|
Predictions
A prediction ( Latin ''præ-'', "before," and ''dicere'', "to say"), or forecast, is a statement about a future event or data. They are often, but not always, based upon experience or knowledge. There is no universal agreement about the exact difference from " estimation"; different authors and disciplines ascribe different connotations. Future events are necessarily uncertain, so guaranteed accurate information about the future is impossible. Prediction can be useful to assist in making plans about possible developments. Opinion In a non-statistical sense, the term "prediction" is often used to refer to an informed guess or opinion. A prediction of this kind might be informed by a predicting person's abductive reasoning, inductive reasoning, deductive reasoning, and experience; and may be useful—if the predicting person is a knowledgeable person in the field. The Delphi method is a technique for eliciting such expert-judgement-based predictions in a controlled way ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Machine Learning
Machine learning (ML) is a field of inquiry devoted to understanding and building methods that 'learn', that is, methods that leverage data to improve performance on some set of tasks. It is seen as a part of artificial intelligence. Machine learning algorithms build a model based on sample data, known as training data, in order to make predictions or decisions without being explicitly programmed to do so. Machine learning algorithms are used in a wide variety of applications, such as in medicine, email filtering, speech recognition, agriculture, and computer vision, where it is difficult or unfeasible to develop conventional algorithms to perform the needed tasks.Hu, J.; Niu, H.; Carrasco, J.; Lennox, B.; Arvin, F.,Voronoi-Based Multi-Robot Autonomous Exploration in Unknown Environments via Deep Reinforcement Learning IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2020. A subset of machine learning is closely related to computational statistics, which focuses on making pred ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Forecasting
Forecasting is the process of making predictions based on past and present data. Later these can be compared (resolved) against what happens. For example, a company might estimate their revenue in the next year, then compare it against the actual results. Prediction is a similar but more general term. Forecasting might refer to specific formal statistical methods employing time series, cross-sectional or longitudinal data, or alternatively to less formal judgmental methods or the process of prediction and resolution itself. Usage can vary between areas of application: for example, in hydrology the terms "forecast" and "forecasting" are sometimes reserved for estimates of values at certain specific future times, while the term "prediction" is used for more general estimates, such as the number of times floods will occur over a long period. Risk and uncertainty are central to forecasting and prediction; it is generally considered a good practice to indicate the degree of uncertai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Autoregressive Moving Average Model
In statistics, econometrics and signal processing, an autoregressive (AR) model is a representation of a type of random process; as such, it is used to describe certain time-varying processes in nature, economics, etc. The autoregressive model specifies that the output variable depends linearly on its own previous values and on a stochastic term (an imperfectly predictable term); thus the model is in the form of a stochastic difference equation (or recurrence relation which should not be confused with differential equation). Together with the moving-average (MA) model, it is a special case and key component of the more general autoregressive–moving-average (ARMA) and autoregressive integrated moving average (ARIMA) models of time series, which have a more complicated stochastic structure; it is also a special case of the vector autoregressive model (VAR), which consists of a system of more than one interlocking stochastic difference equation in more than one evolving random vari ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inductive Reasoning
Inductive reasoning is a method of reasoning in which a general principle is derived from a body of observations. It consists of making broad generalizations based on specific observations. Inductive reasoning is distinct from ''deductive'' reasoning. If the premises are correct, the conclusion of a deductive argument is ''certain''; in contrast, the truth of the conclusion of an inductive argument is '' probable'', based upon the evidence given. Types The types of inductive reasoning include generalization, prediction, statistical syllogism, argument from analogy, and causal inference. Inductive generalization A generalization (more accurately, an ''inductive generalization'') proceeds from a premise about a sample to a conclusion about the population. The observation obtained from this sample is projected onto the broader population. : The proportion Q of the sample has attribute A. : Therefore, the proportion Q of the population has attribute A. For example, say the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Logistic Regression
In statistics, the logistic model (or logit model) is a statistical model that models the probability of an event taking place by having the log-odds for the event be a linear function (calculus), linear combination of one or more independent variables. In regression analysis, logistic regression (or logit regression) is estimation theory, estimating the parameters of a logistic model (the coefficients in the linear combination). Formally, in binary logistic regression there is a single binary variable, binary dependent variable, coded by an indicator variable, where the two values are labeled "0" and "1", while the independent variables can each be a binary variable (two classes, coded by an indicator variable) or a continuous variable (any real value). The corresponding probability of the value labeled "1" can vary between 0 (certainly the value "0") and 1 (certainly the value "1"), hence the labeling; the function that converts log-odds to probability is the logistic function, h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
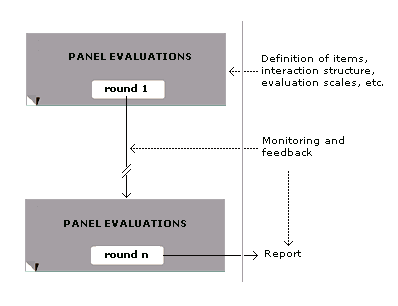
Delphi Method
} The Delphi method or Delphi technique ( ; also known as Estimate-Talk-Estimate or ETE) is a structured communication technique or method, originally developed as a systematic, interactive forecasting method which relies on a panel of experts. The technique can also be adapted for use in face-to-face meetings, and is then called mini-Delphi. Delphi has been widely used for business forecasting and has certain advantages over another structured forecasting approach, prediction markets. Delphi is based on the principle that forecasts (or decisions) from a structured group of individuals are more accurate than those from unstructured groups. The experts answer questionnaires in two or more rounds. After each round, a facilitator or change agent provides an anonymised summary of the experts' forecasts from the previous round as well as the reasons they provided for their judgments. Thus, experts are encouraged to revise their earlier answers in light of the replies of other members of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Time Series
In mathematics, a time series is a series of data points indexed (or listed or graphed) in time order. Most commonly, a time series is a sequence taken at successive equally spaced points in time. Thus it is a sequence of discrete-time data. Examples of time series are heights of ocean tides, counts of sunspots, and the daily closing value of the Dow Jones Industrial Average. A time series is very frequently plotted via a run chart (which is a temporal line chart). Time series are used in statistics, signal processing, pattern recognition, econometrics, mathematical finance, weather forecasting, earthquake prediction, electroencephalography, control engineering, astronomy, communications engineering, and largely in any domain of applied science and engineering which involves temporal measurements. Time series ''analysis'' comprises methods for analyzing time series data in order to extract meaningful statistics and other characteristics of the data. Time series ''for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Linear Regression
In statistics, linear regression is a linear approach for modelling the relationship between a scalar response and one or more explanatory variables (also known as dependent and independent variables). The case of one explanatory variable is called '' simple linear regression''; for more than one, the process is called multiple linear regression. This term is distinct from multivariate linear regression, where multiple correlated dependent variables are predicted, rather than a single scalar variable. In linear regression, the relationships are modeled using linear predictor functions whose unknown model parameters are estimated from the data. Such models are called linear models. Most commonly, the conditional mean of the response given the values of the explanatory variables (or predictors) is assumed to be an affine function of those values; less commonly, the conditional median or some other quantile is used. Like all forms of regression analysis, linear regressio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abductive Reasoning
Abductive reasoning (also called abduction,For example: abductive inference, or retroduction) is a form of logical inference formulated and advanced by American philosopher Charles Sanders Peirce beginning in the last third of the 19th century. It starts with an observation or set of observations and then seeks the simplest and most likely conclusion from the observations. This process, unlike deductive reasoning, yields a plausible conclusion but does not positively verify it. Abductive conclusions are thus qualified as having a remnant of uncertainty or doubt, which is expressed in retreat terms such as "best available" or "most likely". One can understand abductive reasoning as inference to the best explanation, although not all usages of the terms ''abduction'' and ''inference to the best explanation'' are exactly equivalent. In the 1990s, as computing power grew, the fields of law, computer science, and artificial intelligence researchFor examples, seeAbductive Inference ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Statistical Inference
Statistical inference is the process of using data analysis to infer properties of an underlying probability distribution, distribution of probability.Upton, G., Cook, I. (2008) ''Oxford Dictionary of Statistics'', OUP. . Inferential statistical analysis infers properties of a Statistical population, population, for example by testing hypotheses and deriving estimates. It is assumed that the observed data set is Sampling (statistics), sampled from a larger population. Inferential statistics can be contrasted with descriptive statistics. Descriptive statistics is solely concerned with properties of the observed data, and it does not rest on the assumption that the data come from a larger population. In machine learning, the term ''inference'' is sometimes used instead to mean "make a prediction, by evaluating an already trained model"; in this context inferring properties of the model is referred to as ''training'' or ''learning'' (rather than ''inference''), and using a model for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hypothesis
A hypothesis (plural hypotheses) is a proposed explanation for a phenomenon. For a hypothesis to be a scientific hypothesis, the scientific method requires that one can testable, test it. Scientists generally base scientific hypotheses on previous observations that cannot satisfactorily be explained with the available scientific theories. Even though the words "hypothesis" and "theory" are often used interchangeably, a scientific hypothesis is not the same as a scientific theory. A working hypothesis is a provisionally accepted hypothesis proposed for further research in a process beginning with an educated guess or thought. A different meaning of the term ''hypothesis'' is used in formal logic, to denote the antecedent (logic), antecedent of a proposition; thus in the proposition "If ''P'', then ''Q''", ''P'' denotes the hypothesis (or antecedent); ''Q'' can be called a consequent. ''P'' is the :wikt:assumption, assumption in a (possibly Counterfactual conditional, counterfac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uncertainty
Uncertainty refers to Epistemology, epistemic situations involving imperfect or unknown information. It applies to predictions of future events, to physical measurements that are already made, or to the unknown. Uncertainty arises in partially observable or stochastic environments, as well as due to ignorance, Laziness, indolence, or both. It arises in any number of fields, including insurance, philosophy, physics, statistics, economics, finance, medicine, psychology, sociology, engineering, metrology, meteorology, ecology and information science. Concepts Although the terms are used in various ways among the general public, many specialists in decision theory, statistics and other quantitative fields have defined uncertainty, risk, and their measurement as: Uncertainty The lack of certainty, a state of limited knowledge where it is impossible to exactly describe the existing state, a future outcome, or more than one possible outcome. ;Measurement of uncertainty: A set of po ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |