|
Polyetherketones
Polyetherketones (PEK for short) are polymers whose molecular backbone contain alternating ketone (R-CO-R) and Ether (R-O-R) functionalities. The most common are Polyaryletherketones (PAEK), in which there is an aryl group linked in the (1–4)-position between each of the functional groups. The backbone, which is thus very rigid, gives the materials very high glass transition and melting temperatures compared to other plastics. Synthesis Polyetherketones can be obtained by condensation of 4,4′-difluorobenzophenone and potassium or sodium salt of hydroquinone: : Types The most common of these high-temperature resistant materials is polyetheretherketone (PEEK). Other types of polyetherketone are: * PEKK = Polyetherketoneketone * PEEKK = Polyether ether ketone ketone * PEKEKK = Polyetherketoneetherketoneketone Applications Space and aviation: aircraft parts (fins, wing flaps, nose caps, seats). Replacements for metal parts, also in the military field. Machinery an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polymer
A polymer (; Greek '' poly-'', "many" + ''-mer'', "part") is a substance or material consisting of very large molecules called macromolecules, composed of many repeating subunits. Due to their broad spectrum of properties, both synthetic and natural polymers play essential and ubiquitous roles in everyday life. Polymers range from familiar synthetic plastics such as polystyrene to natural biopolymers such as DNA and proteins that are fundamental to biological structure and function. Polymers, both natural and synthetic, are created via polymerization of many small molecules, known as monomers. Their consequently large molecular mass, relative to small molecule compounds, produces unique physical properties including toughness, high elasticity, viscoelasticity, and a tendency to form amorphous and semicrystalline structures rather than crystals. The term "polymer" derives from the Greek word πολύς (''polus'', meaning "many, much") and μέρος (''meros'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
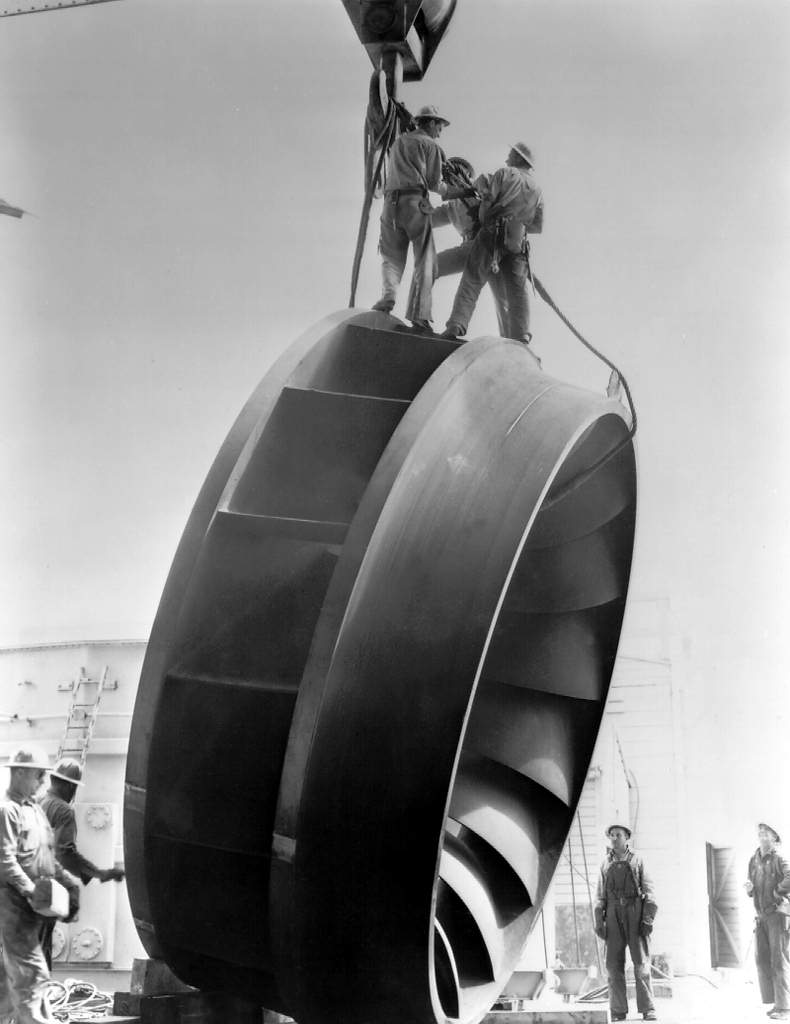
Impeller
An impeller or impellor is a rotor used to increase the pressure and flow of a fluid. It is the opposite of a turbine, which extracts energy from, and reduces the pressure of, a flowing fluid. In pumps An impeller is a rotating component of a centrifugal pump that accelerates fluid outward from the center of rotation, thus transferring energy from the motor that drives the pump to the fluid being pumped. The velocity achieved by the impeller transfers into pressure when the outward movement of the fluid is confined by the pump casing. An impeller is usually a short cylinder with an open inlet (called an eye) to accept incoming fluid, vanes to push the fluid radially, and a splined, keyed, or threaded bore to accept a drive shaft. It can be cheaper to cast an impeller and its spindle as one piece, rather than separately. This combination is sometimes referred to simply as the "rotor." Types Open impellers An open impeller has a hub with attached vanes and is moun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ethers
In organic chemistry, ethers are a class of compounds that contain an ether group—an oxygen atom connected to two alkyl or aryl groups. They have the general formula , where R and R′ represent the alkyl or aryl groups. Ethers can again be classified into two varieties: if the alkyl or aryl groups are the same on both sides of the oxygen atom, then it is a simple or symmetrical ether, whereas if they are different, the ethers are called mixed or unsymmetrical ethers. A typical example of the first group is the solvent and anaesthetic diethyl ether, commonly referred to simply as "ether" (). Ethers are common in organic chemistry and even more prevalent in biochemistry, as they are common linkages in carbohydrates and lignin. Structure and bonding Ethers feature bent C–O–C linkages. In dimethyl ether, the bond angle is 111° and C–O distances are 141 pm. The barrier to rotation about the C–O bonds is low. The bonding of oxygen in ethers, alcohols, and water is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alkali
In chemistry, an alkali (; from ar, القلوي, al-qaly, lit=ashes of the saltwort) is a basic, ionic salt of an alkali metal or an alkaline earth metal. An alkali can also be defined as a base that dissolves in water. A solution of a soluble base has a pH greater than 7.0. The adjective alkaline, and less often, alkalescent, is commonly used in English as a synonym for basic, especially for bases soluble in water. This broad use of the term is likely to have come about because alkalis were the first bases known to obey the Arrhenius definition of a base, and they are still among the most common bases. Etymology The word "alkali" is derived from Arabic ''al qalīy'' (or ''alkali''), meaning ''the calcined ashes'' (see calcination), referring to the original source of alkaline substances. A water-extract of burned plant ashes, called potash and composed mostly of potassium carbonate, was mildly basic. After heating this substance with calcium hydroxide (''slaked lim ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Water Vapor
(99.9839 °C) , - , Boiling point , , - , specific gas constant , 461.5 J/( kg·K) , - , Heat of vaporization , 2.27 MJ/kg , - , Heat capacity , 1.864 kJ/(kg·K) Water vapor, water vapour or aqueous vapor is the gaseous phase of water. It is one state of water within the hydrosphere. Water vapor can be produced from the evaporation or boiling of liquid water or from the sublimation of ice. Water vapor is transparent, like most constituents of the atmosphere. Under typical atmospheric conditions, water vapor is continuously generated by evaporation and removed by condensation. It is less dense than most of the other constituents of air and triggers convection currents that can lead to clouds. Being a component of Earth's hydrosphere and hydrologic cycle, it is particularly abundant in Earth's atmosphere, where it acts as a greenhouse gas and warming feedback, contributing more to total greenhouse effect than non-condensable gases such as carbon diox ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lubricant
A lubricant (sometimes shortened to lube) is a substance that helps to reduce friction between surfaces in mutual contact, which ultimately reduces the heat generated when the surfaces move. It may also have the function of transmitting forces, transporting foreign particles, or heating or cooling the surfaces. The property of reducing friction is known as lubricity. In addition to industrial applications, lubricants are used for many other purposes. Other uses include cooking ( oils and fats in use in frying pans, in baking to prevent food sticking), bioapplications on humans (e.g. lubricants for artificial joints), ultrasound examination, medical examination, and sexual intercourse. It is mainly used to reduce friction and to contribute to a better and efficient functioning of a mechanism. History Lubricants have been in some use for thousands of years. Calcium soaps have been identified on the axles of chariots dated to 1400 BC. Building stones were slid on oil-impregrate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grease (lubricant)
Grease is a solid or semisolid lubricant formed as a dispersion of thickening agents in a liquid lubricant. Grease generally consists of a soap emulsified with mineral or vegetable oil. A common feature of greases is that they possess a high initial viscosity, which upon the application of shear, drops to give the effect of an oil-lubricated bearing of approximately the same viscosity as the base oil used in the grease. This change in viscosity is called shear thinning. Grease is sometimes used to describe lubricating materials that are simply soft solids or high viscosity liquids, but these materials do not exhibit the shear-thinning properties characteristic of the classical grease. For example, petroleum jellies such as Vaseline are not generally classified as greases. Greases are applied to mechanisms that can be lubricated only infrequently and where a lubricating oil would not stay in position. They also act as sealants to prevent ingress of water and incompressible mat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acid
In computer science, ACID ( atomicity, consistency, isolation, durability) is a set of properties of database transactions intended to guarantee data validity despite errors, power failures, and other mishaps. In the context of databases, a sequence of database operations that satisfies the ACID properties (which can be perceived as a single logical operation on the data) is called a ''transaction''. For example, a transfer of funds from one bank account to another, even involving multiple changes such as debiting one account and crediting another, is a single transaction. In 1983, Andreas Reuter and Theo Härder coined the acronym ''ACID'', building on earlier work by Jim Gray who named atomicity, consistency, and durability, but not isolation, when characterizing the transaction concept. These four properties are the major guarantees of the transaction paradigm, which has influenced many aspects of development in database systems. According to Gray and Reuter, the IBM Inf ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
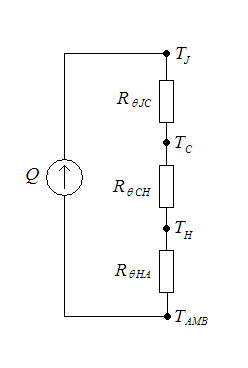
Thermal Resistance
Thermal resistance is a heat property and a measurement of a temperature difference by which an object or material resists a heat flow. Thermal resistance is the reciprocal of thermal conductance. * (Absolute) thermal resistance ''R'' in kelvins per watt (K/W) is a property of a particular component. For example, a characteristic of a heat sink. * Specific thermal resistance or thermal resistivity ''Rλ'' in kelvin–metres per watt (K⋅m/W), is a material constant. * Thermal insulance has the units square metre kelvin per watt (m2⋅K/W) in SI units or square foot degree Fahrenheit–hours per British thermal unit (ft2⋅°F⋅h/Btu) in imperial units. It is the thermal resistance of unit area of a material. In terms of insulation, it is measured by the R-value. Absolute thermal resistance Absolute thermal resistance is the temperature difference across a structure when a unit of heat energy flows through it in unit time. It is the reciprocal of thermal conductance. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sterilization (microbiology)
Sterilization refers to any process that removes, kills, or deactivates all forms of life (particularly microorganisms such as fungi, bacteria, spores, and unicellular eukaryotic organisms) and other biological agents such as prions present in or on a specific surface, object, or fluid. Sterilization can be achieved through various means, including heat, chemicals, irradiation, high pressure, and filtration. Sterilization is distinct from disinfection, sanitization, and pasteurization, in that those methods reduce rather than eliminate all forms of life and biological agents present. After sterilization, an object is referred to as being sterile or aseptic. Applications Foods One of the first steps toward modernized sterilization was made by Nicolas Appert, who discovered that application of heat over a suitable period slowed the decay of foods and various liquids, preserving them for safe consumption for a longer time than was typical. Canning of foods is an extension ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prosthesis
In medicine, a prosthesis (plural: prostheses; from grc, πρόσθεσις, prósthesis, addition, application, attachment), or a prosthetic implant, is an artificial device that replaces a missing body part, which may be lost through trauma, disease, or a condition present at birth (congenital disorder). Prostheses are intended to restore the normal functions of the missing body part. Amputee rehabilitation is primarily coordinated by a physiatrist as part of an inter-disciplinary team consisting of physiatrists, prosthetists, nurses, physical therapists, and occupational therapists. Prostheses can be created by hand or with computer-aided design (CAD), a software interface that helps creators design and analyze the creation with computer-generated 2-D and 3-D graphics as well as analysis and optimization tools. Types A person's prosthesis should be designed and assembled according to the person's appearance and functional needs. For instance, a person may need a trans ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
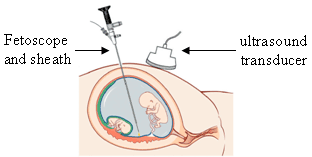
Endoscope
An endoscope is an inspection instrument composed of image sensor, optical lens, light source and mechanical device, which is used to look deep into the body by way of openings such as the mouth or anus. A typical endoscope applies several modern technologies including optics, ergonomics, precision mechanics, electronics, and software engineering. With an endoscope, it is possible to observe lesions that cannot be detected by X-ray, making it useful in medical diagnosis. Endoscopes use tubes which are only a few millimeters thick to transfer illumination in one direction and high-resolution images in real time in the other direction, resulting in minimally invasive surgeries. It is used to examine the internal organs like the throat or esophagus. Specialized instruments are named after their target organ. Examples include the cystoscope (bladder), nephroscope (kidney), bronchoscope ( bronchus), arthroscope (joints) and colonoscope (colon), and laparoscope (abdomen or pelvis). Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |