|
Platinum(II) Acetate
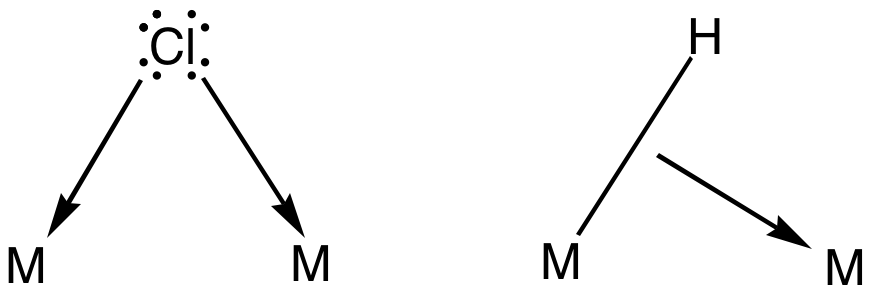
Platinum(II) acetate is a purple-colored coordination complex. The complex adopts an unusual structure consisting of a square array of Pt atoms. Preparation Several syntheses of platinum(II) acetate have been reported. Geoffrey Wilkinson ''et al.'' reported a synthesis from sodium hexahydroxyplatinate, nitric acid, and acetic acid. This intermediate solution was reducted with formic acid. The procedure is not highly reproducible. Alternatively, the complex can be prepared by the reaction of silver acetate with platinum(II) chloride. Structure According to X-ray crystallography X-ray crystallography is the experimental science determining the atomic and molecular structure of a crystal, in which the crystalline structure causes a beam of incident X-rays to diffract into many specific directions. By measuring the angles ..., the complex is tetrameric, in contrast to the trimeric palladium analog. The four platinum atoms form a square cluster, with eight bridging acetate liga ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coordination Complex
A coordination complex consists of a central atom or ion, which is usually metallic and is called the ''coordination centre'', and a surrounding array of bound molecules or ions, that are in turn known as '' ligands'' or complexing agents. Many metal-containing compounds, especially those that include transition metals (elements like titanium that belong to the Periodic Table's d-block), are coordination complexes. Nomenclature and terminology Coordination complexes are so pervasive that their structures and reactions are described in many ways, sometimes confusingly. The atom within a ligand that is bonded to the central metal atom or ion is called the donor atom. In a typical complex, a metal ion is bonded to several donor atoms, which can be the same or different. A polydentate (multiple bonded) ligand is a molecule or ion that bonds to the central atom through several of the ligand's atoms; ligands with 2, 3, 4 or even 6 bonds to the central atom are common. These ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geoffrey Wilkinson
Sir Geoffrey Wilkinson FRS (14 July 1921 – 26 September 1996) was a Nobel laureate English chemist who pioneered inorganic chemistry and homogeneous transition metal catalysis. Education and early life Wilkinson was born at Springside, Todmorden, in the West Riding of Yorkshire. His father, Henry Wilkinson, was a master house painter and decorator; his mother, Ruth, worked in a local cotton mill. One of his uncles, an organist and choirmaster, had married into a family that owned a small chemical company making Epsom and Glauber's salts for the pharmaceutical industry; this is where he first developed an interest in chemistry. He was educated at the local council primary school and, after winning a County Scholarship in 1932, went to Todmorden Grammar School. His physics teacher there, Luke Sutcliffe, had also taught Sir John Cockcroft, who received a Nobel Prize for "splitting the atom". In 1939 he obtained a Royal Scholarship for study at Imperial College London, from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Silver Acetate
Silver acetate is an coordination compound with the empirical formula CH3CO2Ag (or AgC2H3O2). A photosensitive, white, crystalline solid, it is a useful reagent in the laboratory as a source of silver ions lacking an oxidizing anion. Synthesis and structure Silver acetate can be synthesized by the reaction of acetic acid and silver carbonate. :2 CH3CO2H + Ag2CO3 → 2 AgO2CCH3 + H2O + CO2 Solid silver acetate precipitates upon concentration of solutions of silver nitrate and sodium acetate. The structure of silver acetate consists of 8-membered Ag2O4C2 rings formed by a pair of acetate ligands bridging a pair of silver centres. Reactions Silver acetate finds use in certain transformations in organic synthesis. Sulfenamide synthesis Silver acetate is used to prepare sulfenamides from disulfides and secondary amines: : R2NH + AgOAc + (RS)2 → R2NSR + AgSR + HOAc Hydrogenation A solution of silver acetate in pyridine absorbs hydrogen, producing metallic silver: :2 CH3CO2Ag + ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Platinum(II) Chloride
Platinum(II) chloride is the chemical compound Pt Cl2. It is an important precursor used in the preparation of other platinum compounds. It exists in two crystalline forms, but the main properties are somewhat similar: dark brown, insoluble in water, diamagnetic, and odorless. Structure The structures of PtCl2 and PdCl2 are similar. These dichlorides exist in both polymeric, or "α", and hexameric, or "β" structures. The β form converts to the α form at 500 °C. In the β form, the Pt-Pt distances are 3.32–3.40 Å, indicative of some bonding between the pairs of metals. In both forms of PtCl2, each Pt center is four-coordinate, being surrounded by four chloride ligands. Complementarily, each Cl center is two-coordinate, being connected to two platinum atoms. The structure of α-PtCl2 is reported to be disordered and contain edge- and/or corner-sharing square-planar PtCl4 units. Preparation β-PtCl2 is prepared by heating chloroplatinic acid to 350 °C in a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inorganica Chimica Acta
''Inorganica Chimica Acta'' is a peer-reviewed scientific journal published since 1967 that covers original research and reviews of fundamental and applied aspects of inorganic chemistry. See also * List of scientific journals in chemistry A ''list'' is any set of items in a row. List or lists may also refer to: People * List (surname) Organizations * List College, an undergraduate division of the Jewish Theological Seminary of America * SC Germania List, German rugby unio ... External links * Elsevier academic journals Inorganic chemistry journals Publications established in 1967 English-language journals Journals published between 13 and 25 times per year {{chem-journal-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
X-ray Crystallography
X-ray crystallography is the experimental science determining the atomic and molecular structure of a crystal, in which the crystalline structure causes a beam of incident X-rays to diffract into many specific directions. By measuring the angles and intensities of these diffracted beams, a crystallographer can produce a three-dimensional picture of the density of electrons within the crystal. From this electron density, the mean positions of the atoms in the crystal can be determined, as well as their chemical bonds, their crystallographic disorder, and various other information. Since many materials can form crystals—such as salts, metals, minerals, semiconductors, as well as various inorganic, organic, and biological molecules—X-ray crystallography has been fundamental in the development of many scientific fields. In its first decades of use, this method determined the size of atoms, the lengths and types of chemical bonds, and the atomic-scale differences among variou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bridging Ligand
In coordination chemistry, a bridging ligand is a ligand that connects two or more atoms, usually metal ions. The ligand may be atomic or polyatomic. Virtually all complex organic compounds can serve as bridging ligands, so the term is usually restricted to small ligands such as pseudohalides or to ligands that are specifically designed to link two metals. In naming a complex wherein a single atom bridges two metals, the bridging ligand is preceded by the Greek letter mu, μ, with a subscript number denoting the number of metals bound to the bridging ligand. μ2 is often denoted simply as μ. When describing coordination complexes care should be taken not to confuse μ with η ('eta'), which relates to hapticity. Ligands that are not bridging are called terminal ligands. List of bridging ligands Virtually all ligands are known to bridge, with the exception of amines and ammonia. Common bridging ligands include most of the common anions. Many simple organic ligands form st ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coordination Complexes
A coordination complex consists of a central atom or ion, which is usually metallic and is called the ''coordination centre'', and a surrounding array of bound molecules or ions, that are in turn known as ''ligands'' or complexing agents. Many metal-containing compounds, especially those that include transition metals (elements like titanium that belong to the Periodic Table's d-block), are coordination complexes. Nomenclature and terminology Coordination complexes are so pervasive that their structures and reactions are described in many ways, sometimes confusingly. The atom within a ligand that is bonded to the central metal atom or ion is called the donor atom. In a typical complex, a metal ion is bonded to several donor atoms, which can be the same or different. A polydentate (multiple bonded) ligand is a molecule or ion that bonds to the central atom through several of the ligand's atoms; ligands with 2, 3, 4 or even 6 bonds to the central atom are common. These compl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Platinum(II) Compounds
Platinum is a chemical element with the symbol Pt and atomic number 78. It is a dense, malleable, ductile, highly unreactive, precious, silverish-white transition metal. Its name originates from Spanish , a diminutive of "silver". Platinum is a member of the platinum group of elements and group 10 of the periodic table of elements. It has six naturally occurring isotopes. It is one of the rarer elements in Earth's crust, with an average abundance of approximately 5 μg/kg. It occurs in some nickel and copper ores along with some native deposits, mostly in South Africa, which accounts for ~80% of the world production. Because of its scarcity in Earth's crust, only a few hundred tonnes are produced annually, and given its important uses, it is highly valuable and is a major precious metal commodity. Platinum is one of the least reactive metals. It has remarkable resistance to corrosion, even at high temperatures, and is therefore considered a noble metal. Conseq ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |