|
Postulates Of Special Relativity
In physics, Albert Einstein's 1905 theory of special relativity is derived from first principles now called the postulates of special relativity. Einstein's formulation only uses two postulates, though his derivation implies a few more assumptions. Postulates of special relativity 1. First postulate (principle of relativity) : The laws of physics take the same form in all inertial frames of reference. 2. Second postulate (invariance of '' c'') : As measured in any inertial frame of reference, light is always propagated in empty space with a definite velocity ''c'' that is independent of the state of motion of the emitting body. Or: the speed of light in free space has the same value ''c'' in all inertial frames of reference. The two-postulate basis for special relativity is the one historically used by Einstein, and it remains the starting point today. As Einstein himself later acknowledged, the derivation of the Lorentz transformation tacitly makes use of some additional assu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Albert Einstein
Albert Einstein ( ; ; 14 March 1879 – 18 April 1955) was a German-born theoretical physicist, widely acknowledged to be one of the greatest and most influential physicists of all time. Einstein is best known for developing the theory of relativity, but he also made important contributions to the development of the theory of quantum mechanics. Relativity and quantum mechanics are the two pillars of modern physics. His mass–energy equivalence formula , which arises from relativity theory, has been dubbed "the world's most famous equation". His work is also known for its influence on the philosophy of science. He received the 1921 Nobel Prize in Physics "for his services to theoretical physics, and especially for his discovery of the law of the photoelectric effect", a pivotal step in the development of quantum theory. His intellectual achievements and originality resulted in "Einstein" becoming synonymous with "genius". In 1905, a year sometimes described as his ' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
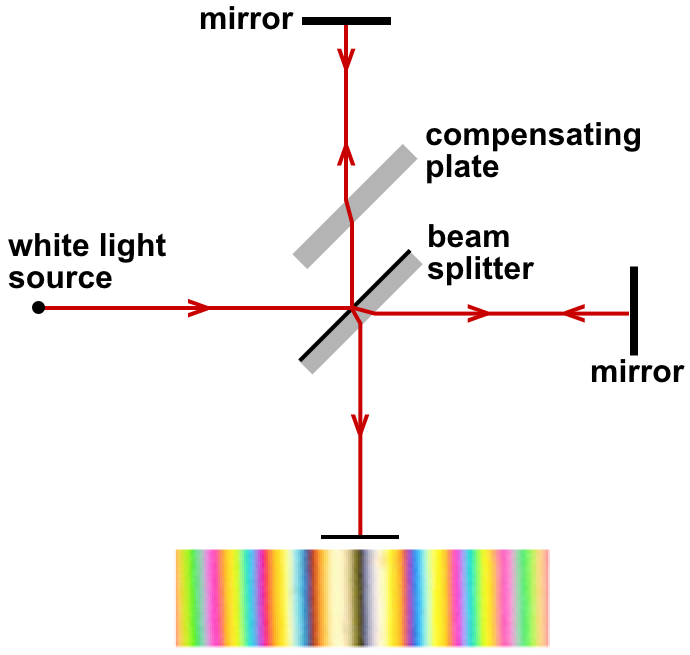
Luminiferous Aether
Luminiferous aether or ether ("luminiferous", meaning "light-bearing") was the postulated medium for the propagation of light. It was invoked to explain the ability of the apparently wave-based light to propagate through empty space (a vacuum), something that waves should not be able to do. The assumption of a spatial plenum of luminiferous aether, rather than a spatial vacuum, provided the theoretical medium that was required by wave theories of light. The aether hypothesis was the topic of considerable debate throughout its history, as it required the existence of an invisible and infinite material with no interaction with physical objects. As the nature of light was explored, especially in the 19th century, the physical qualities required of an aether became increasingly contradictory. By the late 1800s, the existence of the aether was being questioned, although there was no physical theory to replace it. The negative outcome of the Michelson–Morley experiment (1887) suggeste ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spacetime
In physics, spacetime is a mathematical model that combines the three dimensions of space and one dimension of time into a single four-dimensional manifold. Spacetime diagrams can be used to visualize relativistic effects, such as why different observers perceive differently where and when events occur. Until the 20th century, it was assumed that the three-dimensional geometry of the universe (its spatial expression in terms of coordinates, distances, and directions) was independent of one-dimensional time. The physicist Albert Einstein helped develop the idea of spacetime as part of his theory of relativity. Prior to his pioneering work, scientists had two separate theories to explain physical phenomena: Isaac Newton's laws of physics described the motion of massive objects, while James Clerk Maxwell's electromagnetic models explained the properties of light. However, in 1905, Einstein based a work on special relativity on two postulates: * The laws of physics are invariant ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vacuum Permittivity
Vacuum permittivity, commonly denoted (pronounced "epsilon nought" or "epsilon zero"), is the value of the absolute dielectric permittivity of classical vacuum. It may also be referred to as the permittivity of free space, the electric constant, or the distributed capacitance of the vacuum. It is an ideal (baseline) physical constant. Its CODATA value is: : ( farads per meter), with a relative uncertainty of It is a measure of how dense of an electric field is "permitted" to form in response to electric charges, and relates the units for electric charge to mechanical quantities such as length and force. For example, the force between two separated electric charges with spherical symmetry (in the vacuum of classical electromagnetism) is given by Coulomb's law: :F_\text = \frac \frac Here, ''q''1 and ''q''2 are the charges, ''r'' is the distance between their centres, and the value of the constant fraction 1/4 \pi \varepsilon_0 (known as the Coulomb constant, ''k''e) is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hermann Rothe
Hermann Rothe (28 December 1882 in Vienna – 18 December 1923 in Vienna) was an Austrian mathematician. Rothe studied at the University of Vienna and the University of Göttingen. He attained the Doctorate in Engineering in 1909 in Vienna. Then he was assistant at the Vienna University of Technology, where he attained the Habilitation in 1910. In 1913 Rothe married and began to teach mathematics at the Vienna University of Technology as Professor extraordinarius, and from 1920 as Professor ordinarius. In 1923 he died after a long disease. Rothe is known for his collaboration (1910–1912) with Philipp Frank on special relativity. Based on group theory, they tried to derive the Lorentz transformation without the postulate of the constancy of the speed of light. In English: Furthermore, Rothe worked — outside his teaching activity — on mathematical problems like Hermann Grassmann's "Ausdehnungslehre" (theory of extension, or exterior algebra). Publications * * See ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Philipp Frank
Philipp Frank (March 20, 1884 – July 21, 1966) was a physicist, mathematician and philosopher of the early-to-mid 20th century. He was a logical positivist, and a member of the Vienna Circle. He was influenced by Mach and was one of the Machists criticised by Lenin in ''Materialism and Empirio-criticism''. Biography He studied physics at the University of Vienna and graduated in 1907 with a thesis in theoretical physics under the supervision of Ludwig Boltzmann. He joined the faculty there in 1910. Albert Einstein recommended him as his successor for a professorship at the German Charles-Ferdinand University of Prague, a position which he held from 1912 until 1938. Doctoral students included Reinhold Furth and Peter Bergmann. In 1938, he was invited by Harvard University to America as a visiting lecturer on quantum theory and the philosophy of modern physics. The Germans having invaded Czechoslovakia as he was about to begin his scheduled lecture tour, Frank, a Jew, never retu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vladimir Ignatowski
Vladimir Sergeyevitch Ignatowski, or Waldemar Sergius von Ignatowsky and similar names in other publications (* March 8/20, 1875 in Tbilisi, Georgia; † January 13, 1942 in Leningrad), was a Russian physicist. Life and work Ignatowski graduated in 1906 in Saint Petersburg. 1906-1908 he continued to study at the University of Giessen, with his dissertation in 1909. 1911-1914 he taught at the Higher Technical School in Berlin. Afterwards he worked for different institutions in the Soviet Union. Then he became a corresponding member of the Soviet Academy of Sciences. Aleksandr Solzhenitsyn reported in his book The Gulag Archipelago, that Ignatowski was put under arrest by Soviet officials, who raised absurd allegations against him. It was claimed that Ignatowski was recruited by the German secret service in 1909, not to spy in the next war (World War I), but to spy in the "''war after the next war''" (World War II). So Ignatowski was executed in 1942 in Leningrad.Solschenizyn, 1973, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Group Theory
In abstract algebra, group theory studies the algebraic structures known as group (mathematics), groups. The concept of a group is central to abstract algebra: other well-known algebraic structures, such as ring (mathematics), rings, field (mathematics), fields, and vector spaces, can all be seen as groups endowed with additional operation (mathematics), operations and axioms. Groups recur throughout mathematics, and the methods of group theory have influenced many parts of algebra. Linear algebraic groups and Lie groups are two branches of group theory that have experienced advances and have become subject areas in their own right. Various physical systems, such as crystals and the hydrogen atom, and Standard Model, three of the four known fundamental forces in the universe, may be modelled by symmetry groups. Thus group theory and the closely related representation theory have many important applications in physics, chemistry, and materials science. Group theory is also ce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)