|
Primordial Fluctuations
Primordial fluctuations are density variations in the early universe which are considered the seeds of all structure in the universe. Currently, the most widely accepted explanation for their origin is in the context of cosmic inflation. According to the inflationary paradigm, the exponential growth of the scale factor during inflation caused quantum fluctuations of the inflation field to be stretched to macroscopic scales, and, upon leaving the horizon, to "freeze in". At the later stages of radiation- and matter-domination, these fluctuations re-entered the horizon, and thus set the initial conditions for structure formation. The statistical properties of the primordial fluctuations can be inferred from observations of anisotropies in the cosmic microwave background and from measurements of the distribution of matter, e.g., galaxy redshift surveys. Since the fluctuations are believed to arise from inflation, such measurements can also set constraints on parameters within inflat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Density
Density (volumetric mass density or specific mass) is the substance's mass per unit of volume. The symbol most often used for density is ''ρ'' (the lower case Greek letter rho), although the Latin letter ''D'' can also be used. Mathematically, density is defined as mass divided by volume: : \rho = \frac where ''ρ'' is the density, ''m'' is the mass, and ''V'' is the volume. In some cases (for instance, in the United States oil and gas industry), density is loosely defined as its weight per unit volume, although this is scientifically inaccurate – this quantity is more specifically called specific weight. For a pure substance the density has the same numerical value as its mass concentration. Different materials usually have different densities, and density may be relevant to buoyancy, purity and packaging. Osmium and iridium are the densest known elements at standard conditions for temperature and pressure. To simplify comparisons of density across different s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
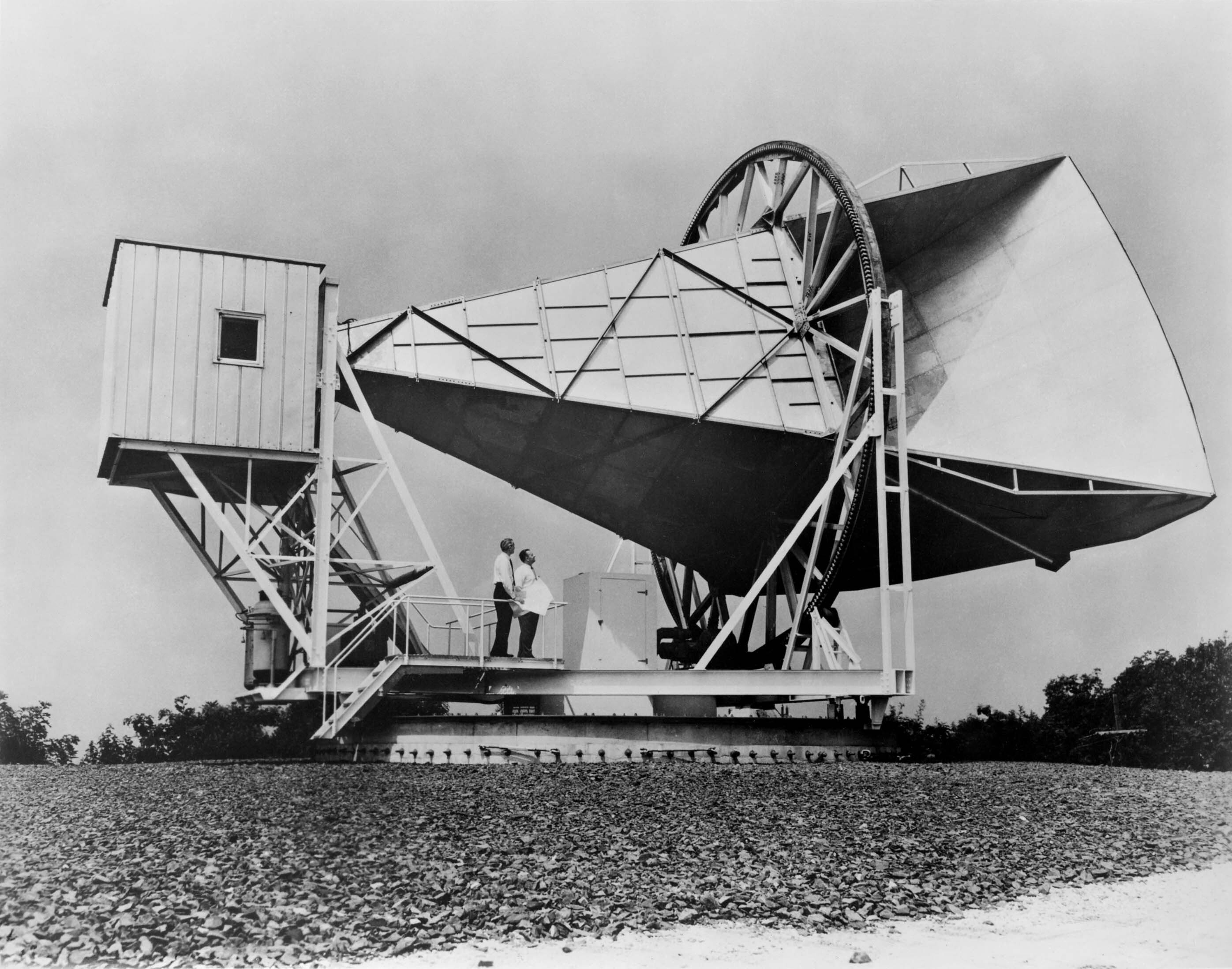
Cosmic Microwave Background
In Big Bang cosmology the cosmic microwave background (CMB, CMBR) is electromagnetic radiation that is a remnant from an early stage of the universe, also known as "relic radiation". The CMB is faint cosmic background radiation filling all space. It is an important source of data on the early universe because it is the oldest electromagnetic radiation in the universe, dating to the epoch of recombination when the first atoms were formed. With a traditional optical telescope, the space between stars and galaxies (the background) is completely dark (see: Olbers' paradox). However, a sufficiently sensitive radio telescope shows a faint background brightness, or glow, almost uniform, that is not associated with any star, galaxy, or other object. This glow is strongest in the microwave region of the radio spectrum. The accidental discovery of the CMB in 1965 by American radio astronomers Arno Penzias and Robert Wilson was the culmination of work initiated in the 1940s, and earned ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
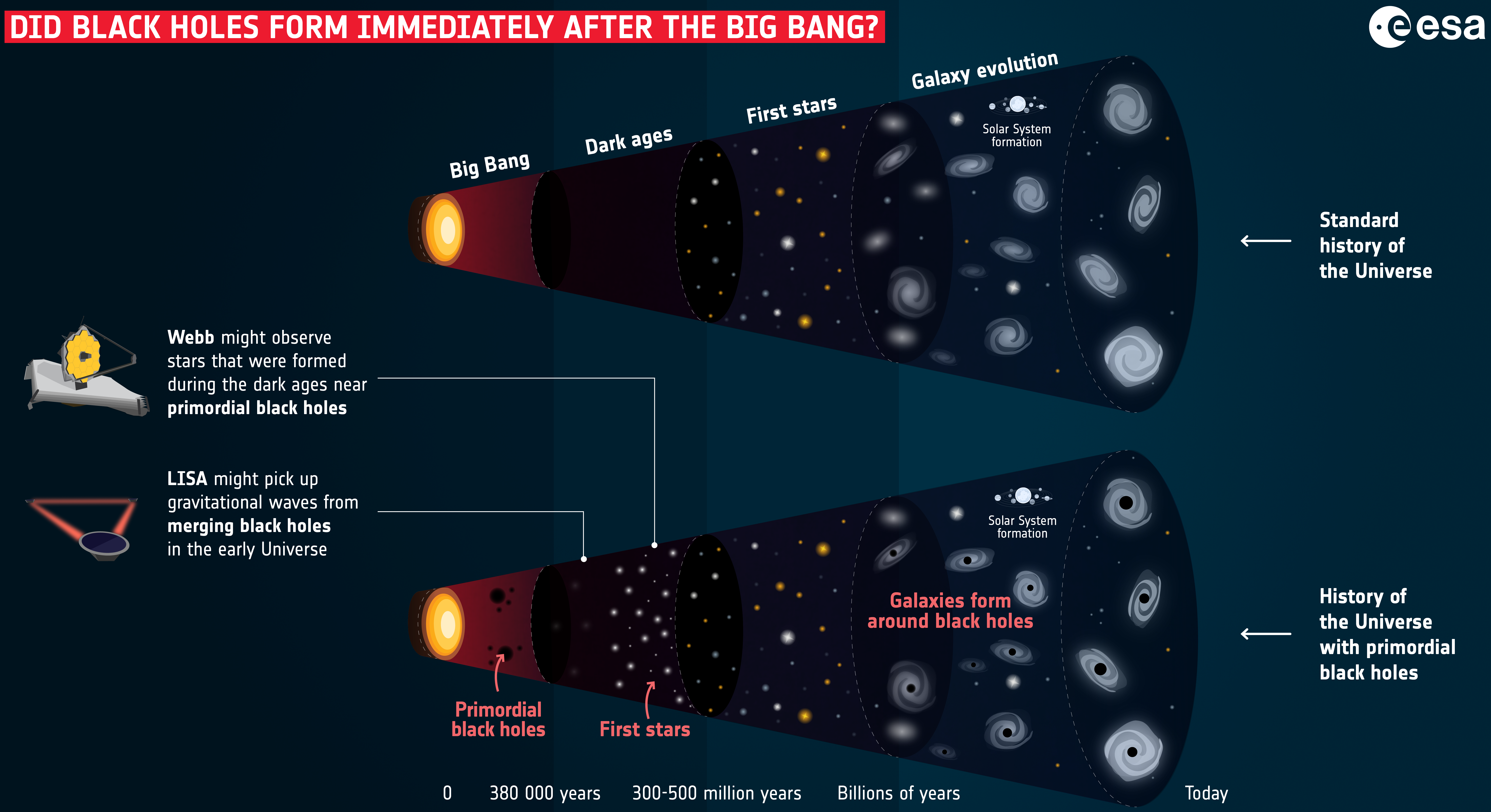
Primordial Black Hole
Primordial black holes (also abbreviated as PBH) are hypothetical black holes that formed soon after the Big Bang. Due to the extreme environment of the newly born universe, extremely dense pockets of sub-atomic matter had been tightly packed to the point of gravitational collapse, creating a primordial black hole that bypasses the density needed to make black holes today due to the densely packed, high-energy state present in the moments just after the Big Bang. Seeing as the creation of primordial black holes pre-date the creation of known stars, they can be formed with less mass than what are known as stellar black holes. Yakov Borisovich Zel'dovich and Igor Dmitriyevich Novikov in 1966 first proposed the existence of such black holes, while the first in-depth study was conducted by Stephen Hawking in 1971. However, their existence has not been proven and remains theoretical. Theoretical history Depending on the model, primordial black holes could have initial masses ra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Primordial Gravitational Wave
In Big Bang cosmology the cosmic microwave background (CMB, CMBR) is electromagnetic radiation that is a remnant from an early stage of the universe, also known as "relic radiation". The CMB is faint cosmic background radiation filling all space. It is an important source of data on the early universe because it is the oldest electromagnetic radiation in the universe, dating to the epoch of recombination when the first atoms were formed. With a traditional optical telescope, the space between stars and galaxies (the background) is completely dark (see: Olbers' paradox). However, a sufficiently sensitive radio telescope shows a faint background brightness, or glow, almost uniform, that is not associated with any star, galaxy, or other object. This glow is strongest in the microwave region of the radio spectrum. The accidental discovery of the CMB in 1965 by American radio astronomers Arno Penzias and Robert Wilson was the culmination of work initiated in the 1940s, and earned the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Press–Schechter Formalism
The Press–Schechter formalism is a mathematical model for predicting the number of objects (such as galaxies, galaxy clusters or dark matter halos) of a certain mass within a given volume of the Universe. It was described in an academic paper by William H. Press and Paul Schechter in 1974. Background In the context of cold dark matter cosmological models, perturbations on all scales are imprinted on the universe at very early times, for example by quantum fluctuations during an inflationary era. Later, as radiation redshifts away, these become mass perturbations, and they start to grow linearly. Only long after that, starting with small mass scales and advancing over time to larger mass scales, do the perturbations actually collapse to form (for example) galaxies or clusters of galaxies, in so-called hierarchical structure formation (see Physical cosmology Physical cosmology is a branch of cosmology concerned with the study of cosmological models. A cosmological model, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cosmic Microwave Background Spectral Distortions
CMB spectral distortions are tiny departures of the average cosmic microwave background (CMB) frequency spectrum from the predictions given by a perfect black body. They can be produced by a number of standard and non-standard processes occurring at the early stages of cosmic history, and therefore allow us to probe the standard picture of cosmology. Importantly, the CMB frequency spectrum and its distortions should not be confused with the CMB anisotropy power spectrum, which relates to spatial fluctuations of the CMB temperature in different directions of the sky. Overview The energy spectrum of the CMB is extremely close to that of a perfect blackbody with a temperature of 2.7255 K. This is expected because in the early Universe matter and radiation are in thermal equilibrium. However, at redshifts z<2\times10^6, several mechanisms, both standard and non-standard, can modify the CMB spectrum and introduce departures from a blackbody spectrum. These departures are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cosmological Perturbation Theory
In physical cosmology, cosmological perturbation theory is the theory by which the ''evolution of structure'' is understood in the Big Bang model. It uses general relativity to compute the gravitational forces causing small perturbations to grow and eventually seed the formation of stars, quasars, galaxies and clusters. It only applies to situations in which the universe is predominantly homogeneous, such as during cosmic inflation and large parts of the Big Bang. The universe is believed to still be homogeneous enough that the theory is a good approximation on the largest scales, but on smaller scales more involved techniques, such as N-body simulations, must be used. Because of the gauge invariance of general relativity, the correct formulation of cosmological perturbation theory is subtle. In particular, when describing an inhomogeneous spacetime there is often not a preferred coordinate choice. There are currently two distinct approaches to perturbation theory in classical gener ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Big Bang
The Big Bang event is a physical theory that describes how the universe expanded from an initial state of high density and temperature. Various cosmological models of the Big Bang explain the evolution of the observable universe from the earliest known periods through its subsequent large-scale form. These models offer a comprehensive explanation for a broad range of observed phenomena, including the abundance of light elements, the cosmic microwave background (CMB) radiation, and large-scale structure. The overall uniformity of the Universe, known as the flatness problem, is explained through cosmic inflation: a sudden and very rapid expansion of space during the earliest moments. However, physics currently lacks a widely accepted theory of quantum gravity that can successfully model the earliest conditions of the Big Bang. Crucially, these models are compatible with the Hubble–Lemaître law—the observation that the farther away a galaxy is, the faster it is mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cold Dark Matter
In cosmology and physics, cold dark matter (CDM) is a hypothetical type of dark matter. According to the current standard model of cosmology, Lambda-CDM model, approximately 27% of the universe is dark matter and 68% is dark energy, with only a small fraction being the ordinary baryonic matter that composes stars, planets, and living organisms. ''Cold'' refers to the fact that the dark matter moves slowly compared to the speed of light, while ''dark'' indicates that it interacts very weakly with ordinary matter and electromagnetic radiation. Proposed candidates for CDM include weakly interacting massive particles, primordial black holes, and axions. History The theory of cold dark matter was originally published in 1982 by James Peebles; while the warm dark matter picture was proposed independently at the same time by J. Richard Bond, Alex Szalay, and Michael Turner; and George Blumenthal, H. Pagels, and Joel Primack. A review article in 1984 by Blumenthal, Sandra Moore ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electron
The electron ( or ) is a subatomic particle with a negative one elementary electric charge. Electrons belong to the first generation of the lepton particle family, and are generally thought to be elementary particles because they have no known components or substructure. The electron's mass is approximately 1/1836 that of the proton. Quantum mechanical properties of the electron include an intrinsic angular momentum ( spin) of a half-integer value, expressed in units of the reduced Planck constant, . Being fermions, no two electrons can occupy the same quantum state, in accordance with the Pauli exclusion principle. Like all elementary particles, electrons exhibit properties of both particles and waves: They can collide with other particles and can be diffracted like light. The wave properties of electrons are easier to observe with experiments than those of other particles like neutrons and protons because electrons have a lower mass and hence a longer de Broglie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Photon
A photon () is an elementary particle that is a quantum of the electromagnetic field, including electromagnetic radiation such as light and radio waves, and the force carrier for the electromagnetic force. Photons are massless, so they always move at the speed of light in vacuum, (or about ). The photon belongs to the class of bosons. As with other elementary particles, photons are best explained by quantum mechanics and exhibit wave–particle duality, their behavior featuring properties of both waves and particles. The modern photon concept originated during the first two decades of the 20th century with the work of Albert Einstein, who built upon the research of Max Planck. While trying to explain how matter and electromagnetic radiation could be in thermal equilibrium with one another, Planck proposed that the energy stored within a material object should be regarded as composed of an integer number of discrete, equal-sized parts. To explain the photoelectr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Energy
In physics, energy (from Ancient Greek: ἐνέργεια, ''enérgeia'', “activity”) is the quantitative property that is transferred to a body or to a physical system, recognizable in the performance of work and in the form of heat and light. Energy is a conserved quantity—the law of conservation of energy states that energy can be converted in form, but not created or destroyed. The unit of measurement for energy in the International System of Units (SI) is the joule (J). Common forms of energy include the kinetic energy of a moving object, the potential energy stored by an object (for instance due to its position in a field), the elastic energy stored in a solid object, chemical energy associated with chemical reactions, the radiant energy carried by electromagnetic radiation, and the internal energy contained within a thermodynamic system. All living organisms constantly take in and release energy. Due to mass–energy equivalence, any object th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |