|
Propionyl-CoA
Propionyl-CoA is a coenzyme A derivative of propionic acid. It is composed of a 24 total carbon chain (without the coenzyme, it is a 3 carbon structure) and its production and metabolic fate depend on which organism it is present in. Several different pathways can lead to its production, such as through the catabolism of specific amino acids or the oxidation of odd-chain fatty acids. It later can be broken down by propionyl-CoA carboxylase or through the methylcitrate cycle. In different organisms, however, propionyl-CoA can be sequestered into controlled regions, to alleviate its potential toxicity through accumulation. Genetic deficiencies regarding the production and breakdown of propionyl-CoA also have great clinical and human significance. Production There are several different pathways through which propionyl-CoA can be produced: * Propionyl-CoA, a three-carbon structure, is considered to be a minor species of propionic acid. Therefore, odd-number chains of fatty acids a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Propionyl-CoA Carboxylase
Propionyl-CoA carboxylase (, PCC) catalyses the carboxylation reaction of propionyl-CoA in the mitochondrial matrix. PCC has been classified both as a ligase and a lyase. The enzyme is biotin-dependent. The product of the reaction is (S)- methylmalonyl CoA. : ATP + propionyl-CoA + HCO3− ADP + phosphate + (S)-methylmalonyl-CoA (S)-Methylmalonyl-CoA cannot be directly utilized by animals. It is acted upon by a racemase, yielding (R)-methylmalonyl-CoA, which is then converted into succinyl-CoA by methylmalonyl-CoA mutase (one of the few metabolic enzymes which requires vitamin B12 as a cofactor). Succinyl-CoA, a Krebs cycle intermediate, is further metabolized into fumarate, then malate, and then oxaloacetate. Oxaloacetate may be transported into the cytosol to form phosphoenol pyruvate and other gluconeogenic intermediates. Propionyl-CoA is therefore an important precursor to glucose. Propionyl-CoA is the end product of odd-chain fatty acid metabolism, including most methylat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Methylmalonyl-CoA
Methylmalonyl-CoA is the thioester consisting of coenzyme A linked to methylmalonic acid. It is an important intermediate in the biosynthesis of succinyl-CoA, which plays an essential role in the tricarboxylic acid cycle (aka the Citric Acid Cycle, or Krebs Cycle). The compound is sometimes referred to as "methylmalyl-CoA". Biosynthesis and metabolism Methylmalonyl-CoA results from the metabolism of fatty acid with an odd number of carbons or from cholesterol side-chains, forming Propionyl-CoA. Propionyl-CoA and bicarbonate are converted to Methylmalonyl-CoA by the enzyme propionyl-CoA Carboxylase. It then is converted into succinyl-CoA by methylmalonyl-CoA mutase (MUT). This reaction is a reversible isomerization. In this way, the compound enters the Citric Acid Cycle. The following diagram demonstrates the aforementioned reaction: Propionyl CoA + Bicarbonate → Methylmalonyl CoA → Succinyl CoA Vitamin B12 Vitamin B12 plays an integral role in this reaction. Coenzyme ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Odd-chain Fatty Acid
Odd-chain fatty acids are those fatty acids that contain an odd number of carbon atoms. In addition to being classified according to their saturation or unsaturation, fatty acids are also classified according to their odd or even numbers of constituent carbon atoms. With respect to natural abundance, most fatty acids are even chain, e.g. palmitic (C16) and stearic (C18). In terms of physical properties, odd and even fatty acids are similar, generally being colorless, soluble in alcohols, and often somewhat oily. The odd-chain fatty acids are biosynthesized and metabolized slightly differently from the even-chained relatives. In addition to the usual C12-C22 long chain fatty acids, some very long chain fatty acids (VLCFAs) are also known. Some of these VLCFAs are also of the odd-chain variety. Biosynthesis The most common OCFA are the saturated C15 and C17 derivatives, respectively pentadecanoic acid and heptadecanoic acid. The synthesis of even-chained fatty acid synthesis is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coenzyme A
Coenzyme A (CoA, SHCoA, CoASH) is a coenzyme, notable for its role in the synthesis and oxidation of fatty acids, and the oxidation of pyruvate in the citric acid cycle. All genomes sequenced to date encode enzymes that use coenzyme A as a substrate, and around 4% of cellular enzymes use it (or a thioester) as a substrate. In humans, CoA biosynthesis requires cysteine, pantothenate (vitamin B5), and adenosine triphosphate (ATP). In its acetyl form, coenzyme A is a highly versatile molecule, serving metabolic functions in both the anabolic and catabolic pathways. Acetyl-CoA is utilised in the post-translational regulation and allosteric regulation of pyruvate dehydrogenase and carboxylase to maintain and support the partition of pyruvate synthesis and degradation. Discovery of structure Coenzyme A was identified by Fritz Lipmann in 1946, who also later gave it its name. Its structure was determined during the early 1950s at the Lister Institute, London, together by L ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Isoleucine
Isoleucine (symbol Ile or I) is an α-amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins. It contains an α-amino group (which is in the protonated −NH form under biological conditions), an α-carboxylic acid group (which is in the deprotonated −COO form under biological conditions), and a hydrocarbon side chain with a branch (a central carbon atom bound to three other carbon atoms). It is classified as a non-polar, uncharged (at physiological pH), branched-chain, aliphatic amino acid. It is essential in humans, meaning the body cannot synthesize it, and must be ingested in our diet. Isoleucine is synthesized from pyruvate employing leucine biosynthesis enzymes in other organisms such as bacteria. It is encoded by the codons AUU, AUC, and AUA. Metabolism Biosynthesis As an essential nutrient, it is not synthesized in the body, hence it must be ingested, usually as a component of proteins. In plants and microorganisms, it is synthesized via several steps, sta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Methylmalonyl-CoA Racemase
Methylmalonyl CoA epimerase (, ''methylmalonyl-CoA racemase'', ''methylmalonyl coenzyme A racemase'', ''DL-methylmalonyl-CoA racemase'', ''2-methyl-3-oxopropanoyl-CoA 2-epimerase ncorrect') is an enzyme involved in fatty acid catabolism that is encoded in human by the "MCEE" gene located on chromosome 2. It is routinely and incorrectly labeled as "methylmalonyl-CoA racemase". It is not a racemase because the CoA moiety has 5 other stereocenters. Structure The "MCEE" gene is located in the 2p13 region and contains 4 exons, and encodes for a protein that is approximately 18 kDa in size and located to the mitochondrial matrix. Several natural variants in amino acid sequences exist. The structure of the MCEE protein has been resolved by X-ray crystallography at 1.8-angstrom resolution. Function The MCEE gene encodes an enzyme that interconverts D- and L- methylmalonyl-CoA during the degradation of branched-chain amino acids, odd chain-length fatty acids, and other metabolites. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biotin
Biotin (or vitamin B7) is one of the B vitamins. It is involved in a wide range of metabolic processes, both in humans and in other organisms, primarily related to the utilization of fats, carbohydrates, and amino acids. The name ''biotin'', borrowed from the German , derives from the Ancient Greek word (; 'life') and the suffix "-in" (a suffix used in chemistry usually to indicate 'forming'). Chemical description Biotin is classified as a heterocyclic compound, with a sulfur-containing ring fused ureido and tetrahydrothiophene group. A C5-carboxylic acid side chain is appended to one of the rings. The ureido ring, containing the −N−CO−N− group, serves as the carbon dioxide carrier in carboxylation reactions. Biotin is a coenzyme for five carboxylase enzymes, which are involved in the catabolism of amino acids and fatty acids, synthesis of fatty acids, and gluconeogenesis. Biotinylation of histone proteins in nuclear chromatin plays a role in chromatin stability ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Succinyl-CoA
Succinyl-coenzyme A, abbreviated as succinyl-CoA () or SucCoA, is a thioester of succinic acid and coenzyme A. Sources It is an important intermediate in the citric acid cycle, where it is synthesized from α-ketoglutarate by α-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase through decarboxylation. During the process, coenzyme A is added. With B12 as an enzymatic cofactor, it is also synthesized from propionyl CoA, the odd-numbered fatty acid, which cannot undergo beta-oxidation. Propionyl-CoA is carboxylated to D-methylmalonyl-CoA, isomerized to L-methylmalonyl-CoA, and rearranged to yield succinyl-CoA via a vitamin B12-dependent enzyme. While Succinyl-CoA is an intermediate of the citric acid cycle, it cannot be readily incorporated there because there is no net consumption of Succinyl-CoA. Succinyl-CoA is first converted to malate, and then to pyruvate where it is then transported to the matrix to enter the citric acid cycle. Fate It is converted into succinate through the hydrolytic relea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
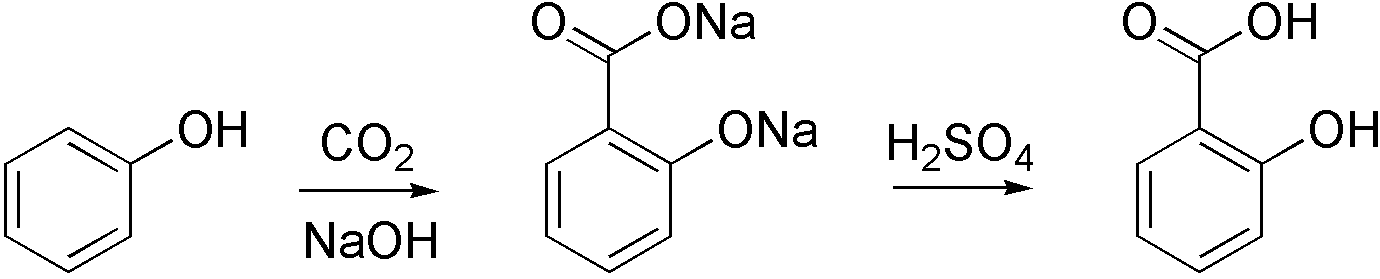
Carboxylation
Carboxylation is a chemical reaction in which a carboxylic acid is produced by treating a substrate with carbon dioxide. The opposite reaction is decarboxylation. In chemistry, the term carbonation is sometimes used synonymously with carboxylation, especially when applied to the reaction of carbanionic reagents with CO2. More generally, carbonation usually describes the production of carbonates. Organic chemistry Carboxylation is a standard conversion in organic chemistry. Specifically carbonation (i.e. carboxylation) of Grignard reagents and organolithium compounds is a classic way to convert organic halides into carboxylic acids. Sodium salicylate, precursor to aspirin, is commercially prepared by treating sodium phenolate (the sodium salt of phenol) with carbon dioxide at high pressure (100 atm) and high temperature (390 K) – a method known as the Kolbe-Schmitt reaction. Acidification of the resulting salicylate salt gives salicylic acid. : Many detailed procedures are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anaerobic Respiration
Anaerobic respiration is respiration using electron acceptors other than molecular oxygen (O2). Although oxygen is not the final electron acceptor, the process still uses a respiratory electron transport chain. In aerobic organisms undergoing respiration, electrons are shuttled to an electron transport chain, and the final electron acceptor is oxygen. Molecular oxygen is an excellent electron acceptor. Anaerobes instead use less-oxidizing substances such as nitrate (), fumarate (), sulfate (), or elemental sulfur (S). These terminal electron acceptors have smaller reduction potentials than O2. Less energy per oxidized molecule is released. Therefore, anaerobic respiration is less efficient than aerobic. As compared with fermentation Anaerobic cellular respiration and fermentation generate ATP in very different ways, and the terms should not be treated as synonyms. Cellular respiration (both aerobic and anaerobic) uses highly reduced chemical compounds such as NADH an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aerobic Organism
{{disambiguation ...
Aerobic means "requiring air," in which "air" usually means oxygen. Aerobic may also refer to * Aerobic exercise, prolonged exercise of moderate intensity * Aerobics, a form of aerobic exercise * Aerobic respiration, the aerobic process of cellular respiration * Aerobic organism, a living thing with an oxygen-based metabolism See also * Anaerobic (other) Anaerobic means "living, active, occurring, or existing in the absence of free oxygen", as opposed to aerobic which means "living, active, or occurring only in the presence of oxygen." Anaerobic may also refer to: * Anaerobic adhesive, a bonding a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glutamate
Glutamic acid (symbol Glu or E; the ionic form is known as glutamate) is an α-amino acid that is used by almost all living beings in the biosynthesis of proteins. It is a non-essential nutrient for humans, meaning that the human body can synthesize enough for its use. It is also the most abundant excitatory neurotransmitter in the vertebrate nervous system. It serves as the precursor for the synthesis of the inhibitory gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) in GABA-ergic neurons. Its molecular formula is . Glutamic acid exists in three optically isomeric forms; the dextrorotatory -form is usually obtained by hydrolysis of gluten or from the waste waters of beet-sugar manufacture or by fermentation.Webster's Third New International Dictionary of the English Language Unabridged, Third Edition, 1971. Its molecular structure could be idealized as HOOC−CH()−()2−COOH, with two carboxyl groups −COOH and one amino group −. However, in the solid state and mildly acidic water solu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |