|
Primary Hyperoxaluria
Primary hyperoxaluria is a rare condition (autosomal recessive), resulting in increased excretion of oxalate (up to 600 mg a day from normal 50 mg a day), with oxalate stones being common. Signs and symptoms Primary hyperoxaluria is an autosomal recessive disease, meaning both copies of the gene contain the mutation. Both parents must have one copy of this mutated gene to pass it on to their child, but they do not typically show signs or symptoms of the disease. A single kidney stone in children or recurrent stones in adults is often the first warning sign of primary hyperoxaluria. Other symptoms range from recurrent urinary tract infections, severe abdominal pain or pain in the side, blood in the urine, to chronic kidney disease and kidney failure. The age of symptom onset, progression and severity can vary greatly from one person to another, even among members of the same family. Some individuals may have mild cases that go undiagnosed well into adulthood; others may ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Autosomal Recessive
In genetics, dominance is the phenomenon of one variant (allele) of a gene on a chromosome masking or overriding the effect of a different variant of the same gene on the other copy of the chromosome. The first variant is termed dominant and the second recessive. This state of having two different variants of the same gene on each chromosome is originally caused by a mutation in one of the genes, either new (''de novo'') or inherited. The terms autosomal dominant or autosomal recessive are used to describe gene variants on non-sex chromosomes ( autosomes) and their associated traits, while those on sex chromosomes (allosomes) are termed X-linked dominant, X-linked recessive or Y-linked; these have an inheritance and presentation pattern that depends on the sex of both the parent and the child (see Sex linkage). Since there is only one copy of the Y chromosome, Y-linked traits cannot be dominant or recessive. Additionally, there are other forms of dominance such as incomplete d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HOGA1
4-Hydroxy-2-oxoglutarate aldolase, mitochondrial (HOGA1) also known as dihydrodipicolinate synthase-like (DHDPSL) is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the HOGA1 gene. The protein is one of the enzymes (4-hydroxy-2-oxoglutarate aldolase) involved in metabolism of hydroxyproline to glyoxylate. The enzyme overactivity can form excessive glyoxylate from hydroxyproline. Glyoxylate is catabolised to oxalate, resulting in excess excretion of oxalate in urine, predisposing to oxalate stone; a condition known as primary hyperoxaluria type III. References {{gene-10-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
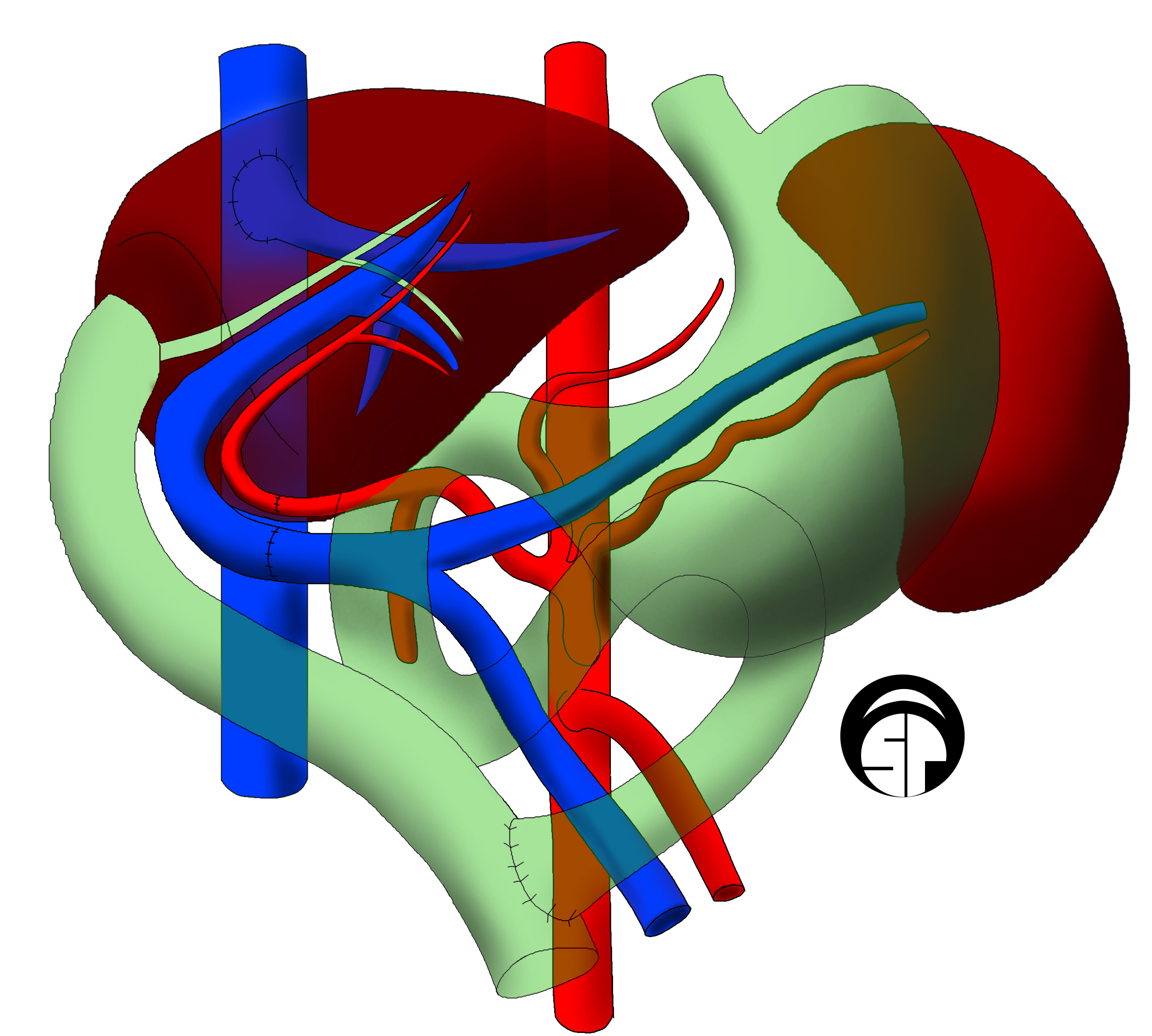
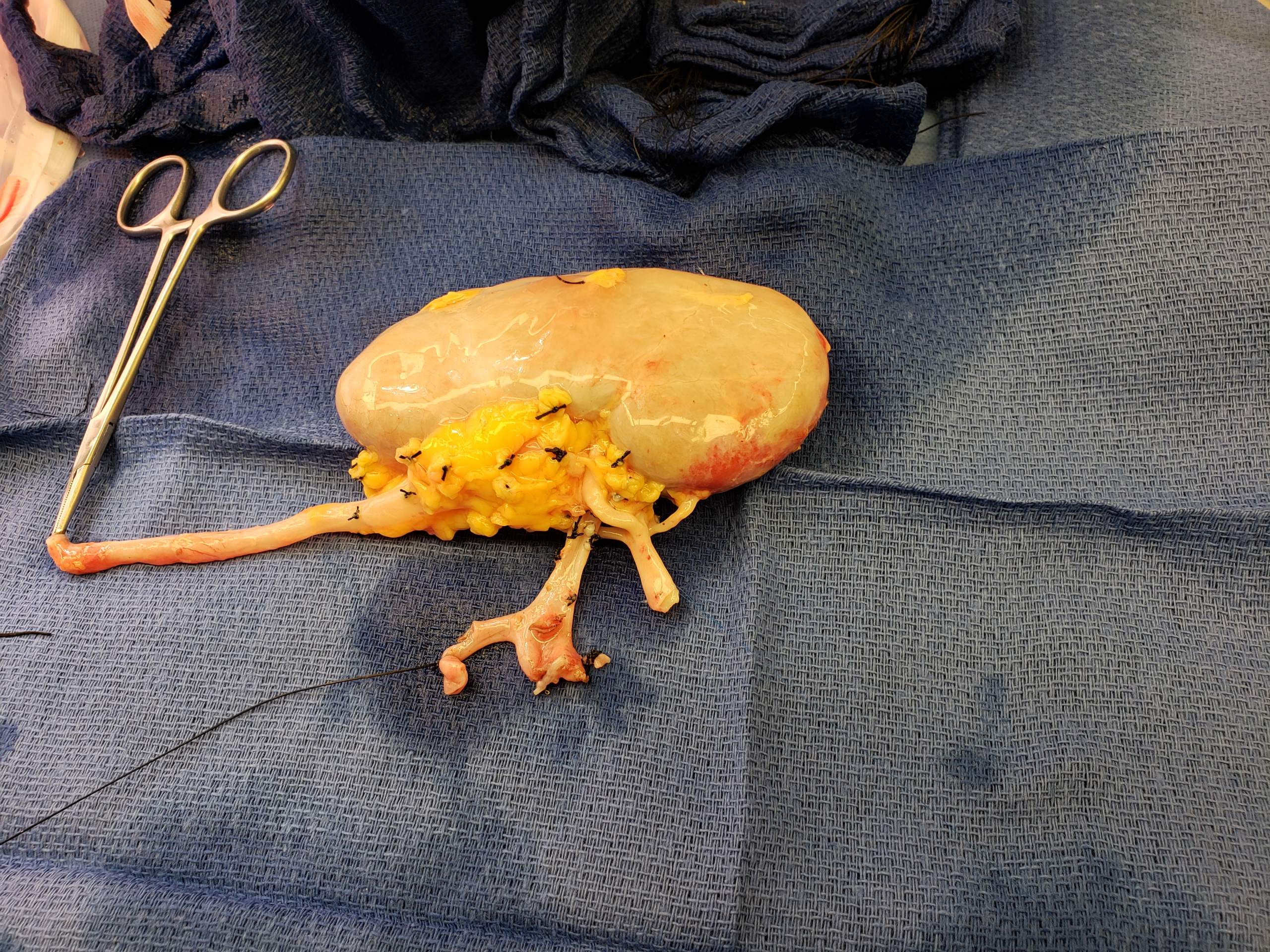
Liver Transplantation
Liver transplantation or hepatic transplantation is the replacement of a diseased liver with the healthy liver from another person (allograft). Liver transplantation is a treatment option for end-stage liver disease and acute liver failure, although availability of donor organs is a major limitation. The most common technique is orthotopic transplantation, in which the native liver is removed and replaced by the donor organ in the same anatomic position as the original liver. The surgical procedure is complex, requiring careful harvest of the donor organ and meticulous implantation into the recipient. Liver transplantation is highly regulated, and only performed at designated transplant medical centers by highly trained transplant physicians and supporting medical team. The duration of the surgery ranges from 4 to 18 hours depending on outcome. Favorable outcomes require careful screening for eligible recipient, as well as a well-calibrated live or cadaveric donor match. Medic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Renal Transplant
Kidney transplant or renal transplant is the organ transplant of a kidney into a patient with end-stage kidney disease (ESRD). Kidney transplant is typically classified as deceased-donor (formerly known as cadaveric) or living-donor transplantation depending on the source of the donor organ. Living-donor kidney transplants are further characterized as genetically related (living-related) or non-related (living-unrelated) transplants, depending on whether a biological relationship exists between the donor and recipient. Before receiving a kidney transplant, a person with ESRD must undergo a thorough medical evaluation to make sure that they are healthy enough to undergo transplant surgery. If they are deemed a good candidate, they can be placed on a waiting list to receive a kidney from a deceased donor. Once they are placed on the waiting list, they can receive a new kidney very quickly, or they may have to wait many years; in the United States, the average waiting time is three t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
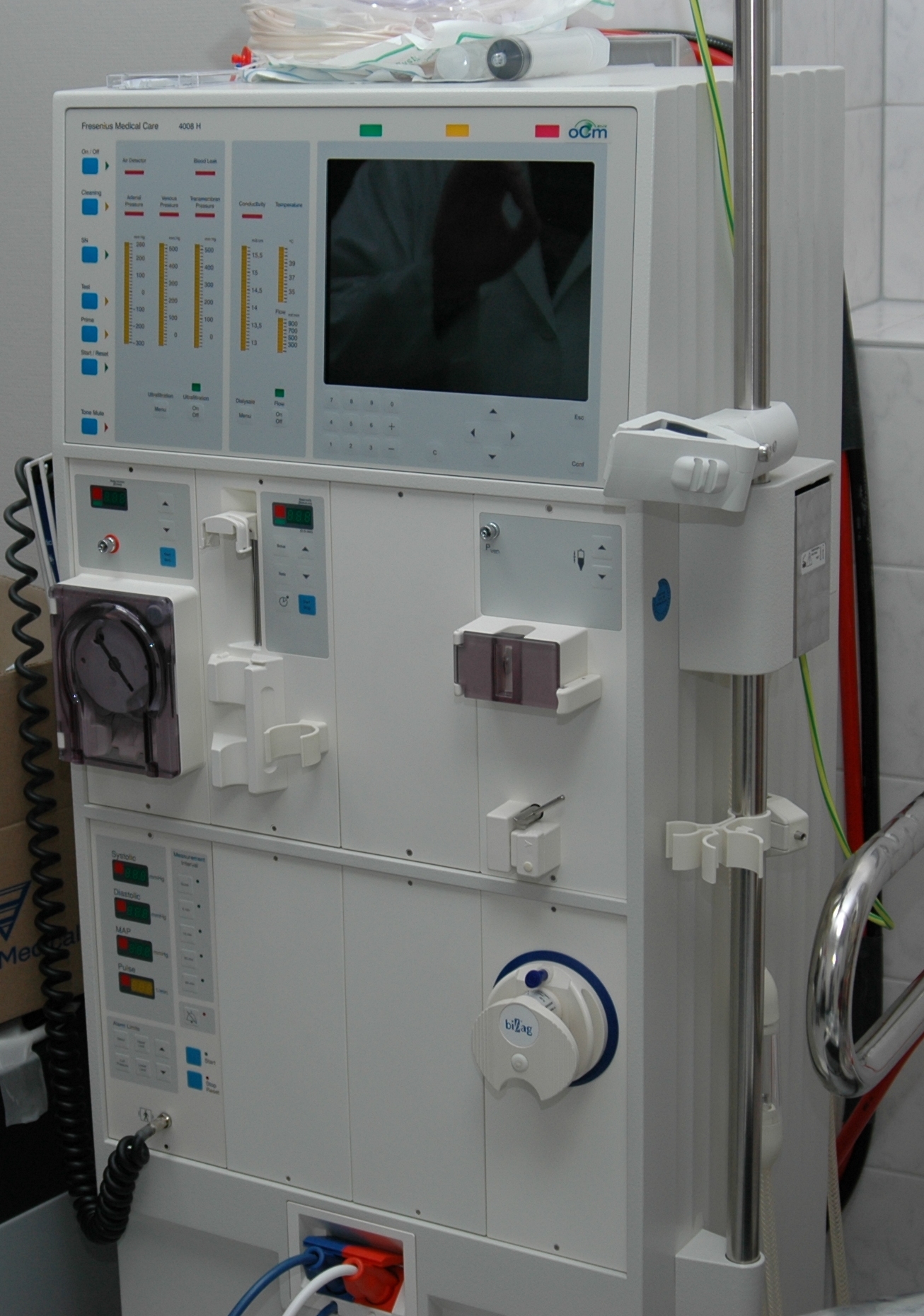
Kidney Dialysis
Kidney dialysis (from Greek , , 'dissolution'; from , , 'through', and , , 'loosening or splitting') is the process of removing excess water, solutes, and toxins from the blood in people whose kidneys can no longer perform these functions naturally. This is referred to as renal replacement therapy. The first successful dialysis was performed in 1943. Dialysis may need to be initiated when there is a sudden rapid loss of kidney function, known as acute kidney injury (previously called acute renal failure), or when a gradual decline in kidney function, chronic kidney disease, reaches stage 5. Stage 5 chronic renal failure is reached when the glomerular filtration rate is 10–15% of normal, creatinine clearance is less than 10 mL per minute and uremia is present. Dialysis is used as a temporary measure in either acute kidney injury or in those awaiting kidney transplant and as a permanent measure in those for whom a transplant is not indicated or not possible.Pendse S, Singh A, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Food And Drug Administration
The United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA or US FDA) is a List of United States federal agencies, federal agency of the United States Department of Health and Human Services, Department of Health and Human Services. The FDA is responsible for protecting and promoting public health through the control and supervision of food safety, tobacco products, caffeine products, dietary supplements, Prescription drug, prescription and Over-the-counter drug, over-the-counter pharmaceutical drugs (medications), vaccines, biopharmaceuticals, blood transfusions, medical devices, electromagnetic radiation emitting devices (ERED), cosmetics, Animal feed, animal foods & feed and Veterinary medicine, veterinary products. The FDA's primary focus is enforcement of the Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act (FD&C), but the agency also enforces other laws, notably Section 361 of the Public Health Service Act, as well as associated regulations. Much of this regulatory-enforcement work is not d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
European Medicines Agency
The European Medicines Agency (EMA) is an agency of the European Union (EU) in charge of the evaluation and supervision of medicinal products. Prior to 2004, it was known as the European Agency for the Evaluation of Medicinal Products or European Medicines Evaluation Agency (EMEA).Set up by EC Regulation No. 2309/93 as the European Agency for the Evaluation of Medicinal Products, and renamed by EC Regulation No. 726/2004 to the European Medicines Agency, it had the acronym EMEA until December 2009. The European Medicines Agency does not call itself EMA either – it has no official acronym but may reconsider if EMA becomes commonly accepted (secommunication on new visual identity an). The EMA was set up in 1995, with funding from the European Union and the pharmaceutical industry, as well as indirect subsidy from member states, its stated intention to harmonise (but not replace) the work of existing national medicine regulatory bodies. The hope was that this plan would not onl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Medicines And Healthcare Products Regulatory Agency
The Medicines and Healthcare products Regulatory Agency (MHRA) is an executive agency of the Department of Health and Social Care in the United Kingdom which is responsible for ensuring that medicines and medical devices work and are acceptably safe. The MHRA was formed in 2003 with the merger of the Medicines Control Agency (MCA) and the Medical Devices Agency (MDA). In April 2013, it merged with the National Institute for Biological Standards and Control (NIBSC) and was rebranded, with the MHRA identity being used solely for the regulatory centre within the group. The agency employs more than 1,200 people in London, York and South Mimms, Hertfordshire. Structure The MHRA is divided into three main centres: * MHRA Regulatory – the regulator for the pharmaceutical and medical devices industries * Clinical Practice Research Datalink – licences anonymised health care data to pharmaceutical companies, academics and other regulators for research * National Institute for Biolog ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
RNA Interference
RNA interference (RNAi) is a biological process in which RNA molecules are involved in sequence-specific suppression of gene expression by double-stranded RNA, through translational or transcriptional repression. Historically, RNAi was known by other names, including ''co-suppression'', ''post-transcriptional gene silencing'' (PTGS), and ''quelling''. The detailed study of each of these seemingly different processes elucidated that the identity of these phenomena were all actually RNAi. Andrew Fire and Craig C. Mello shared the 2006 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine for their work on RNAi in the nematode worm '' Caenorhabditis elegans'', which they published in 1998. Since the discovery of RNAi and its regulatory potentials, it has become evident that RNAi has immense potential in suppression of desired genes. RNAi is now known as precise, efficient, stable and better than antisense therapy for gene suppression. Antisense RNA produced intracellularly by an expression vector m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lumasiran
Lumasiran, sold under the brand name Oxlumo, is a medication for the treatment of primary hyperoxaluria type 1 (PH1). The most common side effects include injection site reactions and abdominal pain. Lumasiran is a double-stranded small interfering ribonucleic acid (siRNA) that reduces levels of glycolate oxidase (GO) enzyme by targeting the HAO1 messenger ribonucleic acid (mRNA) in hepatocytes through RNA interference. Decreased GO enzyme levels reduce the amount of available glyoxylate, a substrate for oxalate production. This results in reduction of urinary and plasma oxalate levels, the underlying cause of disease manifestations in people with PH1. As the GO enzyme is upstream of the deficient alanine:glyoxylate aminotransferase (AGT) enzyme that causes PH1, the mechanism of action of lumasiran is independent of the underlying AGXT gene mutation. Lumasiran was approved for medical use in the European Union and in the United States in November 2020. The U.S. Food and Dru ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pyridoxine
Pyridoxine, is a form of vitamin B6 found commonly in food and used as a dietary supplement. As a supplement it is used to treat and prevent pyridoxine deficiency, sideroblastic anaemia, pyridoxine-dependent epilepsy, certain metabolic disorders, side effects or complications of isoniazid use, and certain types of mushroom poisoning. It is used by mouth or by injection. It is usually well tolerated. Occasionally side effects include headache, numbness, and sleepiness. Normal doses are safe during pregnancy and breastfeeding. Pyridoxine is in the vitamin B family of vitamins. It is required by the body to metabolise amino acids, carbohydrates, and lipids. Sources in the diet include fruit, vegetables, and grain. Medical uses As a treatment (oral or injection), it is used to treat or prevent pyridoxine deficiency, sideroblastic anaemia, pyridoxine-dependent epilepsy, certain metabolic disorders, side effects of isoniazid treatment and certain types of mushroom poisoning. Iso ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
OMIM
Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man (OMIM) is a continuously updated catalog of human genes and genetic disorders and traits, with a particular focus on the gene-phenotype relationship. , approximately 9,000 of the over 25,000 entries in OMIM represented phenotypes; the rest represented genes, many of which were related to known phenotypes. Versions and history OMIM is the online continuation of Dr. Victor A. McKusick's ''Mendelian Inheritance in Man'' (MIM), which was published in 12 editions between 1966 and 1998.McKusick, V. A. ''Mendelian Inheritance in Man. Catalogs of Autosomal Dominant, Autosomal Recessive and X-Linked Phenotypes.'' Baltimore, MD: Johns Hopkins University Press, 1st ed, 1996; 2nd ed, 1969; 3rd ed, 1971; 4th ed, 1975; 5th ed, 1978; 6th ed, 1983; 7th ed, 1986; 8th ed, 1988; 9th ed, 1990; 10th ed, 1992. Nearly all of the 1,486 entries in the first edition of MIM discussed phenotypes. MIM/OMIM is produced and curated at the Johns Hopkins School of Medicine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)