|
Porphyroclast
350px, A mylonite showing a number of (rotated) porphyroclasts: a clear red garnet left in the picture while smaller white feldspar porphyroclasts can be found all over. ''Location'': the tectonics, tectonic contact between the wiktionary:autochthonous, autochthonous Western Gneiss Region and rocks of the allochthonous Blåhø nappe on Otrøy, Caledonides, Central Norway. A porphyroclast is a clast or mineral fragment in a metamorphic rock, surrounded by a groundmass of finer grained crystals. Porphyroclasts are fragments of the original rock before dynamic recrystallisation or cataclasis produced the groundmass. This means they are older than the groundmass. They were stronger pieces of the original rock, that could not as easily deform and were therefore not or hardly affected by recrystallisation. They may have been phenocrysts or porphyroblasts in the original rock. Porphyroclasts are often confused with porphyroblasts. The latter are also large crystals in a finer matrix, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shear Zone
In geology, a shear zone is a thin zone within the Earth's crust or upper mantle that has been strongly deformed, due to the walls of rock on either side of the zone slipping past each other. In the upper crust, where rock is brittle, the shear zone takes the form of a fracture called a Fault (geology), fault. In the lower crust and mantle, the extreme conditions of pressure and temperature make the rock ductile. That is, the rock is capable of slowly deforming without fracture, like hot metal being worked by a blacksmith. Here the shear zone is a wider zone, in which the ductile rock has slowly flowed to accommodate the relative motion of the rock walls on either side. Because shear zones are found across a wide depth-range, a great variety of different rock types with their characteristic structures are associated with shear zones. General introduction A shear zone is a zone of strong deformation (with a high strain rate) surrounded by rocks with a lower state of Deforma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Augen Mylonite
Augen (from German "eyes") are large, lenticular eye-shaped mineral grains or mineral aggregates visible in some foliated metamorphic rocks. In cross section they have the shape of an eye. Feldspar, quartz, and garnet are common minerals which form augen. Augen form in rocks which have undergone metamorphism and shearing. The core of the augen is a porphyroblast or porphyroclast of a hard, resilient mineral such as garnet. The augen grows by crystallisation of a ''mantle'' of new mineral around the porphyroblast. The mantle is formed contiguous with the foliation which is imparted upon the rock, and forms a blanket which tapers off from either side of the porphyroblast within the strain shadows. During shearing, the porphyroblast may rotate, to form a characteristic augen texture of asymmetric shearing. In this case, the position of the tails is unequal across the foliation, with some augen showing clear drag folding of the mantle into the strain shadow. This derives a form o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Porphyroblast
A porphyroblast is a large mineral crystal in a metamorphic rock which has grown within the finer grained matrix. Porphyroblasts are commonly euhedral crystals, but can also be partly to completely irregular in shape. The most common porphyroblasts in metapelites (metamorphosed mudstones and siltstones) are garnets and staurolites, which stand out in well- foliated metapelites (such as schists) against the platy mica matrix. A similar type of crystal is a ''phenocryst'', a large crystal in an igneous rock. Porphyroblasts are often confused with ''porphyroclasts'', which can also be large outstanding crystals, but which are ''older'' than the matrix of the rock. If a porphyroblastic mineral has small inclusions of minerals within it, the mineral is described as poikiloblastic. This observation can help interpret deformation history. A rock which has many porphyroblasts is described as having a ''porphyroblastic texture''. As porphyroblasts grow, the foliation may be preser ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Garnet Porphyroblast
Garnets () are a group of silicate minerals that have been used since the Bronze Age as gemstones and abrasives. All species of garnets possess similar physical properties and crystal forms, but differ in chemical composition. The different species are pyrope, almandine, spessartine, grossular (varieties of which are hessonite or cinnamon-stone and tsavorite), uvarovite and andradite. The garnets make up two solid solution series: pyrope-almandine-spessartine (pyralspite), with the composition range ; and uvarovite-grossular-andradite (ugrandite), with the composition range . Etymology The word ''garnet'' comes from the 14th-century Middle English word ''gernet'', meaning 'dark red'. It is borrowed from Old French ''grenate'' from Latin ''granatus,'' from ''granum'' ('grain, seed'). This is possibly a reference to ''mela granatum'' or even ''pomum granatum'' ('pomegranate', ''Punica granatum''), a plant whose fruits contain abundant and vivid red seed covers (arils), which are s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shear Stress
Shear stress, often denoted by (Greek: tau), is the component of stress coplanar with a material cross section. It arises from the shear force, the component of force vector parallel to the material cross section. ''Normal stress'', on the other hand, arises from the force vector component perpendicular to the material cross section on which it acts. General shear stress The formula to calculate average shear stress is force per unit area.: : \tau = , where: : = the shear stress; : = the force applied; : = the cross-sectional area of material with area parallel to the applied force vector. Other forms Wall shear stress Wall shear stress expresses the retarding force (per unit area) from a wall in the layers of a fluid flowing next to the wall. It is defined as: \tau_w:=\mu\left(\frac\right)_ Where \mu is the dynamic viscosity, u the flow velocity and y the distance from the wall. It is used, for example, in the description of arterial blood flow in which case which ther ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rotation
Rotation, or spin, is the circular movement of an object around a '' central axis''. A two-dimensional rotating object has only one possible central axis and can rotate in either a clockwise or counterclockwise direction. A three-dimensional object has an infinite number of possible central axes and rotational directions. If the rotation axis passes internally through the body's own center of mass, then the body is said to be ''autorotating'' or '' spinning'', and the surface intersection of the axis can be called a ''pole''. A rotation around a completely external axis, e.g. the planet Earth around the Sun, is called ''revolving'' or ''orbiting'', typically when it is produced by gravity, and the ends of the rotation axis can be called the ''orbital poles''. Mathematics Mathematically, a rotation is a rigid body movement which, unlike a translation, keeps a point fixed. This definition applies to rotations within both two and three dimensions (in a plane and in space, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Matrix (geology)
The matrix or groundmass of a rock is the finer-grained mass of material in which larger grains, crystals, or clasts are embedded. The matrix of an igneous rock consists of finer-grained, often microscopic, crystals in which larger crystals, called phenocrysts, are embedded. This porphyritic texture is indicative of multi-stage cooling of magma. For example, porphyritic andesite will have large phenocrysts of plagioclase in a fine-grained matrix. Also in South Africa, diamonds are often mined from a matrix of weathered clay-like rock (kimberlite) called "yellow ground". The matrix of sedimentary rocks is finer-grained sedimentary material, such as clay or silt, in which larger grains or clasts are embedded. It is also used to describe the rock material in which a fossil is embedded. Cementation All sediments are at first in an incoherent condition (e.g. sands, clays and gravels, beds of shells), and they may remain in this state for an indefinite period. Millions of years have ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phenocryst
300px, feldspathic phenocrysts. This granite, from the Switzerland">Swiss side of the Mont Blanc massif, has large white plagioclase phenocrysts, triclinic minerals that give trapezoid shapes when cut through). 1 euro coins, 1 euro coin (diameter 2.3 cm) for scale. A phenocryst is an early forming, relatively large and usually conspicuous crystal distinctly larger than the grains of the rock groundmass of an igneous rock. Such rocks that have a distinct difference in the size of the crystals are called porphyries, and the adjective porphyritic is used to describe them. Phenocrysts often have euhedral forms, either due to early growth within a magma, or by post-emplacement recrystallization. Normally the term ''phenocryst'' is not used unless the crystals are directly observable, which is sometimes stated as greater than .5 millimeter in diameter. Phenocrysts below this level, but still larger than the groundmass crystals, are termed ''microphenocrysts''. Very large phenocrysts a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
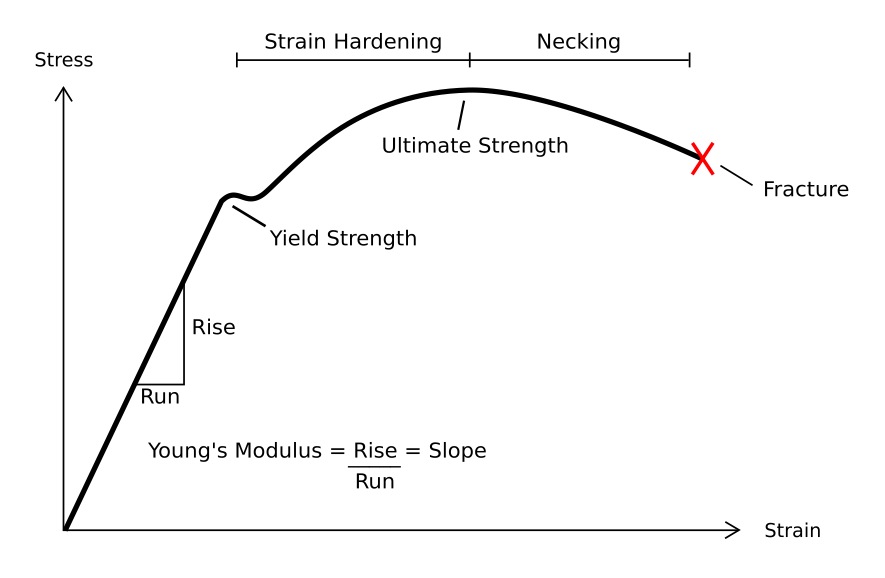
Strength Of Materials
The field of strength of materials, also called mechanics of materials, typically refers to various methods of calculating the stresses and strains in structural members, such as beams, columns, and shafts. The methods employed to predict the response of a structure under loading and its susceptibility to various failure modes takes into account the properties of the materials such as its yield strength, ultimate strength, Young's modulus, and Poisson's ratio. In addition, the mechanical element's macroscopic properties (geometric properties) such as its length, width, thickness, boundary constraints and abrupt changes in geometry such as holes are considered. The theory began with the consideration of the behavior of one and two dimensional members of structures, whose states of stress can be approximated as two dimensional, and was then generalized to three dimensions to develop a more complete theory of the elastic and plastic behavior of materials. An important founding pion ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deformation (engineering)
In engineering, deformation refers to the change in size or shape of an object. ''Displacements'' are the ''absolute'' change in position of a point on the object. Deflection is the relative change in external displacements on an object. Strain is the ''relative'' internal change in shape of an infinitesimally small cube of material and can be expressed as a non-dimensional change in length or angle of distortion of the cube. Strains are related to the forces acting on the cube, which are known as stress, by a stress-strain curve. The relationship between stress and strain is generally linear and reversible up until the yield point and the deformation is elastic. The linear relationship for a material is known as Young's modulus. Above the yield point, some degree of permanent distortion remains after unloading and is termed plastic deformation. The determination of the stress and strain throughout a solid object is given by the field of strength of materials and for a structure ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dynamic Recrystallisation
Dynamic recrystallization (DRX) is a type of recrystallization process, found within the fields of metallurgy and geology. In dynamic recrystallization, as opposed to static recrystallization, the nucleation and growth of new grains occurs during deformation rather than afterwards as part of a separate heat treatment. The reduction of grain size increases the risk of grain boundary sliding at elevated temperatures, while also decreasing dislocation mobility within the material. The new grains are less strained, causing a decrease in the hardening of a material. Dynamic recrystallization allows for new grain sizes and orientation, which can prevent crack propagation. Rather than strain causing the material to fracture, strain can initiate the growth of a new grain, consuming atoms from neighboring pre-existing grains. After dynamic recrystallization, the ductility of the material increases. In a stress–strain curve, the onset of dynamic recrystallization can be recognized by a dis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crystal
A crystal or crystalline solid is a solid material whose constituents (such as atoms, molecules, or ions) are arranged in a highly ordered microscopic structure, forming a crystal lattice that extends in all directions. In addition, macroscopic single crystals are usually identifiable by their geometrical shape, consisting of flat faces with specific, characteristic orientations. The scientific study of crystals and crystal formation is known as crystallography. The process of crystal formation via mechanisms of crystal growth is called crystallization or solidification. The word ''crystal'' derives from the Ancient Greek word (), meaning both "ice" and "rock crystal", from (), "icy cold, frost". Examples of large crystals include snowflakes, diamonds, and table salt. Most inorganic solids are not crystals but polycrystals, i.e. many microscopic crystals fused together into a single solid. Polycrystals include most metals, rocks, ceramics, and ice. A third category of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |