|
Progressive-scan
Progressive scanning (alternatively referred to as noninterlaced scanning) is a format of displaying, storing, or transmitting moving images in which all the lines of each frame are drawn in sequence. This is in contrast to interlaced video used in traditional analog television systems where only the odd lines, then the even lines of each frame (each image called a video field) are drawn alternately, so that only half the number of actual image frames are used to produce video. The system was originally known as "sequential scanning" when it was used in the Baird 240 line television transmissions from Alexandra Palace, United Kingdom in 1936. It was also used in Baird's experimental transmissions using 30 lines in the 1920s. Burns, R.W. ''John Logie Baird, Television Pioneer'', Herts: The Institution of Electrical Engineers, 2000. 316. Progressive scanning became universally used in computer screens beginning in the early 21st century. Interline twitter This rough animation c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Interline Twitter
Interlaced video (also known as interlaced scan) is a technique for doubling the perceived frame rate of a video display without consuming extra Bandwidth (signal processing), bandwidth. The interlaced signal contains two field (video), fields of a video frame captured consecutively. This enhances motion perception to the viewer, and reduces flicker (screen), flicker by taking advantage of the phi phenomenon. This effectively doubles the time resolution (also called ''temporal resolution'') as compared to non-interlaced footage (for frame rates equal to field rates). Interlaced signals require a display that is natively capable of showing the individual fields in a sequential order. cathode-ray tube, CRT displays and ALiS plasma displays are made for displaying interlaced signals. Interlaced scan refers to one of two common methods for "painting" a video image on an electronic display screen (the other being progressive video, progressive scan) by scanning or displaying each li ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Interlaced Video
Interlaced video (also known as interlaced scan) is a technique for doubling the perceived frame rate of a video display without consuming extra bandwidth. The interlaced signal contains two fields of a video frame captured consecutively. This enhances motion perception to the viewer, and reduces flicker by taking advantage of the phi phenomenon. This effectively doubles the time resolution (also called ''temporal resolution'') as compared to non-interlaced footage (for frame rates equal to field rates). Interlaced signals require a display that is natively capable of showing the individual fields in a sequential order. CRT displays and ALiS plasma displays are made for displaying interlaced signals. Interlaced scan refers to one of two common methods for "painting" a video image on an electronic display screen (the other being progressive scan) by scanning or displaying each line or row of pixels. This technique uses two fields to create a frame. One field contains all od ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Interlaced Video
Interlaced video (also known as interlaced scan) is a technique for doubling the perceived frame rate of a video display without consuming extra bandwidth. The interlaced signal contains two fields of a video frame captured consecutively. This enhances motion perception to the viewer, and reduces flicker by taking advantage of the phi phenomenon. This effectively doubles the time resolution (also called ''temporal resolution'') as compared to non-interlaced footage (for frame rates equal to field rates). Interlaced signals require a display that is natively capable of showing the individual fields in a sequential order. CRT displays and ALiS plasma displays are made for displaying interlaced signals. Interlaced scan refers to one of two common methods for "painting" a video image on an electronic display screen (the other being progressive scan) by scanning or displaying each line or row of pixels. This technique uses two fields to create a frame. One field contains all od ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Television
Television, sometimes shortened to TV, is a telecommunication medium for transmitting moving images and sound. The term can refer to a television set, or the medium of television transmission. Television is a mass medium for advertising, entertainment, news, and sports. Television became available in crude experimental forms in the late 1920s, but only after several years of further development was the new technology marketed to consumers. After World War II, an improved form of black-and-white television broadcasting became popular in the United Kingdom and the United States, and television sets became commonplace in homes, businesses, and institutions. During the 1950s, television was the primary medium for influencing public opinion.Diggs-Brown, Barbara (2011''Strategic Public Relations: Audience Focused Practice''p. 48 In the mid-1960s, color broadcasting was introduced in the U.S. and most other developed countries. The availability of various types of archival st ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deinterlacing
Deinterlacing is the process of converting interlaced video into a non-interlaced or Progressive scan, progressive form. Interlaced video signals are commonly found in analog television, digital television (HDTV) when in the 1080i format, some DVD titles, and a smaller number of Blu-ray discs. An interlaced video frame consists of two Video field, fields taken in sequence: the first containing all the odd lines of the image, and the second all the even lines. Analog television employed this technique because it allowed for less transmission bandwidth while keeping a high frame rate for smoother and more life-like motion. A non-interlaced (or progressive scan) signal that uses the same bandwidth only updates the display half as often and was found to create a perceived flicker or stutter. CRT-based displays were able to display interlaced video correctly due to their complete analog nature, blending in the alternating lines seamlessly. However, since the early 2000s, displays such ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
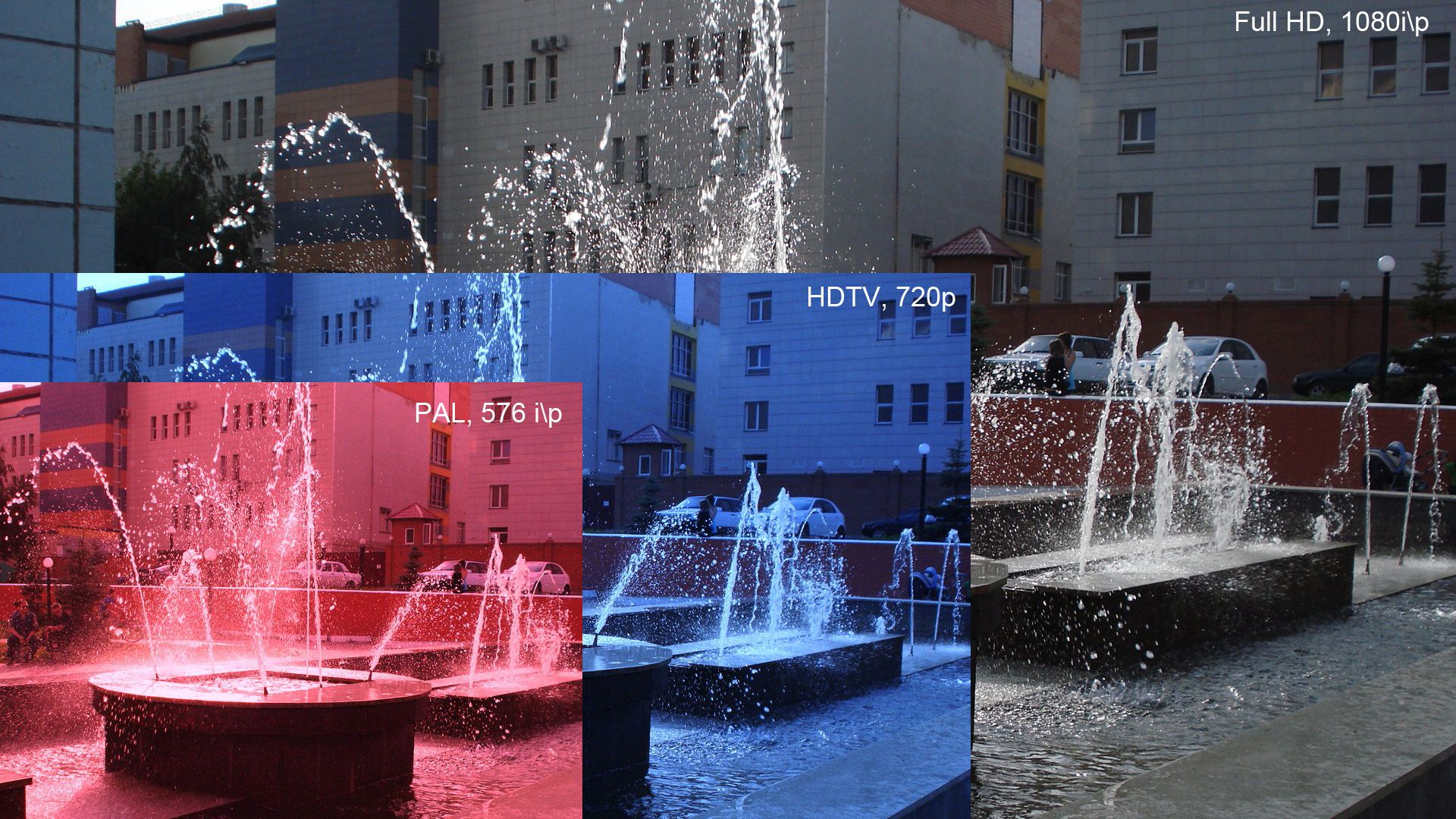
HDTV
High-definition television (HD or HDTV) describes a television system which provides a substantially higher image resolution than the previous generation of technologies. The term has been used since 1936; in more recent times, it refers to the generation following standard-definition television (SDTV), often abbreviated to HDTV or HD-TV. It is the current de facto standard video format used in most broadcasts: terrestrial broadcast television, cable television, satellite television and Blu-ray Discs. Formats HDTV may be transmitted in various formats: * 720p (1280 horizontal pixels × 720 lines): 921,600 pixels * 1080i (1920×1080) interlaced scan: 1,036,800 pixels (~1.04 MP). * 1080p (1920×1080) progressive scan: 2,073,600 pixels (~2.07 MP). ** Some countries also use a non-standard CEA resolution, such as 1440×1080i: 777,600 pixels (~0.78 MP) per field or 1,555,200 pixels (~1.56 MP) per frame When transmitted at two megapixels per frame, HDTV provides about five times a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
High-definition Television
High-definition television (HD or HDTV) describes a television system which provides a substantially higher image resolution than the previous generation of technologies. The term has been used since 1936; in more recent times, it refers to the generation following standard-definition television (SDTV), often abbreviated to HDTV or HD-TV. It is the current de facto standard video format used in most broadcasts: terrestrial broadcast television, cable television, satellite television and Blu-ray Discs. Formats HDTV may be transmitted in various formats: * 720p (1280 horizontal pixels × 720 lines): 921,600 pixels * 1080i (1920×1080) interlaced scan: 1,036,800 pixels (~1.04 MP). * 1080p (1920×1080) progressive scan: 2,073,600 pixels (~2.07 MP). ** Some countries also use a non-standard CEA resolution, such as 1440×1080i: 777,600 pixels (~0.78 MP) per field or 1,555,200 pixels (~1.56 MP) per frame When transmitted at two megapixels per frame, HDTV provides about five times ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1080p
1080p (1920×1080 progressively displayed pixels; also known as Full HD or FHD, and BT.709) is a set of HDTV high-definition video modes characterized by 1,920 pixels displayed across the screen horizontally and 1,080 pixels down the screen vertically; the ''p'' stands for progressive scan, ''i.e.'' non-interlaced. The term usually assumes a widescreen aspect ratio of 16:9, implying a resolution of 2.1 megapixels. It is often marketed as Full HD or FHD, to contrast 1080p with 720p resolution screens. Although 1080p is sometimes informally referred to as 2K, these terms reflect two distinct technical standards, with differences including resolution and aspect ratio. 1080p video signals are supported by ATSC standards in the United States and DVB standards in Europe. Applications of the 1080p standard include television broadcasts, Blu-ray Discs, smartphones, Internet content such as YouTube videos and Netflix TV shows and movies, consumer-grade televisions and projector ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
PALPlus
PALplus (or ''PAL+'') is an analogue television broadcasting system aimed to improve and enhance the PAL format by allowing 16:9 (or 1.77:1) aspect ratio broadcasts, while remaining compatible with existing television receivers, defined by ITU recommendation BT.1197-1. Introduced in 1993, it followed experiences with the HD-MAC (high definition) and D2-MAC, hybrid analogue-digital widescreen formats that were incompatible with PAL receivers. It was developed at the University of Dortmund in Germany, in cooperation with German terrestrial broadcasters and European and Japanese manufacturers. The system had some adoption across Europe during the late 1990s and helped introduce widescreen TVs in the market, but never became mainstream. A similar system, developed in Japan at the same time and named EDTV-II/ Wide-aspect Clear-vision, allows for 16:9 NTSC broadcasts. History The MAC family of standards was adopted in Europe in 1983, primarily for Direct Broadcasting by Satellite ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Progressive Scan DVD Player
A progressive scan DVD player is a DVD player that can produce video in a progressive scan format such as 480p (NTSC) or 576p (PAL). Players which can output resolutions higher than 480p or 576p are often called upconverting DVD players. Before HDTVs became common, players were sold which could produce 480p or 576p. TVs with this feature were often in the upper price range of a manufacturer's line. To utilize this feature, a TV or other display with a progressive scan input was needed. HDTVs usually have a progressive scan input; progressive scan inputs are less common on standard definition TVs (often called SDTVs.) Some players have a feature called " 3:2 pulldown detection" or "inverse telecine" which attempts to better handle the artifacts which result from differing film and video rates in conjunction with interlaced scanning of the film. However most line doublers used in these players are not able to achieve the anticipated inverse telecine functionality. (See Line dou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moving Image
A film also called a movie, motion picture, moving picture, picture, photoplay or (slang) flick is a work of visual art that simulates experiences and otherwise communicates ideas, stories, perceptions, feelings, beauty, or atmosphere through the use of moving images. These images are generally accompanied by sound and, more rarely, other sensory stimulations. The word "cinema", short for cinematography, is often used to refer to filmmaking and the film industry, and to the art form that is the result of it. Recording and transmission of film The moving images of a film are created by photography, photographing actual scenes with a movie camera, motion-picture camera, by photographing drawings or miniature models using traditional animation techniques, by means of computer-generated imagery, CGI and computer animation, or by a combination of some or all of these techniques, and other visual effects. Before the introduction of digital production, series of still imag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ultra-high-definition Television
Ultra-high-definition television (also known as Ultra HD television, Ultra HD, UHDTV, UHD and Super Hi-Vision) today includes 4K UHD and 8K UHD, which are two digital video formats with an aspect ratio of 16:9. These were first proposed by NHK Science & Technology Research Laboratories and later defined and approved by the International Telecommunication Union (ITU). The Consumer Electronics Association announced on October 17, 2012, that "Ultra High Definition", or "Ultra HD", would be used for displays that have an aspect ratio of 16:9 or wider and at least one digital input capable of carrying and presenting native video at a minimum resolution of . In 2015, the Ultra HD Forum was created to bring together the end-to-end video production ecosystem to ensure interoperability and produce industry guidelines so that adoption of ultra-high-definition television could accelerate. From just 30 in Q3 2015, the forum published a list up to 55 commercial services available aroun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |