|
Presentation Complex
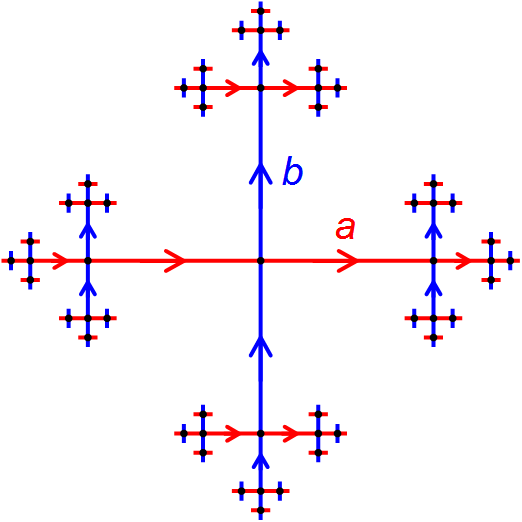
In geometric group theory, a presentation complex is a 2-dimensional cell complex associated to any presentation of a group, presentation of a group (mathematics), group ''G''. The complex has a single vertex, and one loop at the vertex for each generating set of a group, generator of ''G''. There is one 2-cell for each relation in the presentation, with the boundary of the 2-cell attached along the appropriate word (group theory), word. Properties * The fundamental group of the presentation complex is the group ''G'' itself. * The universal cover of the presentation complex is a Cayley complex for ''G'', whose 1-skeleton is the Cayley graph of ''G''. * Any presentation complex for ''G'' is the 2-skeleton of an Eilenberg–MacLane space K(G,1). Examples Let G= \Z^2 be the two-dimensional integer lattice (group), lattice, with presentation : G=\langle x,y, xyx^y^\rangle. Then the presentation complex for ''G'' is a torus, obtained by gluing the opposite sides of a square, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geometric Group Theory
Geometric group theory is an area in mathematics devoted to the study of finitely generated groups via exploring the connections between algebraic properties of such group (mathematics), groups and topology, topological and geometry, geometric properties of spaces on which these groups Group action (mathematics), act (that is, when the groups in question are realized as geometric symmetries or continuous transformations of some spaces). Another important idea in geometric group theory is to consider finitely generated groups themselves as geometric objects. This is usually done by studying the Cayley graphs of groups, which, in addition to the graph (discrete mathematics), graph structure, are endowed with the structure of a metric space, given by the so-called word metric. Geometric group theory, as a distinct area, is relatively new, and became a clearly identifiable branch of mathematics in the late 1980s and early 1990s. Geometric group theory closely interacts with low-dimens ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Infinite Dihedral Group
In mathematics, the infinite dihedral group Dih∞ is an infinite group with properties analogous to those of the finite dihedral groups. In two-dimensional geometry, the infinite dihedral group represents the frieze group symmetry, ''p1m1'', seen as an infinite set of parallel reflections along an axis. Definition Every dihedral group is generated by a rotation ''r'' and a reflection; if the rotation is a rational multiple of a full rotation, then there is some integer ''n'' such that ''rn'' is the identity, and we have a finite dihedral group of order 2''n''. If the rotation is ''not'' a rational multiple of a full rotation, then there is no such ''n'' and the resulting group has infinitely many elements and is called Dih∞. It has presentations :\langle r, s \mid s^2 = 1, srs = r^ \rangle \,\! :\langle x, y \mid x^2 = y^2 = 1 \rangle \,\! and is isomorphic to a semidirect product of Z and Z/2, and to the free product Z/2 * Z/2. It is the automorphism group of the graph con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ronald Brown (mathematician)
Ronald Brown is an English mathematician. Emeritus Professor in the School of Computer Science at Bangor University, he has authored many books and more than 160 journal articles. Education and career Born on 4 January 1935 in London, Brown attended Oxford University, obtaining a B.A. in 1956 and a D.Phil. in 1962. Brown began his teaching career during his doctorate work, serving as an assistant lecturer at the University of Liverpool before assuming the position of Lecturer. In 1964, he took a position at the University of Hull, serving first as a Senior Lecturer and then as a Reader before becoming a Professor of pure mathematics at Bangor University, then a part of the University of Wales, in 1970. Brown served as Professor of Pure Mathematics for 30 years; he also served during the 1983–84 term as a Professor for one month at Louis Pasteur University in Strasbourg. In 1999, Brown took a half-time research professorship until he became Professor Emeritus in 2001. He was ele ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Springer Science+Business Media
Springer Science+Business Media, commonly known as Springer, is a German multinational publishing company of books, e-books and peer-reviewed journals in science, humanities, technical and medical (STM) publishing. Originally founded in 1842 in Berlin, it expanded internationally in the 1960s, and through mergers in the 1990s and a sale to venture capitalists it fused with Wolters Kluwer and eventually became part of Springer Nature in 2015. Springer has major offices in Berlin, Heidelberg, Dordrecht, and New York City. History Julius Springer founded Springer-Verlag in Berlin in 1842 and his son Ferdinand Springer grew it from a small firm of 4 employees into Germany's then second largest academic publisher with 65 staff in 1872.Chronology ". Springer Science+Business Media. In 1964, Springer expanded its business internationally, o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ergebnisse Der Mathematik Und Ihrer Grenzgebiete
''Ergebnisse der Mathematik und ihrer Grenzgebiete''/''A Series of Modern Surveys in Mathematics'' is a series of scholarly monographs published by Springer Science+Business Media. The title literally means "Results in mathematics and related areas". Most of the books were published in German or English, but there were a few in French and Italian. There have been several sequences, or ''Folge'': the original series, neue Folge, and 3.Folge. Some of the most significant mathematical monographs of 20th century appeared in this series. Original series The series started in 1932 with publication of ''Knotentheorie'' by Kurt Reidemeister as "Band 1" (English: volume 1). There seems to have been double numeration in this sequence. Neue Folge This sequence started in 1950 with the publication of ''Transfinite Zahlen'' by Heinz Bachmann. The volumes are consecutively numbered, designated as either "Band" or "Heft". A total of 100 volumes was published, often in multiple editions, but pre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paul E
Paul may refer to: *Paul (given name), a given name (includes a list of people with that name) *Paul (surname), a list of people People Christianity *Paul the Apostle (AD c.5–c.64/65), also known as Saul of Tarsus or Saint Paul, early Christian missionary and writer *Pope Paul (other), multiple Popes of the Roman Catholic Church *Saint Paul (other), multiple other people and locations named "Saint Paul" Roman and Byzantine empire *Lucius Aemilius Paullus Macedonicus (c. 229 BC – 160 BC), Roman general *Julius Paulus Prudentissimus (), Roman jurist *Paulus Catena (died 362), Roman notary *Paulus Alexandrinus (4th century), Hellenistic astrologer *Paul of Aegina or Paulus Aegineta (625–690), Greek surgeon Royals *Paul I of Russia (1754–1801), Tsar of Russia *Paul of Greece (1901–1964), King of Greece Other people *Paul the Deacon or Paulus Diaconus (c. 720 – c. 799), Italian Benedictine monk *Paul (father of Maurice), the father of Maurice, Byzan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roger Lyndon
Roger Conant Lyndon (December 18, 1917 – June 8, 1988) was an American mathematician, for many years a professor at the University of Michigan.. He is known for Lyndon words, the Curtis–Hedlund–Lyndon theorem, Craig–Lyndon interpolation and the Lyndon–Hochschild–Serre spectral sequence. Biography Lyndon was born on December 18, 1917, in Calais, Maine, the son of a Unitarian minister. His mother died when he was two years old, after which he and his father moved several times to towns in Massachusetts and New York. He did his undergraduate studies at Harvard University, originally intending to study literature but eventually settling on mathematics, and graduated in 1939. He took a job as a banker, but soon afterwards returned to graduate school at Harvard, earning a master's degree in 1941. After a brief teaching stint at the Georgia Institute of Technology, he returned to Harvard for the third time in 1942 and while there taught navigation as part of the V-12 Navy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cambridge University Press
Cambridge University Press is the university press of the University of Cambridge. Granted letters patent by Henry VIII of England, King Henry VIII in 1534, it is the oldest university press A university press is an academic publishing house specializing in monographs and scholarly journals. Most are nonprofit organizations and an integral component of a large research university. They publish work that has been reviewed by schola ... in the world. It is also the King's Printer. Cambridge University Press is a department of the University of Cambridge and is both an academic and educational publisher. It became part of Cambridge University Press & Assessment, following a merger with Cambridge Assessment in 2021. With a global sales presence, publishing hubs, and offices in more than 40 Country, countries, it publishes over 50,000 titles by authors from over 100 countries. Its publishing includes more than 380 academic journals, monographs, reference works, school and uni ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CW Complex
A CW complex (also called cellular complex or cell complex) is a kind of a topological space that is particularly important in algebraic topology. It was introduced by J. H. C. Whitehead (open access) to meet the needs of homotopy theory. This class of spaces is broader and has some better categorical properties than simplicial complexes, but still retains a combinatorial nature that allows for computation (often with a much smaller complex). The ''C'' stands for "closure-finite", and the ''W'' for "weak" topology. Definition CW complex A CW complex is constructed by taking the union of a sequence of topological spaces\emptyset = X_ \subset X_0 \subset X_1 \subset \cdotssuch that each X_k is obtained from X_ by gluing copies of k-cells (e^k_\alpha)_\alpha, each homeomorphic to D^k, to X_ by continuous gluing maps g^k_\alpha: \partial e^k_\alpha \to X_. The maps are also called attaching maps. Each X_k is called the k-skeleton of the complex. The topology of X = \cup_ X_ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Projective Plane
In mathematics, a projective plane is a geometric structure that extends the concept of a plane. In the ordinary Euclidean plane, two lines typically intersect in a single point, but there are some pairs of lines (namely, parallel lines) that do not intersect. A projective plane can be thought of as an ordinary plane equipped with additional "points at infinity" where parallel lines intersect. Thus ''any'' two distinct lines in a projective plane intersect at exactly one point. Renaissance artists, in developing the techniques of drawing in perspective, laid the groundwork for this mathematical topic. The archetypical example is the real projective plane, also known as the extended Euclidean plane. This example, in slightly different guises, is important in algebraic geometry, topology and projective geometry where it may be denoted variously by , RP2, or P2(R), among other notations. There are many other projective planes, both infinite, such as the complex projective plane, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wedge Sum
In topology, the wedge sum is a "one-point union" of a family of topological spaces. Specifically, if ''X'' and ''Y'' are pointed spaces (i.e. topological spaces with distinguished basepoints x_0 and y_0) the wedge sum of ''X'' and ''Y'' is the quotient space of the disjoint union of ''X'' and ''Y'' by the identification x_0 \sim y_0: X \vee Y = (X \amalg Y)\;/, where \,\sim\, is the equivalence closure of the relation \left\. More generally, suppose \left(X_i\right)_ is a indexed family of pointed spaces with basepoints \left(p_i\right)_. The wedge sum of the family is given by: \bigvee_ X_i = \coprod_ X_i\;/, where \,\sim\, is the equivalence closure of the relation \left\. In other words, the wedge sum is the joining of several spaces at a single point. This definition is sensitive to the choice of the basepoints \left(p_i\right)_, unless the spaces \left(X_i\right)_ are homogeneous. The wedge sum is again a pointed space, and the binary operation is associative and commuta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plane (mathematics)
In mathematics, a plane is a Euclidean space, Euclidean (flatness (mathematics), flat), two-dimensional surface (mathematics), surface that extends indefinitely. A plane is the two-dimensional analogue of a point (geometry), point (zero dimensions), a line (geometry), line (one dimension) and three-dimensional space. Planes can arise as Euclidean subspace, subspaces of some higher-dimensional space, as with one of a room's walls, infinitely extended, or they may enjoy an independent existence in their own right, as in the setting of two-dimensional Euclidean geometry. Sometimes the word ''plane'' is used more generally to describe a two-dimensional surface (mathematics), surface, for example the hyperbolic plane and elliptic plane. When working exclusively in two-dimensional Euclidean space, the definite article is used, so ''the'' plane refers to the whole space. Many fundamental tasks in mathematics, geometry, trigonometry, graph theory, and graph of a function, graphing are p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |