|
Primary Headache Disorder
The International Classification of Headache Disorders (ICHD) is a detailed hierarchical classification of all headache-related disorders published by the International Headache Society. It is considered the official classification of headaches by the World Health Organization, and, in 1992, was incorporated into the 10th edition of their ''International Classification of Diseases'' (ICD-10). Each class of headache contains explicit diagnostic criteria—meaning that the criteria include quantities rather than vague terms like ''several'' or ''usually''—that are based on clinical and laboratory observations. The ICHD was first published in 1988 (now known as the ICHD-1). A second version, the ICHD-2, was published in 2004. The most current version, ICHD-3, was published in 2018. /www.ichd-3.org/ ''Website The International Classification of Headache Disorders 3rd edition'' Retrieved 15. July 2018. Hierarchy Primary headaches ICHD 1, ICD10 G43: Migraine :Migraine witho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hierarchical
A hierarchy (from Greek: , from , 'president of sacred rites') is an arrangement of items (objects, names, values, categories, etc.) that are represented as being "above", "below", or "at the same level as" one another. Hierarchy is an important concept in a wide variety of fields, such as architecture, philosophy, design, mathematics, computer science, organizational theory, systems theory, systematic biology, and the social sciences (especially political philosophy). A hierarchy can link entities either directly or indirectly, and either vertically or diagonally. The only direct links in a hierarchy, insofar as they are hierarchical, are to one's immediate superior or to one of one's subordinates, although a system that is largely hierarchical can also incorporate alternative hierarchies. Hierarchical links can extend "vertically" upwards or downwards via multiple links in the same direction, following a path. All parts of the hierarchy that are not linked vertically to one ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Retinal Migraine
Retinal migraine is a retinal disease often accompanied by migraine headache and typically affects only one eye. It is caused by ischaemia or vascular spasm in or behind the affected eye. The terms "retinal migraine" and "ocular migraine" are often confused with " visual migraine", which is a far-more-common symptom of vision loss, resulting from the aura phase of migraine with aura. The aura phase of migraine can occur with or without a headache. Ocular or retinal migraines happen in the eye, so only affect the vision in that eye, while visual migraines occur in the brain, so affect the vision in both eyes together. Visual migraines result from cortical spreading depression and are also commonly termed scintillating scotoma. Symptoms Retinal migraine is associated with transient monocular visual loss (scotoma) in one eye lasting less than one hour. During some episodes, the visual loss may occur with no headache and at other times throbbing headache on the same side of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intracranial Hemorrhage
Intracranial hemorrhage (ICH), also known as intracranial bleed, is hemorrhage, bleeding internal bleeding, within the Human skull, skull. Subtypes are intracerebral bleeds (intraventricular bleeds and intraparenchymal bleeds), subarachnoid bleeds, epidural bleeds, and subdural bleeds. More often than not it ends in a death, lethal outcome. Intracerebral bleeding affects 2.5 per 10,000 people each year. Signs and symptoms Intracranial hemorrhage is a serious medical emergency because the buildup of blood within the skull can lead to increases in intracranial pressure, which can crush delicate brain tissue or limit its blood supply. Severe increases in intracranial pressure (ICP) can cause brain herniation, in which parts of the brain are squeezed past structures in the skull. Causes Trauma is the most common cause of intracranial hemorrhage. It can cause epidural hemorrhage, subdural hemorrhage, and subarachnoid hemorrhage. Other condition such as hemorrhagic parenchymal con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
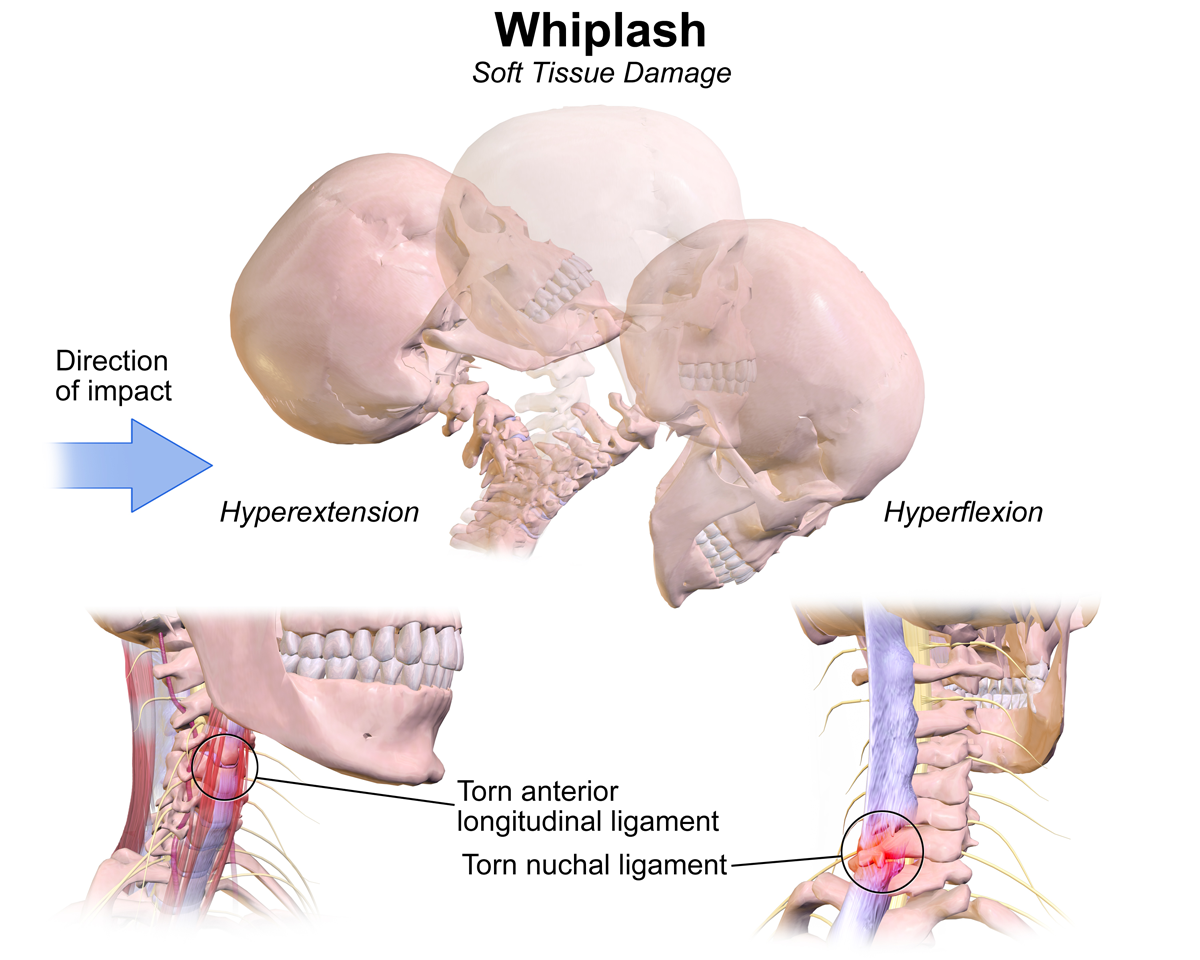
Whiplash Injury
Whiplash is a non-medical term describing a range of injuries to the neck caused by or related to a sudden distortion of the neck associated with extension, although the exact injury mechanisms remain unknown. The term "whiplash" is a colloquialism. "Cervical acceleration–deceleration" (CAD) describes the mechanism of the injury, while the term "whiplash associated disorders" (WAD) describes the subsequent injuries and symptoms. Whiplash is commonly associated with motor vehicle accidents, usually when the vehicle has been hit in the rear; however, the injury can be sustained in many other ways, including headbanging, bungee jumping and falls. It is one of the most frequently claimed injuries on vehicle insurance policies in certain countries; for example, in the United Kingdom 430,000 people made an insurance claim for whiplash in 2007, accounting for 14% of every driver's premium. In the United States, it is estimated that more than 65% of all bodily injury claims are w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Head Injury
A head injury is any injury that results in trauma to the skull or brain. The terms ''traumatic brain injury'' and ''head injury'' are often used interchangeably in the medical literature. Because head injuries cover such a broad scope of injuries, there are many causes—including accidents, falls, physical assault, or traffic accidents—that can cause head injuries. The number of new cases is 1.7 million in the United States each year, with about 3% of these incidents leading to death. Adults have head injuries more frequently than any age group resulting from falls, motor vehicle crashes, colliding or being struck by an object, or assaults. Children, however, may experience head injuries from accidental falls or intentional causes (such as being struck or shaken) leading to hospitalization. Acquired brain injury (ABI) is a term used to differentiate brain injuries occurring after birth from injury, from a genetic disorder, or from a congenital disorder. Unlike a broken bo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New Daily Persistent Headache
New daily persistent headache (NDPH) is a primary headache syndrome which can mimic chronic migraine and chronic tension-type headache. The headache is daily and unremitting from very soon after onset (within 3 days at most), usually in a person who does not have a history of a primary headache disorder. The pain can be intermittent, but lasts more than 3 months. Headache onset is abrupt and people often remember the date, circumstance and, occasionally, the time of headache onset. One retrospective study stated that over 80% of patients could state the exact date their headache began. The cause of NDPH is unknown, and it may have more than one etiology. NDPH onset is commonly associated with an infection or flu-like illness, stressful life event, minor head trauma, and extra cranial surgery. Infection or flu-like illness and stressful life event are most often cited. The pathophysiology of NDPH is poorly understood. The syndrome is difficult to treat and may persist for years. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hemicrania Continua
Hemicrania continua (HC) is a persistent unilateral headache that responds to indomethacin. It is usually unremitting, but rare cases of remission have been documented. Hemicrania continua is considered a primary headache disorder, meaning that it is not caused by another condition. Symptoms In hemicrania continua, basal pain is a dull aching pressure similar to that of TTHs that occurs nearly always on the same side of the head and face. Pain ranges from mild to severe and is characterized by fluctuations where it increases in intensity up to three to five times per 24-hour cycle. The range of duration of exacerbations has no boundaries and varies from a few seconds to up to two weeks. While attacks tend to be more frequent at night, no circadian periodicity such as in cluster headache can be observed. The nature of pain changes during the exacerbation phase, becoming more piercing, throbbing, and intense, generally paired with other highly debilitating symptoms such as nausea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thunderclap Headache
A thunderclap headache is a headache that is severe and has a sudden onset. It is defined as a severe headache that takes seconds to minutes to reach maximum intensity. Although approximately 75% are attributed to "primary" headaches—headache disorder, non-specific headache, idiopathic thunderclap headache, or uncertain headache disorder—the remainder are secondary to other causes, which can include some extremely dangerous acute conditions, as well as infections and other conditions. Usually, further investigations are performed to identify the underlying cause. Signs and symptoms A headache is called "thunderclap headache" if it is severe in character and reaches maximum severity within seconds to minutes of onset. In many cases, there are no other abnormalities, but the various causes of thunderclap headaches may lead to a number of neurological symptoms. Causes Approximately 75% are attributed to "primary" headaches: headache disorder, non-specific headache, idiopathic th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hypnic Headache
Hypnic headaches are benign primary headaches that affect the elderly, with an average age of onset at 63 ± 11 years. They are moderate, throbbing, bilateral or unilateral headaches that wake the sufferer from sleep once or multiple times a night. They typically begin a few hours after sleep begins and can last from 15–180 min. There is normally no nausea, photophobia, phonophobia or autonomic symptoms associated with the headache. They commonly occur at the same time every night possibly linking the headaches with circadian rhythm, but polysomnography has recently revealed that the onset of hypnic headaches may be associated with REM sleep. Diagnosis For diagnosis of hypnic headache syndrome, headaches should occur at least 15 times per month for at least one month. Included in the differential diagnosis of a new onset nighttime headaches in the elderly is drug withdrawal, temporal arteritis, Sleep apnea, oxygen desaturation, Pheochromocytoma, intracranial causes, prim ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Headache Associated With Sexual Activity
Sexual headache is a type of headache that occurs in the skull and neck during sexual activity, including masturbation or orgasm. These headaches are usually benign, but occasionally are caused by intracranial hemorrhage and cerebral infarction, especially if the pain is sudden and severe. They may be caused by general exertion, sexual excitement, or contraction of the neck and facial muscles. Most cases can be successfully treated with medication. Signs and symptoms According to the third edition of the International Classification of Headache Disorders (ICHD), which terms this condition ''primary headache associated with sexual activity'', it normally begins as a dull headache that increases with sexual excitement, and becomes intense at orgasm, which is called sexual benign headache. For some patients, the headache begins suddenly, often at orgasm, which is called orgasm headache. In two thirds of cases, it is bilateral, and unilateral in the rest. The pain lasts from one ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Short-lasting Unilateral Neuralgiform Headache With Conjunctival Injection And Tearing
Short-lasting unilateral neuralgiform headache with conjunctival injection and tearing (SUNCT syndrome) is a rare headache disorder that belongs to the group of headaches called trigeminal autonomic cephalalgia (TACs). Symptoms include excruciating burning, stabbing, or electrical headaches mainly near the eye and typically these sensations are only on one side of the body. The headache attacks are typically accompanied by cranial autonomic signs that are unique to SUNCT. Each attack can last from five seconds to six minutes and may occur up to 200 times daily. TACs are caused by activation of the autonomic nervous system of the trigeminal nerve in the face. As of 2015 about 50 cases have been described in the medical literature. Onset of the symptoms usually come later in life, at an average age of about 50. Although the majority of patients are men over the age of 50, it is not uncommon to find SUNCT present among other age groups, including children and infants. Signs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paroxysmal Hemicrania
Chronic paroxysmal hemicrania (CPH) is a severe debilitating unilateral headache usually affecting the area around the eye. It normally consists of multiple severe, yet short, headache attacks affecting only one side of the cranium. It is more commonly diagnosed in women than in men, but, unlike a migraine, has no neurological symptoms associated with it. CPH headaches are treated through the use of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, with indomethacin found to be usually effective in eliminating symptoms. Paroxysmal hemicrania is classified by the characteristic (high) frequency and (short) duration of attacks experienced by patients that is somewhat similar to cluster headaches, despite some important differences explained below. Episodic paroxysmal hemicrania attacks occur at least twice a year and last anywhere from seven days to a year with pain free periods of a month or longer separating them. Chronic paroxysmal hemicrania attacks occur over the course of more than a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |