|
Proportional Symbol Map
A proportional symbol map or proportional point symbol map is a type of thematic map that uses map symbols that vary in size to represent a quantitative variable. For example, circles may be used to show the location of cities within the map, with the size of each circle sized proportionally to the population of the city. Typically, the size of each symbol is calculated so that its area is mathematically proportional to the variable, but more indirect methods (e.g., categorizing symbols as "small," "medium," and "large") are also used. While all dimensions of geometric primitives (i.e., points, lines, and regions) on a map can be resized according to a variable, this term is generally only applied to point symbols, and different design techniques are used for other dimensionalities. A cartogram is a map that distorts region size proportionally, while a flow map represents lines, often using the width of the symbol (a form of size) to represent a quantitative variable. That said, t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
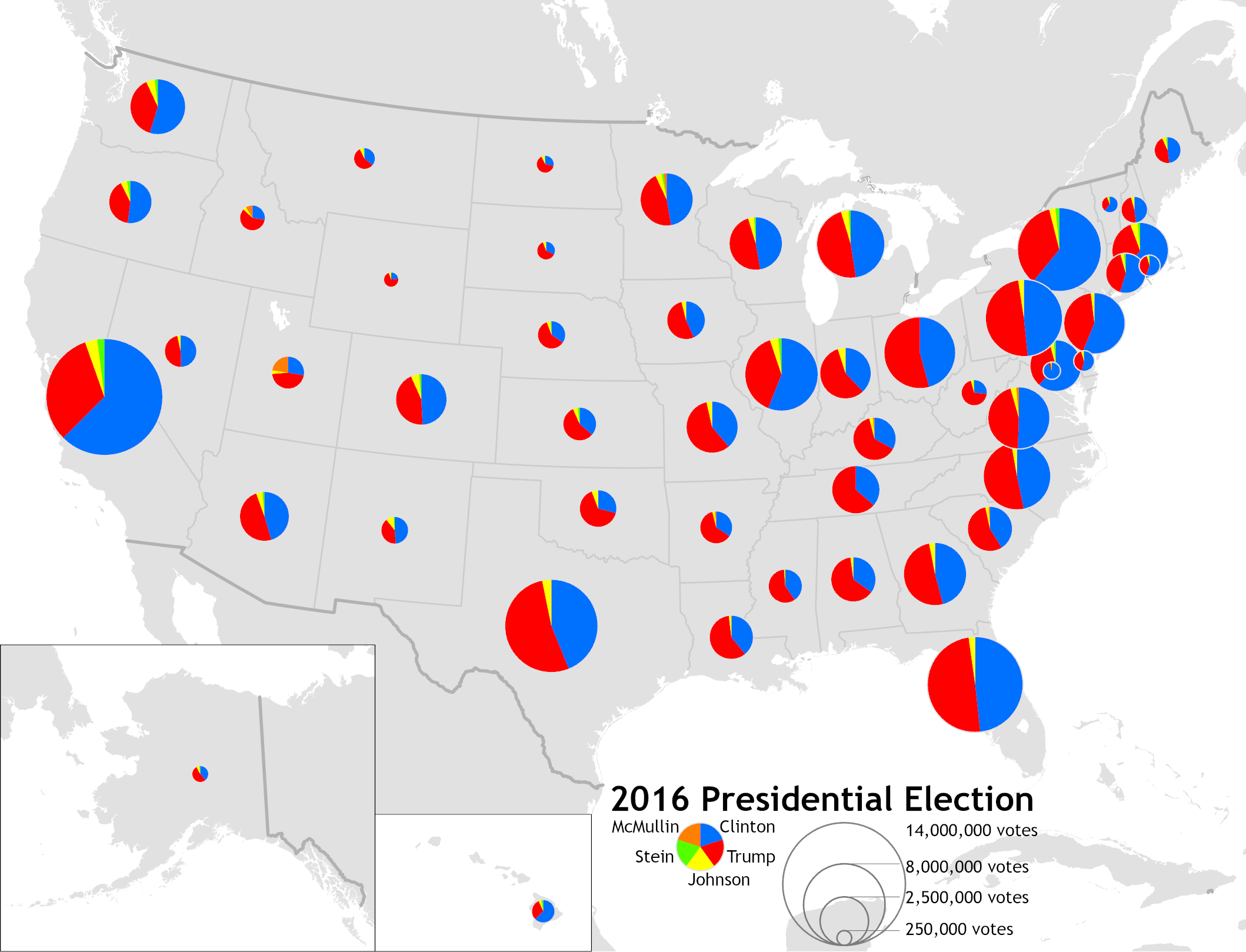
2016 US Presidential Election Pie Charts
Sixteen or 16 may refer to: *16 (number), the natural number following 15 and preceding 17 *one of the years 16 BC, AD 16, 1916, 2016 Films * '' Pathinaaru'' or ''Sixteen'', a 2010 Tamil film * ''Sixteen'' (1943 film), a 1943 Argentine film directed by Carlos Hugo Christensen * ''Sixteen'' (2013 Indian film), a 2013 Hindi film * ''Sixteen'' (2013 British film), a 2013 British film by director Rob Brown Music *The Sixteen, an English choir *16 (band), a sludge metal band *Sixteen (Polish band), a Polish band Albums * ''16'' (Robin album), a 2014 album by Robin * 16 (Madhouse album), a 1987 album by Madhouse * ''Sixteen'' (album), a 1983 album by Stacy Lattisaw *''Sixteen'' , a 2005 album by Shook Ones * ''16'', a 2020 album by Wejdene Songs * "16" (Sneaky Sound System song), 2009 * "Sixteen" (Thomas Rhett song), 2017 * "Sixteen" (Ellie Goulding song), 2019 *"16", by Craig David from ''Following My Intuition'', 2016 *"16", by Green Day from ''39/Smooth'', 1990 *"16", by Hi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Graphics Software
In computer graphics, graphics software refers to a program or collection of programs that enable a person to manipulate images or models visually on a computer. Computer graphics can be classified into two distinct categories: raster graphics and vector graphics, with further 2D and 3D variants. Many graphics programs focus exclusively on either vector or raster graphics, but there are a few that operate on both. It is simple to convert from vector graphics to raster graphics, but going the other way is harder. Some software attempts to do this. In addition to static graphics, there are animation and video editing software. Different types of software are often designed to edit different types of graphics such as video, photos, and vector-based drawings. The exact sources of graphics may vary for different tasks, but most can read and write files. Most graphics programs have the ability to import and export one or more graphics file formats, including those formats written for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Applied Aesthetics
Applied aesthetics is the application of the branch of philosophy of aesthetics to cultural constructs. In a variety of fields, artifacts (whether physical or abstract) are created that have both practical functionality and aesthetic affectation. In some cases, aesthetics is primary, and in others, functionality is primary. At best, the two needs are synergistic, in which "beauty" makes an artifact work better, or in which more functional artifacts are appreciated as aesthetically pleasing. This achievement of form and function, of art and science, of beauty and usefulness, is the primary goal of design, in all of its domains. Architecture and interior design Although structural integrity, cost, the nature of building materials, and the functional utility of the building contribute heavily to the design process, architects can still apply aesthetic considerations to buildings and related architectural structures. Common aesthetic design principles include ornamentation, edge de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Europe GDP Per Capital Map
Europe is a large peninsula conventionally considered a continent in its own right because of its great physical size and the weight of its history and traditions. Europe is also considered a Continent#Subcontinents, subcontinent of Eurasia and it is located entirely in the Northern Hemisphere and mostly in the Eastern Hemisphere. Comprising the westernmost peninsulas of Eurasia, it shares the continental landmass of Afro-Eurasia with both Africa and Asia. It is bordered by the Arctic Ocean to the north, the Atlantic Ocean to the west, the Mediterranean Sea to the south and Asia to the east. Europe is commonly considered to be Boundaries between the continents of Earth#Asia and Europe, separated from Asia by the drainage divide, watershed of the Ural Mountains, the Ural (river), Ural River, the Caspian Sea, the Greater Caucasus, the Black Sea and the waterways of the Turkish Straits. "Europe" (pp. 68–69); "Asia" (pp. 90–91): "A commonly accepted division between Asia and E ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Birth Rate
The birth rate for a given period is the total number of live human births per 1,000 population divided by the length of the period in years. The number of live births is normally taken from a universal registration system for births; population counts from a census, and estimation through specialized demographic techniques. The birth rate (along with mortality and migration rates) is used to calculate population growth. The estimated average population may be taken as the mid-year population. Natality is another term used interchangeably with 'birth rate'. When the crude death rate is subtracted from the crude birth rate (CBR), the result is the rate of natural increase (RNI). This is equal to the rate of population change (excluding migration). The total (crude) birth rate (which includes all births)—typically indicated as births per 1,000 population—is distinguished from a set of age-specific rates (the number of births per 1,000 persons, or more usually 1,000 femal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
GDP Per Capita
Lists of countries by GDP per capita list the countries in the world by their gross domestic product (GDP) per capita. The lists may be based on nominal or purchasing power parity GDP. Gross national income (GNI) per capita accounts for inflows and outflows of foreign capital. Income inequality metrics measure the distribution of income between rich and poor. Lists *GDP ** List of countries by GDP (nominal) per capita ** List of countries by GDP (PPP) per capita *GNI ** List of countries by GNI (nominal) per capita ** List of countries by GNI (PPP) per capita This article includes a list of countries of the world sorted by their Gross National Income (GNI) per capita at purchasing power parity (PPP). For rankings regarding wealth, see list of countries by wealth per adult. List See also *List ... {{DEFAULTSORT:GDP per capita Lists of countries by GDP ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Field (geography)
In the context of spatial analysis, geographic information systems, and geographic information science, a field is a property that fills space, and varies over space, such as temperature or density. This use of the term has been adopted from physics and mathematics, due to their similarity to physical fields (vector or scalar) such as the electromagnetic field or gravitational field. Synonymous terms include spatially dependent variable (geostatistics), statistical surface ( thematic mapping), and intensive property (physics and chemistry) and crossbreeding between these disciplines is common. The simplest formal model for a field is the function, which yields a single value given a point in space (i.e., ''t'' = ''f''(''x'', ''y'', ''z'') ) History The modeling and analysis of fields in geographic applications was developed in five essentially separate movements, all of which arose during the 1950s and 1960s: * Cartographic techniques for visualizing fields in thematic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aggregate Statistical Summaries
Aggregate or aggregates may refer to: Computing and mathematics * collection of objects that are bound together by a root entity, otherwise known as an aggregate root. The aggregate root guarantees the consistency of changes being made within the aggregate by forbidding external objects from holding references to its members. * Aggregate (data warehouse), a part of the dimensional model that is used to speed up query time by summarizing tables * Aggregate analysis, a technique used in amortized analysis in computer science, especially in analysis of algorithms * Aggregate class, a type of class supported by C++ * Aggregate data, in statistics, data combined from several measurements * Aggregate function, aggregation function, in database management is a function wherein the values of multiple rows are grouped together to form a single summary value * Aggregate Level Simulation Protocol (ALSP), a protocol and supporting software that enables simulations to interoperate with one ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Level Of Measurement
Level of measurement or scale of measure is a classification that describes the nature of information within the values assigned to variables. Psychologist Stanley Smith Stevens developed the best-known classification with four levels, or scales, of measurement: nominal, ordinal, interval, and ratio. This framework of distinguishing levels of measurement originated in psychology and is widely criticized by scholars in other disciplines. Other classifications include those by Mosteller and Tukey, and by Chrisman. Stevens's typology Overview Stevens proposed his typology in a 1946 ''Science'' article titled "On the theory of scales of measurement". In that article, Stevens claimed that all measurement in science was conducted using four different types of scales that he called "nominal", "ordinal", "interval", and "ratio", unifying both " qualitative" (which are described by his "nominal" type) and "quantitative" (to a different degree, all the rest of his scales). The conc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Visual Variable
A visual variable, in cartographic design, graphic design, and data visualization, is an aspect of a graphical object that can visually differentiate it from other objects, and can be controlled during the design process. The concept was first systematized by Jacques Bertin, a French cartographer and graphic designer, and published in his 1967 book, ''Sémiologie Graphique.''Jacque Bertin, ''Sémiologie Graphique. Les diagrammes, les réseaux, les cartes''. With Marc Barbut t al. Paris : Gauthier-Villars. ''Semiology of Graphics'', English Edition, Translation by William J. Berg, University of Wisconsin Press, 1983.) Bertin identified a basic set of these variables and provided guidance for their usage; the concept and the set of variables has since been expanded, especially in cartography, where it has become a core principle of education and practice.Roth, Robert EVisual Variables in D. Richardson, N. Castree, M.F. Goodchild, A. Kobayashki, W. Liu, and R.A. Marston, eds. ''The Int ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jacques Bertin
Jacques Bertin (27 July 1918 – 3 May 2010) was a French cartographer and theorist, known from his book ''Semiologie Graphique'' (''Semiology of Graphics''), published in 1967. This monumental work, based on his experience as a cartographer and geographer, represents the first and widest intent to provide a theoretical foundation to Information Visualization,Juan C. Dürsteler (2000-08)Interview with Jacques Bertin Retrieved 23 June 2008. with his most lasting contribution being his set of visual variables that can be used to construct map symbols and other graphical techniques one of then being the Bertin Projection, an innovative map projection type. Biography Jacques Bertin was born in 1918 in Maisons-Laffitte, Yvelines. When he was 10, he received the first prize of cartography at primary school. He never had problems with drawing, and pursued interests including architecture, the teaching of drawing and cartography. Finally he ended up studying geography and cartography ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Europe GDP Map
Europe is a large peninsula conventionally considered a continent in its own right because of its great physical size and the weight of its history and traditions. Europe is also considered a subcontinent of Eurasia and it is located entirely in the Northern Hemisphere and mostly in the Eastern Hemisphere. Comprising the westernmost peninsulas of Eurasia, it shares the continental landmass of Afro-Eurasia with both Africa and Asia. It is bordered by the Arctic Ocean to the north, the Atlantic Ocean to the west, the Mediterranean Sea to the south and Asia to the east. Europe is commonly considered to be separated from Asia by the watershed of the Ural Mountains, the Ural River, the Caspian Sea, the Greater Caucasus, the Black Sea and the waterways of the Turkish Straits. "Europe" (pp. 68–69); "Asia" (pp. 90–91): "A commonly accepted division between Asia and Europe ... is formed by the Ural Mountains, Ural River, Caspian Sea, Caucasus Mountains, and the Black Sea wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |