientific Research (CNRS), affiliated with the Computer-Assisted Medical Interventions team (GMCAO) of the Laboratory for Translational Research and Innovation in Medicine and Complexity (TIMC) at Grenoble Alpes University. After originally specializing in industrial applications of robotics, her interests shifted to medical robotics. Education and career Troccaz was born on 11 June 1959 in Sallanches, an Alpine town near the French borders with Italy and Switzerland. She studied computer science at the Grenoble Institute of Technology, earned licentiates in 1980 and 1981, a diplôme d'études approfondies (master's degree) in 1982, and a doctorate in 1986. She completed her habilitation in computer science and applied mathematics in 1993. She joined CNRS in 1988 and became a director of research in 1998 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Urologist
Urology (from Greek οὖρον ''ouron'' "urine" and ''-logia'' "study of"), also known as genitourinary surgery, is the branch of medicine that focuses on surgical and medical diseases of the urinary-tract system and the reproductive organs. Organs under the domain of urology include the kidneys, adrenal glands, ureters, urinary bladder, urethra, and the male reproductive organs (testes, epididymis, vas deferens, seminal vesicles, prostate, and penis). The urinary and reproductive tracts are closely linked, and disorders of one often affect the other. Thus a major spectrum of the conditions managed in urology exists under the domain of genitourinary disorders. Urology combines the management of medical (i.e., non-surgical) conditions, such as urinary-tract infections and benign prostatic hyperplasia, with the management of surgical conditions such as bladder or prostate cancer, kidney stones, congenital abnormalities, traumatic injury, and stress incontinence. Urological t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Interventional Radiologist
Interventional radiology (IR) is a medical specialty that performs various minimally-invasive procedures using medical imaging guidance, such as x-ray fluoroscopy, computed tomography, magnetic resonance imaging, or ultrasound. IR performs both diagnostic and therapeutic procedures through very small incisions or body orifices. Diagnostic IR procedures are those intended to help make a diagnosis or guide further medical treatment, and include image-guided biopsy of a tumor or injection of an imaging contrast agent into a hollow structure, such as a blood vessel or a duct. By contrast, therapeutic IR procedures provide direct treatment—they include catheter-based medicine delivery, medical device placement (e.g., stents), and angioplasty of narrowed structures. The main benefits of interventional radiology techniques are that they can reach the deep structures of the body through a body orifice or tiny incision using small needles and wires. That decreases risks, pain, an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diffusion-weighted Imaging
Diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging (DWI or DW-MRI) is the use of specific MRI sequences as well as software that generates images from the resulting data that uses the diffusion of water molecules to generate contrast in MR images. It allows the mapping of the diffusion process of molecules, mainly water, in biological tissues, in vivo and non-invasively. Molecular diffusion in tissues is not random, but reflects interactions with many obstacles, such as macromolecules, fibers, and membranes. Water molecule diffusion patterns can therefore reveal microscopic details about tissue architecture, either normal or in a diseased state. A special kind of DWI, diffusion tensor imaging (DTI), has been used extensively to map white matter tractography in the brain. Introduction In diffusion weighted imaging (DWI), the intensity of each image element (voxel) reflects the best estimate of the rate of water diffusion at that location. Because the mobility of water is driven by th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |