|
Process Migration
In computing, process migration is a specialized form of process management whereby processes are moved from one computing environment to another. This originated in distributed computing, but is now used more widely. On multicore machines (multiple cores on one processor or multiple processors) process migration happens as a standard part of process scheduling, and it is quite easy to migrate a process within a given machine, since most resources (memory, files, sockets) do not need to be changed, only the execution context (primarily program counter and registers). The traditional form of process migration is in computer clusters where processes are moved from machine to machine, which is significantly more difficult, as it requires serializing the process image and migrating or reacquiring resources at the new machine. The first implementation of process migration was in the DEMOS/MP operating project at the University of California, Berkeley and was described in a 1983 pap ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Process Management (computing)
A process is a program in execution, and an integral part of any modern-day operating system (OS). The OS must allocate resources to processes, enable processes to share and exchange information, protect the resources of each process from other processes and enable synchronization among processes. To meet these requirements, The OS must maintain a data structure for each process, which describes the state and resource ownership of that process, and which enables the operating system to exert control over each process. Multiprogramming In any modern operating system, there can be more than one instance of a program loaded in memory at the same time. For example, more than one user can be executing the same program, with each user having separate copies of the program loaded into memory. With some programs, it is possible to have one copy loaded into memory, while several users have shared access to it so that they can each execute the same program-code. Such a program is called ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Sprite (operating System)
Sprite is an experimental Unix-like distributed operating system developed at the University of California, Berkeley by John Ousterhout's research group between 1984 and 1992. Its notable features include support for single system image on computer clusters and the introduction of the log-structured file system. The Tcl scripting language also originated in this project. Early work Early work on Sprite was based on the idea of making the operating system more "network aware", and thereby at the same time make it invisible to the user. The primary area of work was the building of a new network file system which made heavy use of local client-side caching in order to improve performance. After opening the file and some initial reads, the network is only used on-demand, and most user actions occur against the cache. Similar utilities allow remote devices to be mapped into the local computer's space, allowing for network printing and similar duties. Many of the key Unix files are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
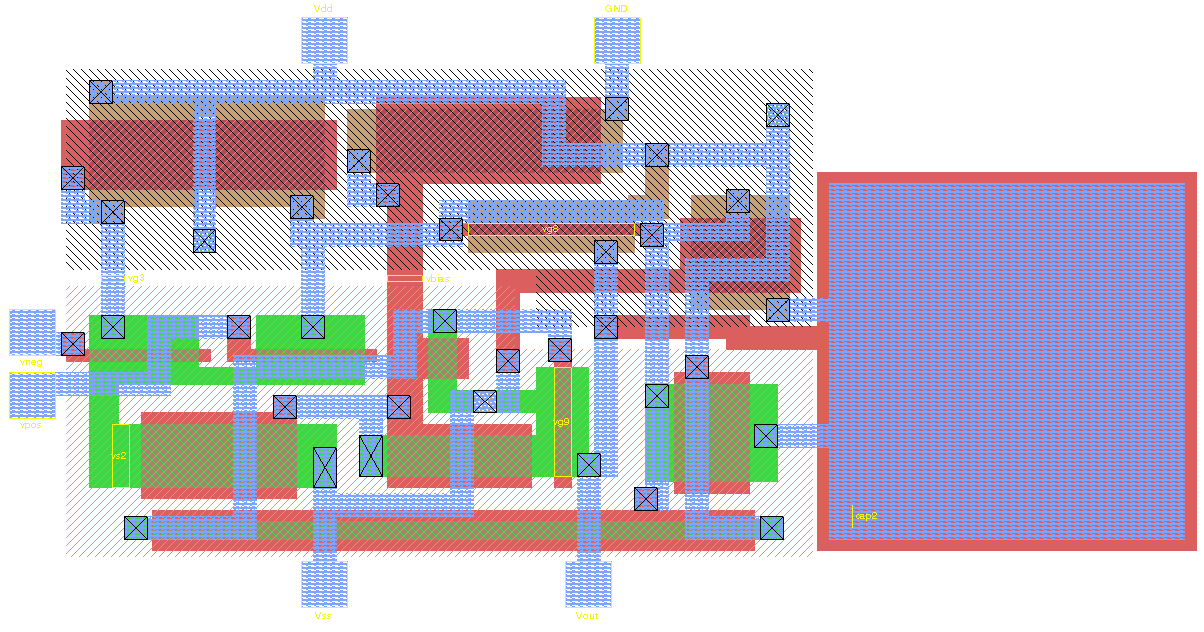
Electronic Design Automation
Electronic design automation (EDA), also referred to as electronic computer-aided design (ECAD), is a category of software tools for designing Electronics, electronic systems such as integrated circuits and printed circuit boards. The tools work together in a Design flow (EDA), design flow that chip designers use to design and analyze entire semiconductor chips. Since a modern semiconductor chip can have billions of components, EDA tools are essential for their design; this article in particular describes EDA specifically with respect to integrated circuits (ICs). History Early days The earliest electronic design automation is attributed to IBM with the documentation of its IBM 700/7000 series, 700 series computers in the 1950s. Prior to the development of EDA, integrated circuits were designed by hand and manually laid out. Some advanced shops used geometric software to generate tapes for a Gerber format, Gerber photoplotter, responsible for generating a monochromatic ex ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Engineering
Engineering is the practice of using natural science, mathematics, and the engineering design process to Problem solving#Engineering, solve problems within technology, increase efficiency and productivity, and improve Systems engineering, systems. Modern engineering comprises many subfields which include designing and improving infrastructure, machinery, vehicles, electronics, Materials engineering, materials, and energy systems. The Academic discipline, discipline of engineering encompasses a broad range of more Academic specialization, specialized fields of engineering, each with a more specific emphasis for applications of applied mathematics, mathematics and applied science, science. See glossary of engineering. The word '':wikt:engineering, engineering'' is derived from the Latin . Definition The American Engineers' Council for Professional Development (the predecessor of the Accreditation Board for Engineering and Technology aka ABET) has defined "engineering" as: ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Integrated Circuit Design
Integrated circuit design, semiconductor design, chip design or IC design, is a sub-field of electronics engineering, encompassing the particular Boolean logic, logic and circuit design techniques required to design integrated circuits (ICs). An IC consists of miniaturized electronic components built into an electrical network on a monolithic semiconductor substrate by photolithography. IC design can be divided into the broad categories of Digital data, digital and analog electronics, analog IC design. Digital IC design is to produce components such as microprocessors, FPGAs, memories (Random-access memory, RAM, Read-only memory, ROM, and flash memory, flash) and digital Application-specific integrated circuit, ASICs. Digital design focuses on logical correctness, maximizing circuit density, and placing circuits so that clock and timing signals are routed efficiently. Analog IC design also has specializations in power IC design and Radio frequency, RF IC design. Analog IC design ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Inter-process Communication
In computer science, interprocess communication (IPC) is the sharing of data between running Process (computing), processes in a computer system. Mechanisms for IPC may be provided by an operating system. Applications which use IPC are often categorized as client–server model, clients and servers, where the client requests data and the server responds to client requests. Many applications are both clients and servers, as commonly seen in distributed computing. IPC is very important to the design process for microkernels and nanokernels, which reduce the number of functionalities provided by the kernel. Those functionalities are then obtained by communicating with servers via IPC, leading to a large increase in communication when compared to a regular monolithic kernel. IPC interfaces generally encompass variable analytic framework structures. These processes ensure compatibility between the multi-vector protocols upon which IPC models rely. An IPC mechanism is either Synchroni ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Preemption (computing)
In computing, preemption is the act performed by an external scheduler — without assistance or cooperation from the task — of temporarily interrupting an executing task, with the intention of resuming it at a later time. This preemptive scheduler usually runs in the most privileged protection ring, meaning that interruption and then resumption are considered highly secure actions. Such changes to the currently executing task of a processor are known as context switching. User mode and kernel mode In any given system design, some operations performed by the system may not be preemptable. This usually applies to kernel functions and service interrupts which, if not permitted to run to completion, would tend to produce race conditions resulting in deadlock. Barring the scheduler from preempting tasks while they are processing kernel functions simplifies the kernel design at the expense of system responsiveness. The distinction between user mode and kernel mode, w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
OpenMosix
openMosix was a free cluster management system that provided single-system image (SSI) capabilities, e.g. automatic work distribution among nodes. It allowed program processes (not threads) to migrate to machines in the node's network that would be able to run that process faster (process migration). It was particularly useful for running parallel applications having low to moderate input/output (I/O). It was released as a Linux kernel patch, but was also available on specialized Live CDs. openMosix development has been halted by its developers, but the LinuxPMI project is continuing development of the former openMosix code. History openMosix was originally forked from MOSIX by Moshe Bar on February 10, 2002 when MOSIX became proprietary software. openMosix was considered stable on Linux kernel 2.4.x for the x86 architecture, but porting to Linux 2.6 kernel remained in the alpha stage. Support for the 64-bit AMD64 architecture only started with the 2.6 version. On July 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Process (computing)
In computing, a process is the Instance (computer science), instance of a computer program that is being executed by one or many thread (computing), threads. There are many different process models, some of which are light weight, but almost all processes (even entire virtual machines) are rooted in an operating system (OS) process which comprises the program code, assigned system resources, physical and logical access permissions, and data structures to initiate, control and coordinate execution activity. Depending on the OS, a process may be made up of multiple threads of execution that execute instructions Concurrency (computer science), concurrently. While a computer program is a passive collection of Instruction set, instructions typically stored in a file on disk, a process is the execution of those instructions after being loaded from the disk into memory. Several processes may be associated with the same program; for example, opening up several instances of the same progra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
University Of California, Berkeley
The University of California, Berkeley (UC Berkeley, Berkeley, Cal, or California), is a Public university, public Land-grant university, land-grant research university in Berkeley, California, United States. Founded in 1868 and named after the Anglo-Irish philosopher George Berkeley, it is the state's first land-grant university and is the founding campus of the University of California system. Berkeley has an enrollment of more than 45,000 students. The university is organized around fifteen schools of study on the same campus, including the UC Berkeley College of Chemistry, College of Chemistry, the UC Berkeley College of Engineering, College of Engineering, UC Berkeley College of Letters and Science, College of Letters and Science, and the Haas School of Business. It is Carnegie Classification of Institutions of Higher Education, classified among "R1: Doctoral Universities – Very high research activity". Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory was originally founded as par ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Process Image
{{Refimprove, date=December 2013 In computing, a system image is a serialized copy of the entire state of a computer system stored in some non-volatile form, such as a binary executable file. If a system has all its state written to a disk (i.e. on a disk image), then a system image can be produced by copying the disk to a file elsewhere, often with disk cloning applications. On many systems a complete system image cannot be created by a disk cloning program running within that system because information can be held outside of disks and volatile memory, for example in non-volatile memory, such as boot ROMs. A system is said to be capable of using system images if it can be shut down and later restored to exactly the same state. In such cases, system images can be used for backup. Hibernation is an example that uses an image of the entire machine's RAM. Process images A process image is a copy of a given process's state at a given point in time. It is often used to create persi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |