|
Predatory Tunicate
The predatory tunicate (''Megalodicopia hians''), also known as the ghostfish, is a species of tunicate which lives anchored along deep-sea canyon walls and the seafloor. It is unique among other tunicates in that rather than being a filter feeder, it has adapted to life as an ambush predator. Its mouth-like siphon is quick to close whenever a small animal such as a crustacean or a fish drifts inside. Once the predatory tunicate catches a meal, it keeps its trap shut until the animal inside is digested. They are known to live in the Monterey Canyon at depths of . They mostly feed on zooplankton and tiny animals, and their bodies are roughly across. Predatory tunicates are hermaphrodites, producing both eggs and sperm which drift into the water. If there are no other tunicates nearby, they can self-fertilize the eggs. Taxonomy The predatory tunicate belongs to the family Octacnemidae, which is a group of deep-sea ascidians. Thanks to the hypertrophied oral siphon, two larger ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
World Register Of Marine Species
The World Register of Marine Species (WoRMS) is a taxonomic database that aims to provide an authoritative and comprehensive list of names of marine organisms. Content The content of the registry is edited and maintained by scientific specialists on each group of organism. These taxonomists control the quality of the information, which is gathered from the primary scientific literature as well as from some external regional and taxon-specific databases. WoRMS maintains valid names of all marine organisms, but also provides information on synonyms and invalid names. It is an ongoing task to maintain the registry, since new species are constantly being discovered and described by scientists; in addition, the nomenclature and taxonomy of existing species is often corrected or changed as new research is constantly being published. Subsets of WoRMS content are made available, and can have separate badging and their own home/launch pages, as "subregisters", such as the ''World List of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Octacnemidae
Octacnemidae is a family of tunicates belonging to the order Phlebobranchia. Genera: * '' Benthascidia'' Ritter, 1907 * '' Cibacapsa'' Monniot & Monniot, 1983 * ''Cryptia'' Monniot & Monniot, 1985 * '' Dicopia'' Sluiter, 1905 * '' Kaikoja'' Monniot, 1998 * '' Megalodicopia'' Oka, 1918 * '' Myopegma'' Monniot & Monniot, 2003 * '' Octacnemus'' Moseley, 1877 * '' Polyoctacnemus'' Ihle, 1935 * ''Situla Situla (plural ''situlae''), from the Latin word for bucket or pail, is the term in archaeology and art history for a variety of elaborate bucket-shaped vessels from the Iron Age to the Middle Ages, usually with a handle at the top. All types ma ...'' Vinogradova, 1969 References {{Taxonbar, from=Q4917581 Tunicates ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Morphology (biology)
Morphology is a branch of biology dealing with the study of the form and structure of organisms and their specific structural features. This includes aspects of the outward appearance (shape, structure, colour, pattern, size), i.e. external morphology (or eidonomy), as well as the form and structure of the internal parts like bones and organs, i.e. internal morphology (or anatomy). This is in contrast to physiology, which deals primarily with function. Morphology is a branch of life science dealing with the study of gross structure of an organism or taxon and its component parts. History The etymology of the word "morphology" is from the Ancient Greek (), meaning "form", and (), meaning "word, study, research". While the concept of form in biology, opposed to function, dates back to Aristotle (see Aristotle's biology), the field of morphology was developed by Johann Wolfgang von Goethe (1790) and independently by the German anatomist and physiologist Karl Friedrich Burdach ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Corellidae
Corellidae is a family of sea squirts belonging to the suborder Phlebobranchia. Genera The World Register of Marine Species includes the following genera in this family: *'' Abyssascidia'' Herdman, 1880 *''Chelyosoma ''Chelyosoma'' is a genus of tunicates belonging to the family Corellidae Corellidae is a family of sea squirts belonging to the suborder Phlebobranchia. Genera The World Register of Marine Species The World Register of Marine Species (WoR ...'' Broderip & Sowerby, 1830 *'' Clatripes'' Monniot F. & Monniot C., 1976 *'' Corella'' Alder & Hancock, 1870 *'' Corelloides'' Oka, 1926 *'' Corellopsis'' Hartmeyer, 1903 *'' Corynascidia'' Herdman, 1882 *'' Dextrogaster'' Monniot F., 1962 *'' Mysterascidia'' Monniot C. & Monniot F., 1982 *'' Rhodosoma'' Ehrenberg, 1828 *'' Xenobranchion'' Ärnbäck-Christie-Linde, 1950 References Enterogona Tunicate families {{tunicata-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cionidae
Cionidae is a family of sea squirts belonging to the suborder Phlebobranchia Phlebobranchia is a suborder of tunicate, sea squirts in the class Ascidiacea. Characteristics The group includes both colonial and solitary animals. They are distinguished from other sea squirts by the presence of longitudinal vessels in the .... References Enterogona Tunicate families {{tunicata-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phylogenetic
In biology, phylogenetics (; from Greek φυλή/ φῦλον [] "tribe, clan, race", and wikt:γενετικός, γενετικός [] "origin, source, birth") is the study of the evolutionary history and relationships among or within groups of organisms. These relationships are determined by Computational phylogenetics, phylogenetic inference methods that focus on observed heritable traits, such as DNA sequences, protein amino acid sequences, or morphology. The result of such an analysis is a phylogenetic tree—a diagram containing a hypothesis of relationships that reflects the evolutionary history of a group of organisms. The tips of a phylogenetic tree can be living taxa or fossils, and represent the "end" or the present time in an evolutionary lineage. A phylogenetic diagram can be rooted or unrooted. A rooted tree diagram indicates the hypothetical common ancestor of the tree. An unrooted tree diagram (a network) makes no assumption about the ancestral line, and does ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hypertrophied
Hypertrophy is the increase in the volume of an organ or tissue due to the enlargement of its component cells. It is distinguished from hyperplasia, in which the cells remain approximately the same size but increase in number.Updated by Linda J. Vorvick. 8/14/1Hyperplasia/ref> Although hypertrophy and hyperplasia are two distinct processes, they frequently occur together, such as in the case of the hormonally-induced proliferation and enlargement of the cells of the uterus during pregnancy. Eccentric hypertrophy is a type of hypertrophy where the walls and chamber of a hollow organ undergo growth in which the overall size and volume are enlarged. It is applied especially to the left ventricle of heart. Sarcomeres are added in series, as for example in dilated cardiomyopathy (in contrast to hypertrophic cardiomyopathy, a type of concentric hypertrophy, where sarcomeres are added in parallel). Gallery File:*+ * Photographic documentation on sexual education - Hypertrophy of brea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
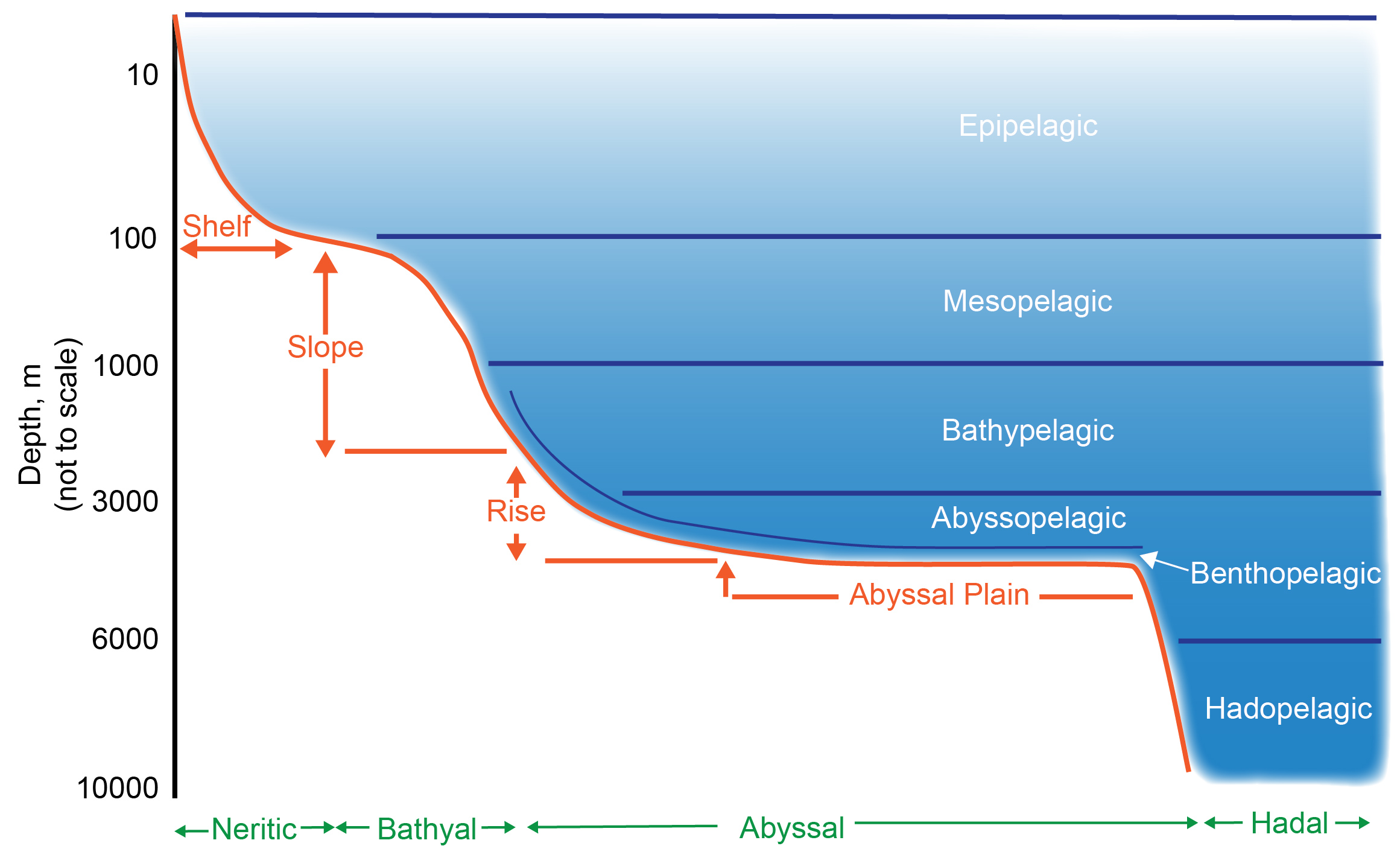
Deep-sea
The deep sea is broadly defined as the ocean depth where light begins to fade, at an approximate depth of 200 metres (656 feet) or the point of transition from continental shelves to continental slopes. Conditions within the deep sea are a combination of low temperatures, darkness and high pressure The deep sea is considered the least explored Earth biome, with the extreme conditions making the environment difficult to access and explore. Organisms living within the deep sea have a variety of adaptations to survive in these conditions. Organisms can survive in the deep sea through a number of feeding methods including scavenging, predation and filtration, with a number of organisms surviving by feeding on marine snow. Marine snow is organic material that has fallen from upper waters into the deep sea. In 1960, the bathyscaphe ''Trieste'' descended to the bottom of the Mariana Trench near Guam, at , the deepest known spot in any ocean. If Mount Everest () were submerged there, its ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zooplankton
Zooplankton are the animal component of the planktonic community ("zoo" comes from the Greek word for ''animal''). Plankton are aquatic organisms that are unable to swim effectively against currents, and consequently drift or are carried along by currents in the ocean, or by currents in seas, lakes or rivers. Zooplankton can be contrasted with phytoplankton, which are the plant component of the plankton community ("phyto" comes from the Greek word for ''plant''). Zooplankton are heterotrophic (other-feeding), whereas phytoplankton are autotrophic (self-feeding). This means zooplankton cannot manufacture their own food but must eat other plants or animals instead — in particular they eat phytoplankton. Zooplankton are generally larger than phytoplankton, most are microscopic, but some (such as jellyfish) are macroscopic and can be seen with the naked eye. Many protozoans (single-celled protists that prey on other microscopic life) are zooplankton, including zooflagellates, fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tunicate
A tunicate is a marine invertebrate animal, a member of the subphylum Tunicata (). It is part of the Chordata, a phylum which includes all animals with dorsal nerve cords and notochords (including vertebrates). The subphylum was at one time called Urochordata, and the term urochordates is still sometimes used for these animals. They are the only chordates that have lost their myomeric segmentation, with the possible exception of the 'seriation of the gill slits'. Some tunicates live as solitary individuals, but others replicate by budding and become colonies, each unit being known as a zooid. They are marine filter feeders with a water-filled, sac-like body structure and two tubular openings, known as siphons, through which they draw in and expel water. During their respiration and feeding, they take in water through the incurrent (or inhalant) siphon and expel the filtered water through the excurrent (or exhalant) siphon. Most adult tunicates are sessile, immobile and perman ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monterey Canyon
Monterey Canyon, or Monterey Submarine Canyon, is a submarine canyon in Monterey Bay, California with steep canyon walls measuring a full 1 mile in height from bottom to top, which height/depth rivals the depth of the Grand Canyon itself. It is the largest such submarine canyon along the West coast of the North American continent, and was formed by the underwater erosion process known as turbidity current erosion. Many questions remain unresolved regarding the exact nature of its origins, and as such it is the subject of several ongoing geological and marine life studies being carried out by scientists stationed at the nearby Monterey Bay Aquarium Research Institute, the Moss Landing Marine Laboratories, and other oceanographic institutions. Monterey Canyon begins at Moss Landing, California, which is situated along the middle of the coast of Monterey Bay, and extends horizontally under the Pacific Ocean where it terminates at the Monterey Canyon submarine fan, reaching dept ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ambush Predator
Ambush predators or sit-and-wait predators are carnivorous animals that capture or trap prey via stealth, luring or by (typically instinctive) strategies utilizing an element of surprise. Unlike pursuit predators, who chase to capture prey using sheer speed or endurance, ambush predators avoid fatigue by staying in concealment, waiting patiently for the prey to get near, before launching a sudden overwhelming attack that quickly incapacitates and captures the prey. The ambush is often opportunistic, and may be set by hiding in a burrow, by camouflage, by aggressive mimicry, or by the use of a trap (e.g. a web). The predator then uses a combination of senses to detect and assess the prey, and to time the strike. Nocturnal ambush predators such as cats and snakes have vertical slit pupils helping them to judge the distance to prey in dim light. Different ambush predators use a variety of means to capture their prey, from the long sticky tongues of chameleons to the expandin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |