|
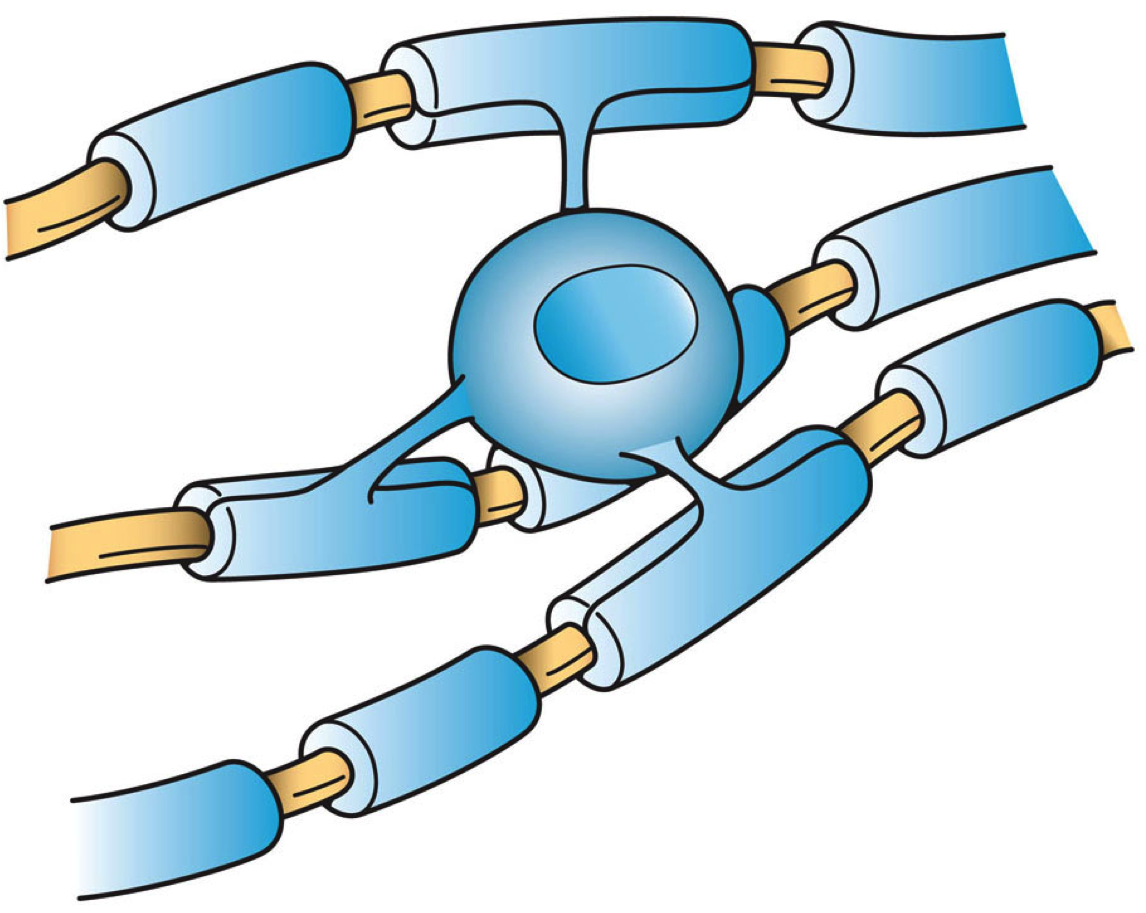
Potassium Spatial Buffering
Potassium spatial buffering is a mechanism for the regulation of extracellular potassium concentration by astrocytes. Other mechanisms for astrocytic potassium clearance are carrier-operated or channel-operated potassium chloride uptake. The repolarization of neurons tends to raise potassium concentration in the extracellular fluid. If a significant rise occurs, it will interfere with neuronal signaling by depolarizing neurons. Astrocytes have large numbers of potassium ion channels facilitating the removal of potassium ions from the extracellular fluid. They are taken up at one region of the astrocyte and then distributed throughout the cytoplasm of the cell, and further to its neighbors via gap junctions. This keeps extracellular potassium at levels that prevent interference with the normal propagation of an action potential. Potassium spatial buffering Glial cells, once believed to have a passive role in CNS, are active regulators of numerous functions in the brain, including cle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Potassium
Potassium is the chemical element with the symbol K (from Neo-Latin ''kalium'') and atomic number19. Potassium is a silvery-white metal that is soft enough to be cut with a knife with little force. Potassium metal reacts rapidly with atmospheric oxygen to form flaky white potassium peroxide in only seconds of exposure. It was first isolated from potash, the ashes of plants, from which its name derives. In the periodic table, potassium is one of the alkali metals, all of which have a single valence electron in the outer electron shell, that is easily removed to create an ion with a positive charge – a cation, that combines with anions to form salts. Potassium in nature occurs only in ionic salts. Elemental potassium reacts vigorously with water, generating sufficient heat to ignite hydrogen emitted in the reaction, and burning with a lilac- colored flame. It is found dissolved in sea water (which is 0.04% potassium by weight), and occurs in many minerals such as orthoclase, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oligodendrocytes
Oligodendrocytes (), or oligodendroglia, are a type of neuroglia whose main functions are to provide support and insulation to axons in the central nervous system of jawed vertebrates, equivalent to the function performed by Schwann cells in the peripheral nervous system. Oligodendrocytes do this by creating the myelin sheath. A single oligodendrocyte can extend its processes to 50 axons, wrapping approximately 1 μm of myelin sheath around each axon; Schwann cells, on the other hand, can wrap around only one axon. Each oligodendrocyte forms one segment of myelin for several adjacent axons. Oligodendrocytes are found only in the central nervous system, which comprises the brain and spinal cord. These cells were originally thought to have been produced in the ventral neural tube; however, research now shows oligodendrocytes originate from the ventral ventricular zone of the embryonic spinal cord and possibly have some concentrations in the forebrain. They are the last cell t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Central Nervous System
The central nervous system (CNS) is the part of the nervous system consisting primarily of the brain and spinal cord. The CNS is so named because the brain integrates the received information and coordinates and influences the activity of all parts of the bodies of bilaterally symmetric and triploblastic animals—that is, all multicellular animals except sponges and diploblasts. It is a structure composed of nervous tissue positioned along the rostral (nose end) to caudal (tail end) axis of the body and may have an enlarged section at the rostral end which is a brain. Only arthropods, cephalopods and vertebrates have a true brain (precursor structures exist in onychophorans, gastropods and lancelets). The rest of this article exclusively discusses the vertebrate central nervous system, which is radically distinct from all other animals. Overview In vertebrates, the brain and spinal cord are both enclosed in the meninges. The meninges provide a barrier to chemicals dissolv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cellular Processes
The cell is the basic structural and functional unit of life forms. Every cell consists of a cytoplasm enclosed within a membrane, and contains many biomolecules such as proteins, DNA and RNA, as well as many small molecules of nutrients and metabolites.Cell Movements and the Shaping of the Vertebrate Body in Chapter 21 of Molecular Biology of the Cell '' fourth edition, edited by Bruce Alberts (2002) published by Garland Science. The Alberts text discusses how the "cellular building blocks" move to shape developing embryos. It is also common to describe small molecules such as < ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cx43
Gap junction alpha-1 protein (GJA1), also known as connexin 43 (Cx43), is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''GJA1'' gene on chromosome 6. As a connexin, GJA1 is a component of gap junctions, which allow for gap junction intercellular communication (GJIC) between cells to regulate cell death, proliferation, and differentiation. As a result of its function, GJA1 is implicated in many biological processes, including muscle contraction, embryonic development, inflammation, and spermatogenesis, as well as diseases, including oculodentodigital dysplasia (ODDD), heart malformations, and cancers. Structure GJA1 is a 43.0 kDa protein composed of 382 amino acids. GJA1 contains a long C-terminal tail, an N-terminal domain, and multiple transmembrane domains. The protein passes through the phospholipid bilayer four times, leaving its C- and N-terminals exposed to the cytoplasm. The C-terminal tail is composed of 50 amino acids and includes post-translational modification sites, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Potassium Channels
Potassium channels are the most widely distributed type of ion channel found in virtually all organisms. They form potassium-selective pores that span cell membranes. Potassium channels are found in most cell types and control a wide variety of cell functions. Function Potassium channels function to conduct potassium ions down their electrochemical gradient, doing so both rapidly (up to the diffusion rate of K+ ions in bulk water) and selectively (excluding, most notably, sodium despite the sub-angstrom difference in ionic radius). Biologically, these channels act to set or reset the resting potential in many cells. In excitable cells, such as neurons, the delayed counterflow of potassium ions shapes the action potential. By contributing to the regulation of the cardiac action potential duration in cardiac muscle, malfunction of potassium channels may cause life-threatening arrhythmias. Potassium channels may also be involved in maintaining vascular tone. They also regulate ce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
TSC2
Tuberous Sclerosis Complex 2 (TSC2), also known as Tuberin, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''TSC2'' gene. Function Mutations in this gene lead to tuberous sclerosis. Its gene product is believed to be a tumor suppressor and is able to stimulate specific GTPases. Hamartin coded by the gene TSC1 functions as a facilitator of Hsp90 in chaperoning of Tuberin, therefore preventing its ubiquitination and degradation in the proteasome. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants encoding different isoforms of the protein. Mutations in TSC2 can cause Lymphangioleiomyomatosis, a disease caused by the enlargement of tissue in the lungs, creating cysts and tumours and causing difficulty breathing. Because Tuberin regulates cell size, along with the protein Hamartin, mutations to TSC1 and TSC2 genes may prevent the control of cell growth in the lungs of individuals. Cell Pathology Cells from individuals with pathogenic mutations in the TSC2 gene display d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
TSC1
Tuberous sclerosis 1 (TSC1), also known as hamartin, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''TSC1'' gene. Function TSC1 functions as a co-chaperone which inhibits the ATPase activity of the chaperone Hsp90 (heat shock protein-90) and decelerates its chaperone cycle. Tsc1 functions as a facilitator of Hsp90 in chaperoning the kinase and non-kinase clients including Tsc2, therefore preventing their ubiquitination and degradation in the proteasome. TSC1, TSC2 anTBC1D7is a multi-protein complex also known as the TSC complex. This complex negatively regulates mTORC1 signaling by functioning as a GTPase-activating protein (GAP) for the small GTPase Rheb, an essential activator of mTORC1. The TSC complex has been implicated as a tumor suppressor. Clinical significance Defects in this gene can cause tuberous sclerosis, due to a functional impairment of the TSC complex. Defects in TSC1 may also be a cause of focal cortical dysplasia. TSC1 may be involved in protecting brain n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tuberous Sclerosis Complex
Tuberous sclerosis complex (TSC) is a rare multisystem autosomal dominant genetic disease that causes non-cancerous tumours to grow in the brain and on other vital organs such as the kidneys, heart, liver, eyes, lungs and skin. A combination of symptoms may include seizures, intellectual disability, developmental delay, behavioral problems, skin abnormalities, lung disease, and kidney disease. TSC is caused by a mutation of either of two genes, ''TSC1'' and ''TSC2'', which code for the proteins hamartin and tuberin, respectively, with ''TSC2'' mutations accounting for the majority and tending to cause more severe symptoms. These proteins act as tumor growth suppressors, agents that regulate cell proliferation and differentiation. Prognosis is highly variable and depends on the symptoms, but life expectancy is normal for many. The prevalence of the disease is estimated to be 7 to 12 in 100,000. The disease is often abbreviated to tuberous sclerosis, which refers to the hard ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Necturus
''Necturus'' is a genus of aquatic salamanders native to the eastern United States and Canada. They are commonly known as waterdogs and mudpuppies. The common mudpuppy ''(N. maculosus)'' is probably the best-known species – as an amphibian with gill slits, it is often dissected in comparative anatomy classes. Taxonomy The genus is under scrutiny by herpetologists. The relationship between the species is still being studied. In 1991 Collins elevated ''N. maculosus louisianensis'' to full species status, usually considered a subspecies of the common mudpuppy (''N. maculosus''), but his interpretation was not largely followed.Petranka, J.W. (1998). Salamanders of the United States and Canada. Smithsonian Institution Press . However, a 2018 study confirmed it as a distinct species, with Amphibian Species of the World following these results, although other authorities do not.'''' Species There are seven to eight species: Two known fossil species, '' N. krausei'' and an unna ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Muller Cell
Muller is a surname. Notable people with the surname include: A–H * A. Charles Muller (born 1953), translator *Bauke Muller (born 1962), Dutch bridge player *Bennie Muller (born 1938), Dutch footballer *Bill Muller (1965–2007), US journalist *Bobby Muller (born 1946), Vietnam veteran * Carl Muller (1935–2019), Sri Lankan Burgher writer, poet, and journalist *David E. Muller (1924–2008), American mathematician and computer scientist *Derek Muller (born 1982), science communicator *Dominique Muller (born 1949), French writer *Édouard Muller (painter) (1823–1876), Swiss-French painter *Édouard Muller (cyclist) (1919–1997), French road racing cyclist *Ellen Preis (Ellen Müller-Preis) (1912–2007), German-born Austrian fencer *Émile Muller (1915–1988), French politician * Filinto Muller (1900-1973), Brazilian politician *Franck Muller (born 1958), Swiss watchmaker *François Muller (1764–1808), French general of the French Revolutionary Wars *Frank Muller (1951 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glia Limitans
The glia limitans, or the glial limiting membrane, is a thin barrier of astrocyte foot processes associated with the parenchymal basal lamina surrounding the brain and spinal cord. It is the outermost layer of neural tissue, and among its responsibilities is the prevention of the over-migration of neurons and neuroglia, the supporting cells of the nervous system, into the meninges. The glia limitans also plays an important role in regulating the movement of small molecules and cells into the brain tissue by working in concert with other components of the central nervous system (CNS) such as the blood–brain barrier (BBB). Location and structure The perivascular feet of astrocytes form a close association with the basal lamina of the brain parenchyma to create the glia limitans. This membrane lies deep to the pia mater and the subpial space and surrounds the perivascular spaces (Virchow-Robin spaces). Any substance entering the central nervous system from the blood or cerebr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |