|
Poneratoxin
Poneratoxin is a paralyzing neurotoxic peptide made by the bullet ant ''Paraponera clavata''. It prevents inactivation of voltage gated sodium channels and therefore blocks the synaptic transmission in the central nervous system. Specifically, poneratoxin acts on voltage gated sodium channels in skeletal muscle fibers, causing paralysis, and nociceptive fibers, causing pain. It is rated as a 4 plus on the Schmidt sting pain index, the highest possible rating with that system, and its effects can cause waves of pain up to twelve hours after a single sting. Schmidt describes it as "pure, intense, brilliant pain...like walking over flaming charcoal with a three-inch nail embedded in your heel." It is additionally being studied for its uses in biological insecticides. Mechanism of action Overall, poneratoxin disrupts normal function of voltage-gated sodium channels in both vertebrates and invertebrates. It causes repetitive firing and prolongation of action potentials, particularl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Poneratoxin Schematic
Poneratoxin is a paralyzing neurotoxic peptide made by the bullet ant '' Paraponera clavata''. It prevents inactivation of voltage gated sodium channels and therefore blocks the synaptic transmission in the central nervous system. Specifically, poneratoxin acts on voltage gated sodium channels in skeletal muscle fibers, causing paralysis, and nociceptive fibers, causing pain. It is rated as a 4 plus on the Schmidt sting pain index, the highest possible rating with that system, and its effects can cause waves of pain up to twelve hours after a single sting. Schmidt describes it as "pure, intense, brilliant pain...like walking over flaming charcoal with a three-inch nail embedded in your heel." It is additionally being studied for its uses in biological insecticides. Mechanism of action Overall, poneratoxin disrupts normal function of voltage-gated sodium channels in both vertebrates and invertebrates. It causes repetitive firing and prolongation of action potentials, partic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Poneratoxin 1
Poneratoxin is a paralyzing neurotoxic peptide made by the bullet ant '' Paraponera clavata''. It prevents inactivation of voltage gated sodium channels and therefore blocks the synaptic transmission in the central nervous system. Specifically, poneratoxin acts on voltage gated sodium channels in skeletal muscle fibers, causing paralysis, and nociceptive fibers, causing pain. It is rated as a 4 plus on the Schmidt sting pain index, the highest possible rating with that system, and its effects can cause waves of pain up to twelve hours after a single sting. Schmidt describes it as "pure, intense, brilliant pain...like walking over flaming charcoal with a three-inch nail embedded in your heel." It is additionally being studied for its uses in biological insecticides. Mechanism of action Overall, poneratoxin disrupts normal function of voltage-gated sodium channels in both vertebrates and invertebrates. It causes repetitive firing and prolongation of action potentials, partic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
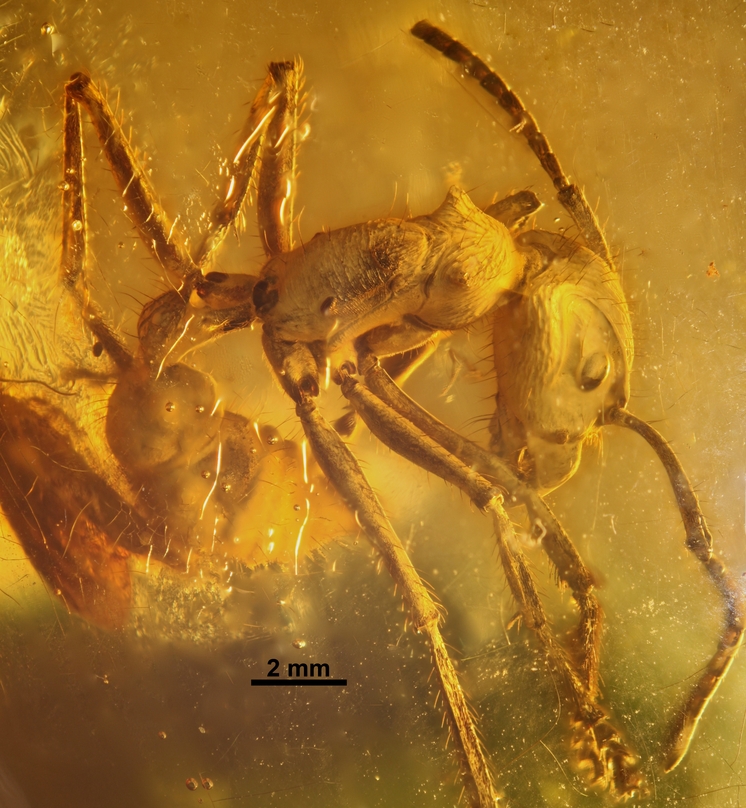
Paraponera Clavata
''Paraponera clavata'' is a species of ant, commonly known as the bullet ant, named for its extremely painful sting. It inhabits humid lowland rainforests in Central and South America. Etymology The specific epithet of the ant, ', means "club-shaped". The generic name, ''Paraponera'', translates to "near-''Ponera''". Due to its notoriety, the ant has several Native American, Spanish, and Portuguese local names in different geographical areas. Perhaps the best known name is the Venezuelan ' (the "24 ant" or "24-hour ant"), referring to the full day of pain that follows being stung; it can also refer to the time it takes to kill a human. In Brazil, the Portuguese names given by locals include ', ', or ' (big black ant), and Native American-derived names are ''tocandira'', ''tocandira'', and ''tocanquibira''. These names derive from the Tupi–Guarani ''tuca-ndy'', which translates to "the one wounding deeply". Other names by which it is referred include ''chacha'', ''cumanagata ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Schmidt Sting Pain Index
The Schmidt sting pain index is a pain scale rating the relative pain caused by different hymenopteran stings. It is mainly the work of Justin O. Schmidt (born 1947), an entomologist at the Carl Hayden Bee Research Center in Arizona, United States. Schmidt has published a number of papers on the subject, and claims to have been stung by the majority of stinging Hymenoptera. His original paper in 1983 was a way to systematize and compare the hemolytic properties of insect venoms. A table contained in the paper included a column that rated sting pain, starting from 0 for stings that are completely ineffective against humans, progressing through 2, a familiar pain such as that caused by a common bee or wasp sting, and finishing at 4 for the most painful stings; in the original paper, only the bullet ant, ''Paraponera clavata'', was given a rating of 4. Later revised versions of the index added '' Synoeca septentrionalis'', along with tarantula hawks as the only species to share this ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Receptor (biochemistry)
In biochemistry and pharmacology, receptors are chemical structures, composed of protein, that receive and transduce signals that may be integrated into biological systems. These signals are typically chemical messengers which bind to a receptor and cause some form of cellular/tissue response, e.g. a change in the electrical activity of a cell. There are three main ways the action of the receptor can be classified: relay of signal, amplification, or integration. Relaying sends the signal onward, amplification increases the effect of a single ligand, and integration allows the signal to be incorporated into another biochemical pathway. Receptor proteins can be classified by their location. Transmembrane receptors include ligand-gated ion channels, G protein-coupled receptors, and enzyme-linked hormone receptors. Intracellular receptors are those found inside the cell, and include cytoplasmic receptors and nuclear receptors. A molecule that binds to a receptor is called a ligand ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acid
In computer science, ACID ( atomicity, consistency, isolation, durability) is a set of properties of database transactions intended to guarantee data validity despite errors, power failures, and other mishaps. In the context of databases, a sequence of database operations that satisfies the ACID properties (which can be perceived as a single logical operation on the data) is called a ''transaction''. For example, a transfer of funds from one bank account to another, even involving multiple changes such as debiting one account and crediting another, is a single transaction. In 1983, Andreas Reuter and Theo Härder coined the acronym ''ACID'', building on earlier work by Jim Gray who named atomicity, consistency, and durability, but not isolation, when characterizing the transaction concept. These four properties are the major guarantees of the transaction paradigm, which has influenced many aspects of development in database systems. According to Gray and Reuter, the IBM Informa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrophobe
In chemistry, hydrophobicity is the physical property of a molecule that is seemingly repelled from a mass of water (known as a hydrophobe). In contrast, hydrophiles are attracted to water. Hydrophobic molecules tend to be nonpolar and, thus, prefer other neutral molecules and nonpolar solvents. Because water molecules are polar, hydrophobes do not dissolve well among them. Hydrophobic molecules in water often cluster together, forming micelles. Water on hydrophobic surfaces will exhibit a high contact angle. Examples of hydrophobic molecules include the alkanes, oils, fats, and greasy substances in general. Hydrophobic materials are used for oil removal from water, the management of oil spills, and chemical separation processes to remove non-polar substances from polar compounds. Hydrophobic is often used interchangeably with lipophilic, "fat-loving". However, the two terms are not synonymous. While hydrophobic substances are usually lipophilic, there are exceptions, suc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amino Acid
Amino acids are organic compounds that contain both amino and carboxylic acid functional groups. Although hundreds of amino acids exist in nature, by far the most important are the alpha-amino acids, which comprise proteins. Only 22 alpha amino acids appear in the genetic code. Amino acids can be classified according to the locations of the core structural functional groups, as Alpha and beta carbon, alpha- , beta- , gamma- or delta- amino acids; other categories relate to Chemical polarity, polarity, ionization, and side chain group type (aliphatic, Open-chain compound, acyclic, aromatic, containing hydroxyl or sulfur, etc.). In the form of proteins, amino acid '' residues'' form the second-largest component (water being the largest) of human muscles and other tissues. Beyond their role as residues in proteins, amino acids participate in a number of processes such as neurotransmitter transport and biosynthesis. It is thought that they played a key role in enabling life ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Agonist
An agonist is a chemical that activates a receptor to produce a biological response. Receptors are cellular proteins whose activation causes the cell to modify what it is currently doing. In contrast, an antagonist blocks the action of the agonist, while an inverse agonist causes an action opposite to that of the agonist. Etymology From the Greek αγωνιστής (agōnistēs), contestant; champion; rival < αγων (agōn), contest, combat; exertion, struggle < αγω (agō), I lead, lead towards, conduct; drive Types of agonists can be activated by either endogenous agonists (such as |
Neurotoxin
Neurotoxins are toxins that are destructive to nerve tissue (causing neurotoxicity). Neurotoxins are an extensive class of exogenous chemical neurological insultsSpencer 2000 that can adversely affect function in both developing and mature nervous tissue.Olney 2002 The term can also be used to classify endogenous compounds, which, when abnormally contacted, can prove neurologically toxic. Though neurotoxins are often neurologically destructive, their ability to specifically target neural components is important in the study of nervous systems. Common examples of neurotoxins include lead, ethanol (drinking alcohol), glutamate,Choi 1987 nitric oxide, botulinum toxin (e.g. Botox), tetanus toxin,Simpson 1986 and tetrodotoxin. Some substances such as nitric oxide and glutamate are in fact essential for proper function of the body and only exert neurotoxic effects at excessive concentrations. Neurotoxins inhibit neuron control over ion concentrations across the cell membrane, or com ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
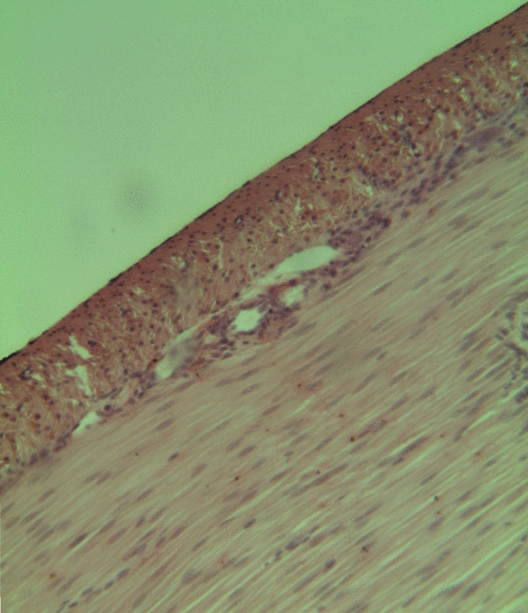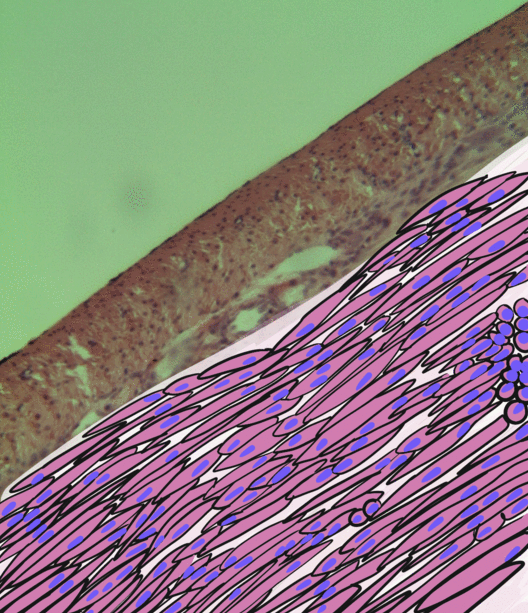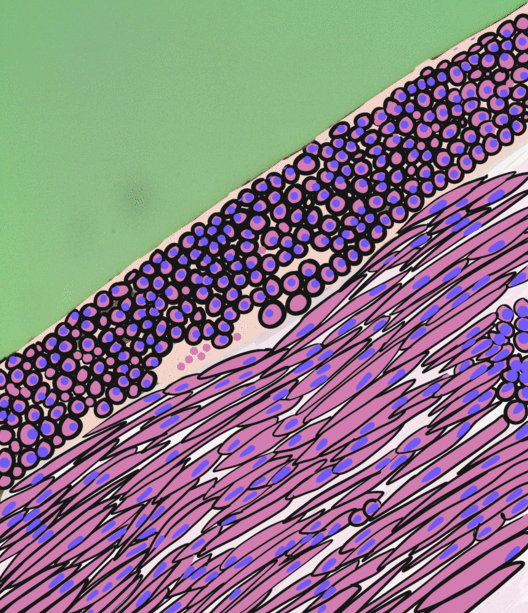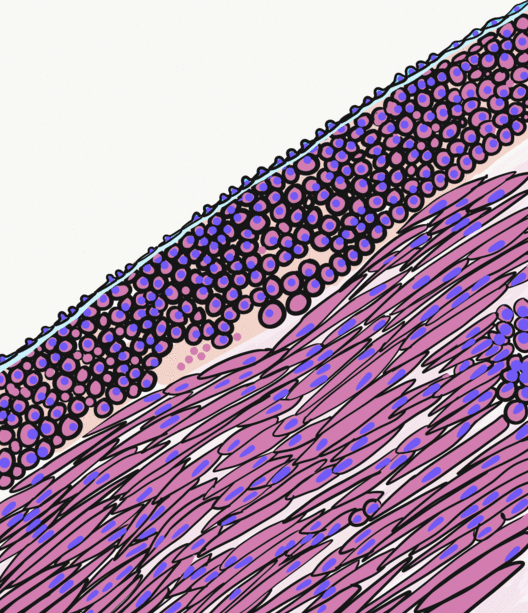
Smooth Muscle Tissue
Smooth muscle is an involuntary non-striated muscle, so-called because it has no sarcomeres and therefore no striations (''bands'' or ''stripes''). It is divided into two subgroups, single-unit and multiunit smooth muscle. Within single-unit muscle, the whole bundle or sheet of smooth muscle cells contracts as a syncytium. Smooth muscle is found in the walls of hollow organs, including the stomach, intestines, bladder and uterus; in the walls of passageways, such as blood, and lymph vessels, and in the tracts of the respiratory, urinary, and reproductive systems. In the eyes, the ciliary muscles, a type of smooth muscle, dilate and contract the iris and alter the shape of the lens. In the skin, smooth muscle cells such as those of the arrector pili cause hair to stand erect in response to cold temperature or fear. Structure Gross anatomy Smooth muscle is grouped into two types: single-unit smooth muscle, also known as visceral smooth muscle, and multiunit smooth muscle. M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scorpion Toxin
Scorpion toxins are proteins found in the venom of scorpions. Their toxic effect may be mammal- or insect-specific and acts by binding with varying degrees of specificity to members of the Voltage-gated ion channel superfamily; specifically, voltage-gated sodium channels, voltage-gated potassium channels, and Transient Receptor Potential (TRP) channels. The result of this action is to activate or inhibit the action of these channels in the nervous and cardiac organ systems. For instance, α-scorpion toxins MeuNaTxα-12 and MeuNaTxα-13 from ''Mesobuthus eupeus'' are neurotoxins that target voltage-gated Na+ channels (Navs), inhibiting fast inactivation. ''In vivo'' assays of MeuNaTxα-12 and MeuNaTxα-13 effects on mammalian and insect Navs show differential potency. These recombinants (MeuNaTxα-12 and MeuNaTxα-13) exhibit their preferential affinity for mammalian and insect Na+ channels at the α-like toxins' active site, site 3, in order to inactivate the cell membrane depolari ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |