|
Polyamorphism
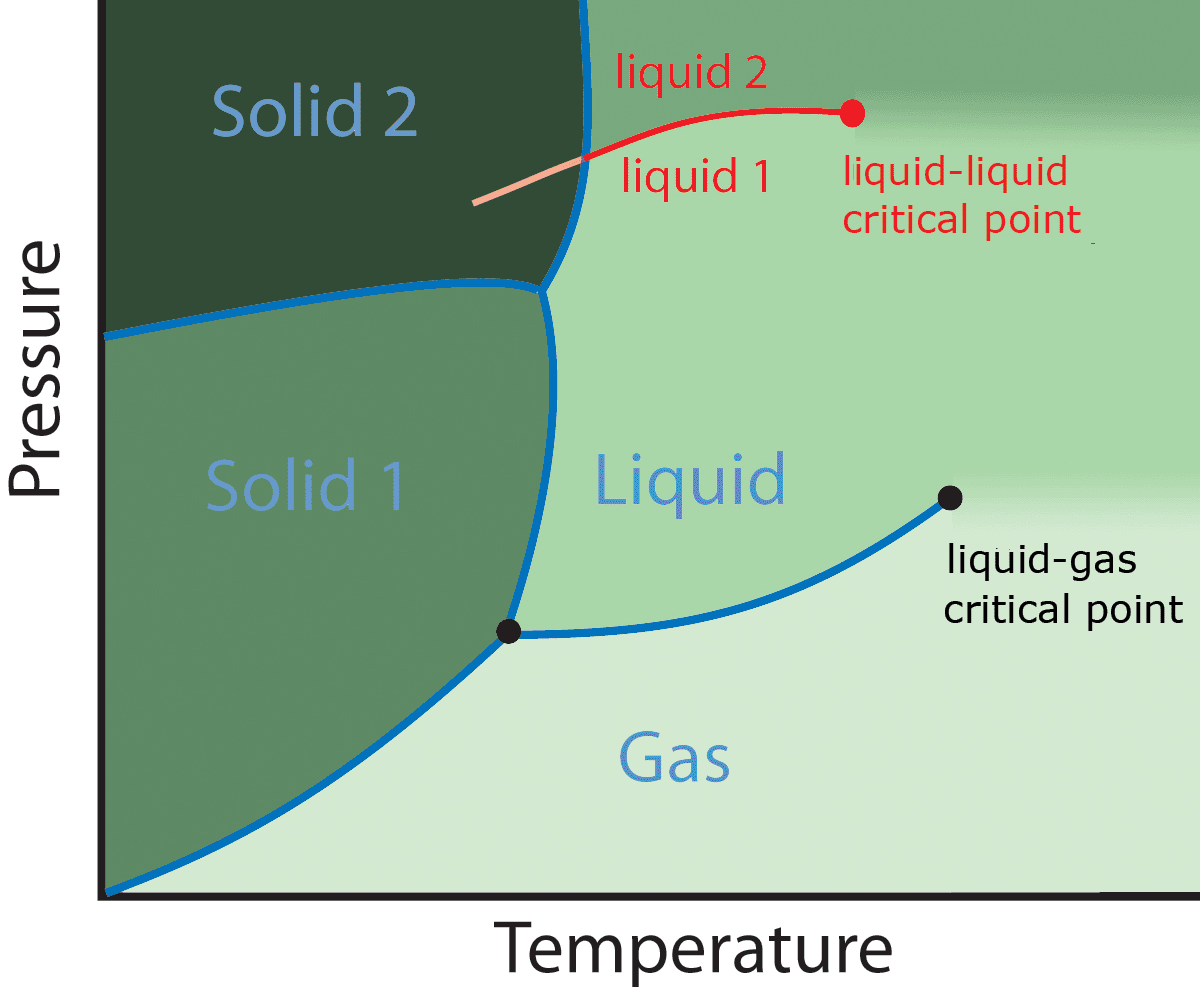
Polyamorphism is the ability of a substance to exist in several different amorphous modifications. It is analogous to the polymorphism of crystalline materials. Many amorphous substances can exist with different amorphous characteristics (e.g. polymers). However, polyamorphism requires ''two distinct'' amorphous states with a clear, discontinuous (first-order) phase transition between them. When such a transition occurs between two stable liquid states, a polyamorphic transition may also be referred to as a liquid–liquid phase transition. Overview Even though amorphous materials exhibit no long-range periodic atomic ordering, there is still significant and varied local structure at inter-atomic length scales (see structure of liquids and glasses). Different local structures can produce amorphous phases of the same chemical composition with different physical properties such as density. In several cases sharp transitions have been observed between two different density amor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Triphenyl Phosphite
Triphenyl phosphite is the organophosphorus compound with the formula P(OC6H5)3. It is a colourless viscous liquid. Preparation Triphenylphosphite is prepared from phosphorus trichloride and phenol in the presence of a catalytic amount of base: :PCl3 + 3 HOC6H5 → P(OC6H5)3 + 3 HCl Reactions Triphenylphosphite is a precursor to trimethylphosphine, it serves as a source of P3+ that is less electrophilic than phosphorus trichloride: : (C6H5O)3P + 3CH3MgBr → P(CH3)3 + 3"MgBrOC6H5" Triphenylphosphite is quaternized by methyl iodide: : (C6H5O)3P + CH3I → H3(C6H5O)3Psup>+I− Coordination complexes Triphenylphosphite is a common ligand in coordination chemistry. It forms zero-valent complexes of the type M (OC6H5)3sub>4 (M = Ni, Pd, Pt). The nickel complex can be prepared by displacement of the diene from bis(cyclooctadiene)nickel: : Ni(COD)2 + 4 P(OC6H5)3 → Ni (OC6H5)3sub>4 + 2 COD Related complexes are homogeneous catalysts for the hydrocyanation of alkenes. It also ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polymorphism (materials Science)
In materials science, polymorphism describes the existence of a solid material in more than one form or crystal structure. Polymorphism is a form of isomerism. Any crystalline material can exhibit the phenomenon. Allotropy refers to polymorphism for chemical elements. Polymorphism is of practical relevance to pharmaceuticals, agrochemicals, pigments, dyestuffs, foods, and explosives. According to IUPAC, a polymorphic transition is "A reversible transition of a solid crystalline phase at a certain temperature and pressure (the inversion point) to another phase of the same chemical composition with a different crystal structure." According to McCrone, polymorphs are "different in crystal structure but identical in the liquid or vapor states." Materials with two polymorphs are called dimorphic, with three polymorphs, trimorphic, etc. Examples Many compounds exhibit polymorphism. It has been claimed that "every compound has different polymorphic forms, and that, in general, the n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crystal
A crystal or crystalline solid is a solid material whose constituents (such as atoms, molecules, or ions) are arranged in a highly ordered microscopic structure, forming a crystal lattice that extends in all directions. In addition, macroscopic single crystals are usually identifiable by their geometrical shape, consisting of flat faces with specific, characteristic orientations. The scientific study of crystals and crystal formation is known as crystallography. The process of crystal formation via mechanisms of crystal growth is called crystallization or solidification. The word ''crystal'' derives from the Ancient Greek word (), meaning both "ice" and "rock crystal", from (), "icy cold, frost". Examples of large crystals include snowflakes, diamonds, and table salt. Most inorganic solids are not crystals but polycrystals, i.e. many microscopic crystals fused together into a single solid. Polycrystals include most metals, rocks, ceramics, and ice. A third category of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polymorphism (materials Science)
In materials science, polymorphism describes the existence of a solid material in more than one form or crystal structure. Polymorphism is a form of isomerism. Any crystalline material can exhibit the phenomenon. Allotropy refers to polymorphism for chemical elements. Polymorphism is of practical relevance to pharmaceuticals, agrochemicals, pigments, dyestuffs, foods, and explosives. According to IUPAC, a polymorphic transition is "A reversible transition of a solid crystalline phase at a certain temperature and pressure (the inversion point) to another phase of the same chemical composition with a different crystal structure." According to McCrone, polymorphs are "different in crystal structure but identical in the liquid or vapor states." Materials with two polymorphs are called dimorphic, with three polymorphs, trimorphic, etc. Examples Many compounds exhibit polymorphism. It has been claimed that "every compound has different polymorphic forms, and that, in general, the n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Structure Of Liquids And Glasses
The structure of liquids, glasses and other non-crystalline solids is characterized by the absence of long-range order which defines crystalline materials. Liquids and amorphous solids do, however, possess a rich and varied array of short to medium range order, which originates from chemical bonding and related interactions. Metallic glasses, for example, are typically well described by the dense random packing of hard spheres, whereas covalent systems, such as silicate glasses, have sparsely packed, strongly bound, tetrahedral network structures. These very different structures result in materials with very different physical properties and applications. The study of liquid and glass structure aims to gain insight into their behavior and physical properties, so that they can be understood, predicted and tailored for specific applications. Since the structure and resulting behavior of liquids and glasses is a complex many body problem, historically it has been too computationally ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yttria
Yttrium oxide, also known as yttria, is Y2 O3. It is an air-stable, white solid substance. The thermal conductivity of yttrium oxide is 27 W/(m·K). Uses Phosphors Yttria is widely used to make Eu:YVO4 and Eu:Y2O3 phosphors that give the red color in color TV picture tubes. Yttria lasers Y2O3 is a prospective solid-state laser material. In particular, lasers with ytterbium as dopant allow the efficient operation both in continuous operation and in pulsed regimes. At high concentration of excitations (of order of 1%) and poor cooling, the quenching of emission at laser frequency and avalanche broadband emission takes place. (Yttria-based lasers are not to be confused with YAG lasers using yttrium aluminum garnet, a widely used crystal host for rare earth laser dopants). Gas Lighting The original use of the mineral yttria and the purpose of its extraction from mineral sources was as part of the process of making gas mantles and other products for turning the flames of artifici ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Silicon Dioxide
Silicon dioxide, also known as silica, is an oxide of silicon with the chemical formula , most commonly found in nature as quartz and in various living organisms. In many parts of the world, silica is the major constituent of sand. Silica is one of the most complex and most abundant families of materials, existing as a compound of several minerals and as a synthetic product. Notable examples include fused quartz, fumed silica, silica gel, opal and aerogels. It is used in structural materials, microelectronics (as an electrical insulator), and as components in the food and pharmaceutical industries. Structure In the majority of silicates, the silicon atom shows tetrahedral coordination, with four oxygen atoms surrounding a central Si atomsee 3-D Unit Cell. Thus, SiO2 forms 3-dimensional network solids in which each silicon atom is covalently bonded in a tetrahedral manner to 4 oxygen atoms. In contrast, CO2 is a linear molecule. The starkly different structures of the dioxid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Germanium Dioxide
Germanium dioxide, also called germanium(IV) oxide, germania, and salt of germanium, is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula Ge O2. It is the main commercial source of germanium. It also forms as a passivation layer on pure germanium in contact with atmospheric oxygen. Structure The two predominant polymorphs of GeO2 are hexagonal and tetragonal. Hexagonal GeO2 has the same structure as β-quartz, with germanium having coordination number 4. Tetragonal GeO2 (the mineral argutite) has the rutile-like structure seen in stishovite. In this motif, germanium has the coordination number 6. An amorphous (glassy) form of GeO2 is similar to fused silica. Germanium dioxide can be prepared in both crystalline and amorphous forms. At ambient pressure the amorphous structure is formed by a network of GeO4 tetrahedra. At elevated pressure up to approximately 9 GPa the germanium average coordination number steadily increases from 4 to around 5 with a corresponding increas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Liquid
A liquid is a nearly incompressible fluid that conforms to the shape of its container but retains a (nearly) constant volume independent of pressure. As such, it is one of the four fundamental states of matter (the others being solid, gas, and plasma), and is the only state with a definite volume but no fixed shape. A liquid is made up of tiny vibrating particles of matter, such as atoms, held together by intermolecular bonds. Like a gas, a liquid is able to flow and take the shape of a container. Most liquids resist compression, although others can be compressed. Unlike a gas, a liquid does not disperse to fill every space of a container, and maintains a fairly constant density. A distinctive property of the liquid state is surface tension, leading to wetting phenomena. Water is by far the most common liquid on Earth. The density of a liquid is usually close to that of a solid, and much higher than that of a gas. Therefore, liquid and solid are both termed condensed matte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
N-Butanol
1-Butanol, also known as butan-1-ol or ''n''-butanol, is a primary alcohol with the chemical formula C4H9OH and a linear structure. Isomers of 1-butanol are isobutanol, butan-2-ol and ''tert''-butanol. The unmodified term butanol usually refers to the straight chain isomer. 1-Butanol occurs naturally as a minor product of the ethanol fermentation of sugars and other saccharides and is present in many foods and drinks... It is also a permitted artificial flavorant in the United States, used in butter, cream, fruit, rum, whiskey, ice cream and ices, candy, baked goods, and cordials. It is also used in a wide range of consumer products. The largest use of 1-butanol is as an industrial intermediate, particularly for the manufacture of butyl acetate (itself an artificial flavorant and industrial solvent). It is a petrochemical derived from propylene. Estimated production figures for 1997 are: United States 784,000 tonnes; Western Europe 575,000 tonnes; Japan 225,000 to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |