|
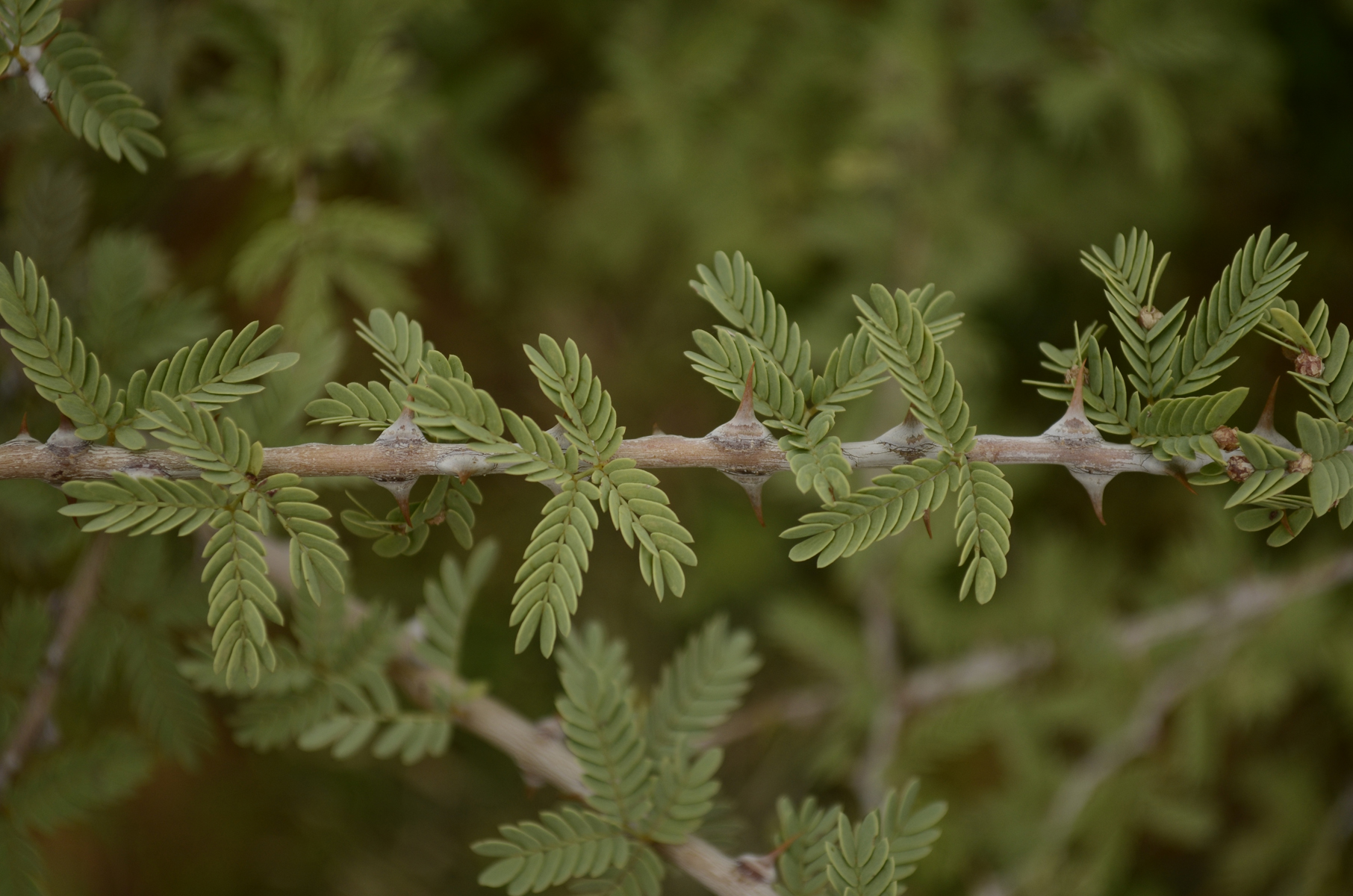
Prosopis Juliflora
''Prosopis juliflora'' ( es, bayahonda blanca, Cuji Venezuela, Trupillo Colombia, Aippia Wayuunaiki and long-thorn kiawe in Hawaii) is a shrub or small tree in the family Fabaceae, a kind of mesquite. It is native to Mexico, South America and the Caribbean. It has become established as an invasive weed in Africa, Asia, Australia and elsewhere. It is a contributing factor to continuing transmission of malaria, especially during dry periods when sugar sources from native plants are largely unavailable to mosquitoes. Description Growing to a height of up to , ''P. juliflora'' has a trunk diameter of up to . Its leaves are deciduous, geminate-pinnate, light green, with 12 to 20 leaflets. Flowers appear shortly after leaf development. The flowers are in long green-yellow cylindrical spikes, which occur in clusters of 2 to 5 at the ends of branches. Pods are long and contain between 10 and 30 seeds per pod. A mature plant can produce hundreds of thousands of seeds. See ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
A Scene Of Prosopis Juliflora
A, or a, is the first letter and the first vowel of the Latin alphabet, used in the modern English alphabet, the alphabets of other western European languages and others worldwide. Its name in English is ''a'' (pronounced ), plural ''aes''. It is similar in shape to the Ancient Greek letter alpha, from which it derives. The uppercase version consists of the two slanting sides of a triangle, crossed in the middle by a horizontal bar. The lowercase version can be written in two forms: the double-storey a and single-storey ɑ. The latter is commonly used in handwriting and fonts based on it, especially fonts intended to be read by children, and is also found in italic type. In English grammar, " a", and its variant " an", are indefinite articles. History The earliest certain ancestor of "A" is aleph (also written 'aleph), the first letter of the Phoenician alphabet, which consisted entirely of consonants (for that reason, it is also called an abjad to distinguish it fro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diameter
In geometry, a diameter of a circle is any straight line segment that passes through the center of the circle and whose endpoints lie on the circle. It can also be defined as the longest chord of the circle. Both definitions are also valid for the diameter of a sphere. In more modern usage, the length d of a diameter is also called the diameter. In this sense one speaks of diameter rather than diameter (which refers to the line segment itself), because all diameters of a circle or sphere have the same length, this being twice the radius r. :d = 2r \qquad\text\qquad r = \frac. For a convex shape in the plane, the diameter is defined to be the largest distance that can be formed between two opposite parallel lines tangent to its boundary, and the is often defined to be the smallest such distance. Both quantities can be calculated efficiently using rotating calipers. For a curve of constant width such as the Reuleaux triangle, the width and diameter are the same because all ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Interspecific
Biological specificity is the tendency of a characteristic such as a behavior or a biochemical variation to occur in a particular species. Biochemist Linus Pauling stated that "Biological specificity is the set of characteristics of living organisms or constituents of living organisms of being special or doing something special. Each animal or plant species is special. It differs in some way from all other species...biological specificity is the major problem about understanding life." Biological specificity within ''Homo sapiens'' ''Homo sapiens'' has many characteristics that show the biological specificity in the form of behavior and morphological traits. Morphologically, humans have an enlarged cranial capacity and more gracile features in comparison to other hominins. The reduction of dentition is a feature that allows for the advantage of adaptability in diet and survival. As a species, humans are culture dependent and much of human survival relies on the culture and soci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prosopis Pallida
''Prosopis pallida'' is a species of mesquite tree. It has the common names kiawe () (in Hawaii), huarango (in its native South America) and American carob, as well as "bayahonda" (a generic term for ''Prosopis''), "algarrobo pálido" (in some parts of Ecuador and Peru), and "algarrobo blanco" (usually used for '' Prosopis alba''). It is a thorny legume, native to Colombia, Ecuador and Peru, particularly drier areas near the coast. While threatened in its native habitat, it is considered an invasive species in many other places. The kiawe is a spreading bush or moderately sized tree, bearing spines, spikes of greenish-yellow flowers, and long pods filled with small brown seeds. It is a successful invasive species due to its ability to reproduce in two ways: production of large numbers of easily dispersed seeds, and suckering to create thick monotypic stands that shade out nearby competing plants. It survives well in dry environments due to a long taproot which can reach deep wate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hybrid (biology)
In biology, a hybrid is the offspring resulting from combining the qualities of two organisms of different breeds, varieties, species or genera through sexual reproduction. Hybrids are not always intermediates between their parents (such as in blending inheritance), but can show hybrid vigor, sometimes growing larger or taller than either parent. The concept of a hybrid is interpreted differently in animal and plant breeding, where there is interest in the individual parentage. In genetics, attention is focused on the numbers of chromosomes. In taxonomy, a key question is how closely related the parent species are. Species are reproductively isolated by strong barriers to hybridisation, which include genetic and morphological differences, differing times of fertility, mating behaviors and cues, and physiological rejection of sperm cells or the developing embryo. Some act before fertilization and others after it. Similar barriers exist in plants, with differences in flowering tim ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gulf Of Mannar
The Gulf of Mannar ( ) is a large shallow bay forming part of the Laccadive Sea in the Indian Ocean with an average depth of .Gulf of Mannar (SE India) Sea-Seek. It lies between the southeastern tip of and the west coast of , in the region. The chain of low islands and reefs known as (aka Adam's Bridge), which includes [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vavunia
Vavuniya (, romanized: ''Vavuṉiyā'', , romanized: ''Vavuniyāva''). Vavuniya City is the capital of Vavuniya District in the Northern Province of Sri Lanka and the largest city in the Northern Province. The municipality is administered by Vavuniya Urban Council. The town has been known since ancient times, but being a heavily forested area, less than 10,000 people lived in the entire district before the Sri Lankan Civil War. The city is situated as a border town that divides the Tamil and Sinhalese population. To the south of the city are the Sinhala cities and to the north are the Tamil cities. The city has a large population of Tamils, Muslims and a significant number of Sinhalese. In the early days, Vavuniya was known as Vanni due to the abundance of Vanni Trees. The Security Forces Headquarters - Wanni is located in Vavuniya. History This city was under the rule of the Nagas during the period of the Yaka and Nagas in ancient Sri Lanka. Many Tanks were constructed by t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prosopis Cineraria
''Prosopis cineraria'', also known as ghaf, is a species of flowering tree in the pea family, Fabaceae. It is native to arid portions of Western Asia and the Indian Subcontinent, including Afghanistan, Bahrain, Iran, India, Oman, Pakistan, Saudi Arabia, the United Arab Emirates and Yemen. Its leaves are shattered and stripy along its branch. It can survive extreme drought. It is an established introduced species in parts of Southeast Asia, including Indonesia. The ʿGhaf is the national tree of the United Arab Emirates. Through the ''Give a Ghaf campaign'' its citizens are urged to plant it in their gardens to combat desertification and to preserve their country's heritage. The desert village of Nazwa in the UAE is home to the Al Ghaf Conservation Reserve. ''Prosopis cineraria'' is also the state tree of Rajasthan (where it is known as Khejri), Western Uttar Pradesh (where it is known as Chhonkara) and Telangana (where it is known as ''Jammi'' ) in India. A large and well-kno ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
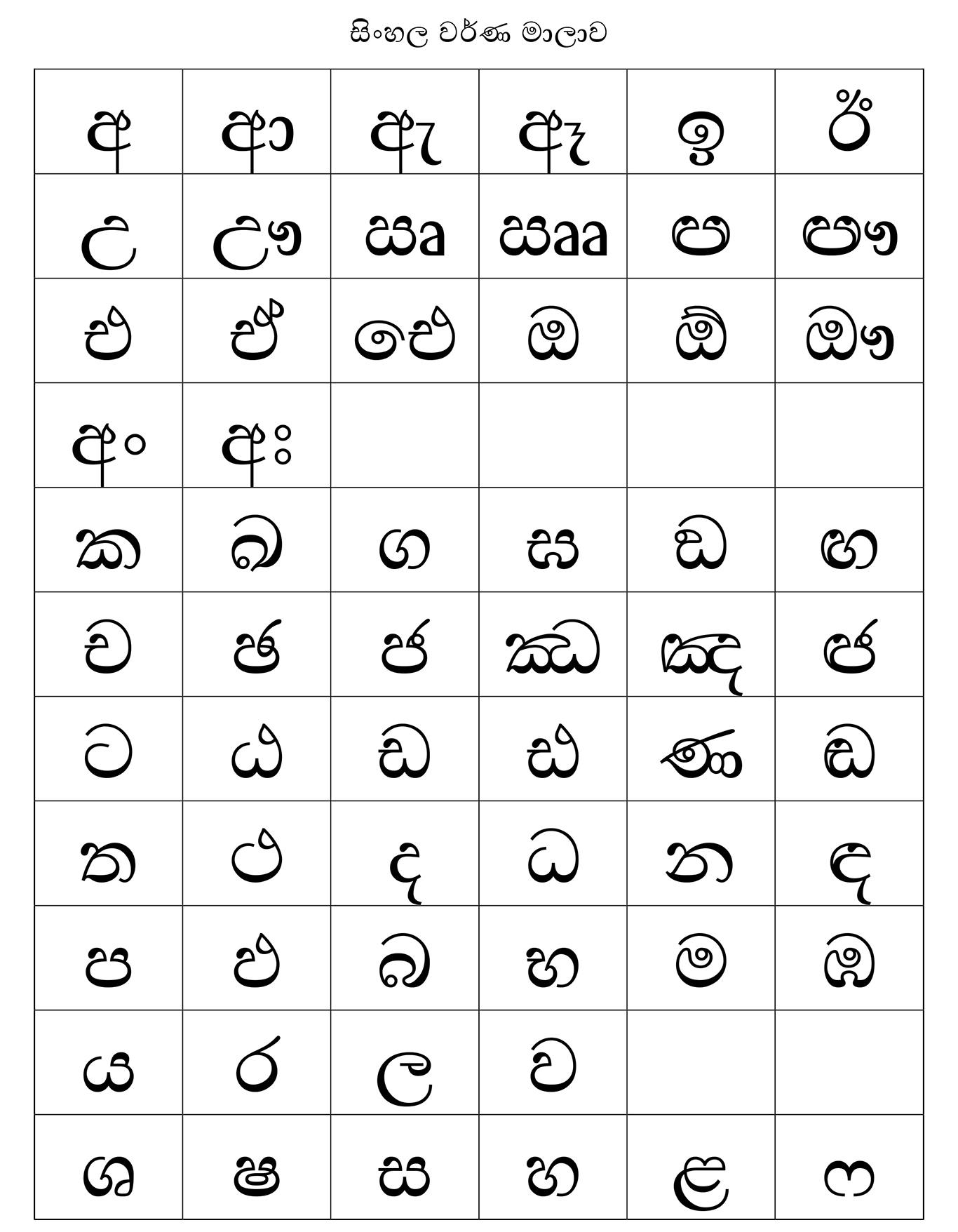
Sinhala Language
Sinhala ( ; , ''siṁhala'', ), sometimes called Sinhalese (), is an Indo-Aryan languages, Indo-Aryan language primarily spoken by the Sinhalese people of Sri Lanka, who make up the largest ethnic group on the island, numbering about 16 million. Sinhala is also spoken as the first language by other ethnic groups in Sri Lanka, totalling about 2 million people as of 2001. It is written using the Sinhala script, which is a Brahmic scripts, Brahmic script closely related to the Grantha script of South India. Sinhala is one of the official and national languages of Sri Lanka. Along with Pali, it played a major role in the development of Theravada, Theravada Buddhist literature. The early form of the Sinhala language, is attested as early as the 3rd century BCE. The language of these inscriptions with long vowels and aspirated consonants is a Prakrit similar to Magadhi, a regional associate of the Middle Indian Prakrits that has been used during the time of the Buddha. The closest ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sri Lanka
Sri Lanka (, ; si, ශ්රී ලංකා, Śrī Laṅkā, translit-std=ISO (); ta, இலங்கை, Ilaṅkai, translit-std=ISO ()), formerly known as Ceylon and officially the Democratic Socialist Republic of Sri Lanka, is an island country in South Asia. It lies in the Indian Ocean, southwest of the Bay of Bengal, and southeast of the Arabian Sea; it is separated from the Indian subcontinent by the Gulf of Mannar and the Palk Strait. Sri Lanka shares a maritime border with India and Maldives. Sri Jayawardenepura Kotte is its legislative capital, and Colombo is its largest city and financial centre. Sri Lanka has a population of around 22 million (2020) and is a multinational state, home to diverse cultures, languages, and ethnicities. The Sinhalese are the majority of the nation's population. The Tamils, who are a large minority group, have also played an influential role in the island's history. Other long established groups include the Moors, the Burghers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Root
In vascular plants, the roots are the organs of a plant that are modified to provide anchorage for the plant and take in water and nutrients into the plant body, which allows plants to grow taller and faster. They are most often below the surface of the soil, but roots can also be aerial or aerating, that is, growing up above the ground or especially above water. Function The major functions of roots are absorption of water, plant nutrition and anchoring of the plant body to the ground. Anatomy Root morphology is divided into four zones: the root cap, the apical meristem, the elongation zone, and the hair. The root cap of new roots helps the root penetrate the soil. These root caps are sloughed off as the root goes deeper creating a slimy surface that provides lubrication. The apical meristem behind the root cap produces new root cells that elongate. Then, root hairs form that absorb water and mineral nutrients from the soil. The first root in seed producing plants is the r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tucson, Arizona
, "(at the) base of the black ill , nicknames = "The Old Pueblo", "Optics Valley", "America's biggest small town" , image_map = , mapsize = 260px , map_caption = Interactive map outlining Tucson , image_map1 = File:Pima County Incorporated and Unincorporated areas Tucson highlighted.svg , mapsize1 = 250px , map_caption1 = Location within Pima County , pushpin_label = Tucson , pushpin_map = USA Arizona#USA , pushpin_map_caption = Location within Arizona##Location within the United States , subdivision_type = Country , subdivision_type1 = State , subdivision_type2 = County , subdivision_name = United States , subdivision_name1 = Arizona , subdivision_name2 = Pima , established_title = Founded , established_date = August 20, 1775 , established_title1 = Incorporated , e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |