|
Procrastination
Procrastination is the action of unnecessarily and voluntarily delaying or postponing something despite knowing that there will be negative consequences for doing so. The word has originated from the Latin word ''procrastinatus'', which itself evolved from the prefix ''pro-'', meaning "forward," and ''crastinus'', meaning "of tomorrow." Oftentimes, it is a habitual human behaviour. It is a common human experience involving delay in everyday chores or even putting off salient tasks such as attending an appointment, submitting a job report or academic assignment, or broaching a stressful issue with a partner. Although typically perceived as a negative trait due to its hindering effect on one's productivity often associated with depression, low self-esteem, guilt and inadequacy, it can also be considered a wise response to certain demands that could present risky or negative outcomes or require waiting for new information to arrive. From a cultural and a social perspective, studen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Time Management
Time management is the process of planning and exercising conscious control of time spent on specific activities, especially to increase effectiveness, efficiency, and productivity. It involves of various demands upon a person relating to Employment, work, Interpersonal relationship, social life, family, hobby, hobbies, personal interests, and commitments with the finite nature of time. Using time effectively gives the person "choice" on spending or managing activities at their own time and expediency. Time management may be aided by a range of skills, tools, and techniques used to management, manage time when accomplishing specific tasks, projects, and goals complying with a due date. Initially, time management referred to just business or work activities, but eventually, the term broadened to include personal activities as well. A time management system is a designed combination of processes, tools, techniques, and methods. Time management is usually a necessity in any project man ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Temporal Motivation Theory
Temporal motivation theory (TMT) is an integrative motivational theory developed by Piers Steel and Cornelius J. König, the theory emphasizes time as a critical and motivational factor. The argument for a broad, integrative theory stems from the absence of a single theory that can address motivation in its entirety. Thus, it incorporates primary aspects of multiple major theories, including expectancy theory, hyperbolic discounting, need theory and cumulative prospect theory. According to Schmidt, Dolis, and Tolli, Temporal Motivation Theory "''may help further the understanding of the impact of time, and particularly deadlines, on dynamic attention allocation''." The Temporal Motivation Theory formula can be applied to human behaviour, procrastinationPetz, Sarah (May 12, 2011).Procrastination down to a science. ''Macleans on Campus''. Retrieved September 21, 2012 and to goal setting. According to Lord, Diefenforff, Schmidt, and Hall, the theory "models the motivating power of appr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coping (psychology)
Coping refers to conscious strategies used to reduce unpleasant emotions. Coping strategies can be cognitions or behaviours and can be individual or social. Theories of coping Hundreds of coping strategies have been proposed in an attempt to understand how people cope. Classification of these strategies into a broader architecture has not been agreed upon. Researchers try to group coping responses rationally, empirically by factor analysis, or through a blend of both techniques. In the early days, Folkman and Richard Lazarus, Lazarus split the coping strategies into four groups, namely problem-focused, emotion-focused, support-seeking, and meaning-making coping. Weiten has identified four types of coping strategies:Weiten, W. & Lloyd, M.A. (2008) ''Psychology Applied to Modern Life (9th ed.)''. Wadsworth Cengage Learning. . appraisal-focused (adaptive cognitive), problem-focused (adaptive behavioral), emotion-focused, and occupation-focused coping. Billings and Moos added avoid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coping Mechanism
Coping refers to conscious strategies used to reduce unpleasant emotions. Coping strategies can be cognitions or behaviours and can be individual or social. Theories of coping Hundreds of coping strategies have been proposed in an attempt to understand how people cope. Classification of these strategies into a broader architecture has not been agreed upon. Researchers try to group coping responses rationally, empirically by factor analysis, or through a blend of both techniques. In the early days, Folkman and Lazarus split the coping strategies into four groups, namely problem-focused, emotion-focused, support-seeking, and meaning-making coping. Weiten has identified four types of coping strategies:Weiten, W. & Lloyd, M.A. (2008) ''Psychology Applied to Modern Life (9th ed.)''. Wadsworth Cengage Learning. . appraisal-focused (adaptive cognitive), problem-focused (adaptive behavioral), emotion-focused, and occupation-focused coping. Billings and Moos added avoidance coping as o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Conscientiousness
Conscientiousness is the personality trait of being careful, or diligent. Conscientiousness implies a desire to do a task well, and to take obligations to others seriously. Conscientious people tend to be efficient and organized as opposed to easy-going and disorderly. They exhibit a tendency to show self-discipline, act dutifully, and aim for achievement; they display planned rather than spontaneous behavior; and they are generally dependable. It is manifested in characteristic behaviors such as being neat, and systematic; also including such elements as carefulness, thoroughness, and deliberation (the tendency to think carefully before acting). Conscientiousness is one of the five traits of both the Five Factor Model and the HEXACO model of personality and is an aspect of what has traditionally been referred to as having character. Conscientious individuals are generally hard-working, and reliable. When taken to an extreme, they may also be "workaholics", perfectio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Distraction
Distraction is the process of diverting the attention of an individual or group from a desired area of focus and thereby blocking or diminishing the reception of desired information. Distraction is caused by: the lack of ability to pay attention; lack of interest in the object of attention; or the great intensity, novelty or attractiveness of something other than the object of attention. Distractions come from both external sources, and internal sources. External distractions include factors such as visual triggers, social interactions, music, text messages, and phone calls. There are also internal distractions such as hunger, fatigue, illness, worrying, and daydreaming. Both external and internal distractions contribute to the interference of focus. In the car Distracted driving is a dangerous threat to road safety across the world. While drunk driving rates have been on the decline since 1983, distracted driving has been increasing in recent years. Many feel this incline is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Counterfactual Thinking
Counterfactual thinking is a concept in psychology that involves the human tendency to create possible alternatives to life events that have already occurred; something that is contrary to what actually happened. Counterfactual thinking is, as it states: "counter to the facts". These thoughts consist of the "What if?" and the "If only..." that occur when thinking of how things could have turned out differently. Counterfactual thoughts include things that – in the present – now could never happen in reality because they solely pertain to events that have occurred in the past. Overview The term ''"Counterfactual"'' is defined by the Merriam-Webster Dictionary as contrary to the facts. A counterfactual thought occurs when a person modifies a factual prior event and then assesses the consequences of that change. A person may imagine how an outcome could have turned out differently, if the antecedents that led to that event were different. For example, a person may reflect upon h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Delayed Gratification
Delayed gratification, or deferred gratification, is the resistance to the temptation of an immediate pleasure in the hope of obtaining a valuable and long-lasting reward in the long-term. In other words, delayed gratification describes the process that the subject undergoes when the subject resists the temptation of an immediate reward in preference for a later reward. Generally, delayed gratification is associated with resisting a smaller but more immediate reward in order to receive a larger or more enduring reward later. A growing body of literature has linked the ability to delay gratification to a host of other positive outcomes, including academic success, physical health, psychological health, and social competence. A person's ability to delay gratification relates to other similar skills such as patience, impulse control, self-control and willpower, all of which are involved in self-regulation. Broadly, self-regulation encompasses a person's capacity to adapt the self ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
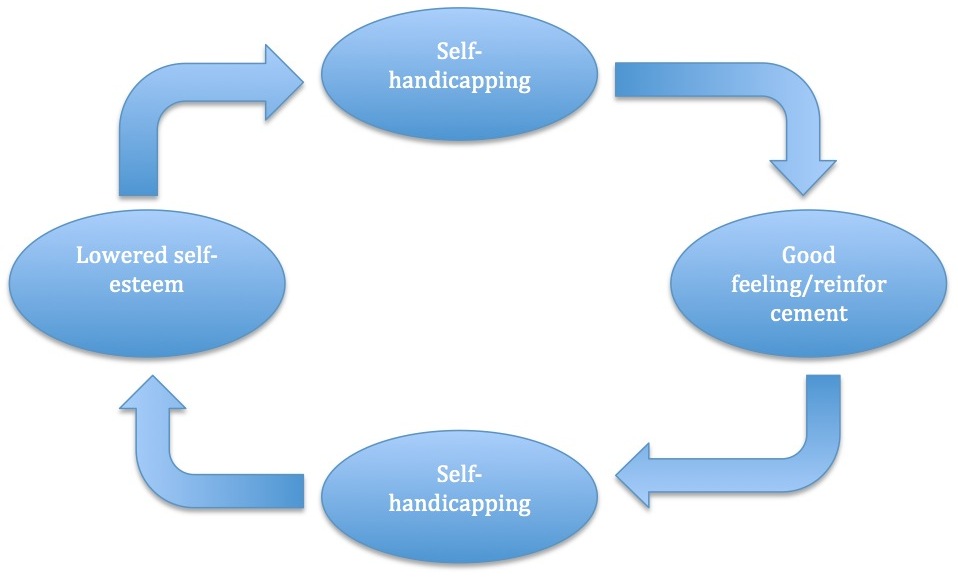
Self-handicapping
Self-handicapping is a cognitive strategy by which people avoid effort in the hopes of keeping potential failure from hurting self-esteem. It was first theorized by Edward E. Jones and Steven Berglas, according to whom self-handicaps are obstacles created, or claimed, by the individual in anticipation of failing performance.Feick, D.L., & Rhodewalt, F. (1997). The Double-Edged Sword of Self-Handicapping: Discounting, Augmentation, and the Protection and Enhancement of Self-Esteem. ''Motivation and Emotion, Vol. 21, No. 2. '' Self-handicapping can be seen as a method of preserving self-esteem but it can also be used for self-enhancement and to manage the impressions of others. Rhodewalt, F., & Vohs, K. D. (2005). Defensive strategies, motivation, and the self. In A. Elliot & C. Dweck (Eds.). ''Handbook of competence and motivation''(pp. 548-565). New York: Guilford Press. This conservation or augmentation of self-esteem is due to changes in causal attributions or the attributions ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Achievement Orientation
Goal orientation, or achievement orientation, is an "individual disposition towards developing or validating one's ability in achievement settings". In general, an individual can be said to be ''mastery'' or ''performance'' oriented, based on whether one's goal is to develop one's ability or to demonstrate one's ability, respectively. A ''mastery'' orientation is also sometimes referred to as a ''learning'' orientation. Goal orientation refers to how an individual interprets and reacts to tasks, resulting in different patterns of cognition, affect and behavior. Developed within a social-cognitive framework, the orientation goal theory proposes that students' motivation and achievement-related behaviors can be understood by considering the reasons or purposes they adopt while engaged in academic work. The focus is on how students think about themselves, their tasks, and their performance. Goal orientations have been shown to be associated with individuals' academic achievement, adjust ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shinobu Kitayama
Shinobu Kitayama (born March 9, 1957) is a Japanese social psychologist and the Robert B. Zajonc Collegiate Professor of Psychology at the University of Michigan. He is also the Social Psychology Area Chair and Director of the Culture & Cognition Program at the University of Michigan. He is the editor-in-chief of the Attitudes and Social Cognition section of the ''Journal of Personality and Social Psychology''. He received his bachelor's degree and master's degree from Kyoto University and his doctorate from the University of Michigan. Together with Mayumi Karasawa, he discovered the birthday-number effect, the subconscious tendency of people to prefer the numbers in the date of their birthday over other numbers. Prof. Kitayama is best known for his work on the social psychology of culture as it relates to the self. He and Hazel Rose Markus have argued that Western selves are constructed as independent from others, and people from many East Asian cultures construct interdependent se ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Collectivism And Individualism
In sociology, a social organization is a pattern of relationships between and among individuals and social groups. Characteristics of social organization can include qualities such as sexual composition, spatiotemporal cohesion, leadership, structure, division of labor, communication systems, and so on. And because of these characteristics of social organization, people can monitor their everyday work and involvement in other activities that are controlled forms of human interaction. These interactions include: affiliation, collective resources, substitutability of individuals and recorded control. These interactions come together to constitute common features in basic social units such as family, enterprises, clubs, states, etc. These are social organizations. Common examples of modern social organizations are government agencies, NGO's and corporations. Elements Social organizations happen in everyday life. Many people belong to various social structures—institutional ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |