|
Placozoan
The Placozoa are a basal form of marine free-living (non-parasitic) multicellular organism. They are the simplest in structure of all animals. Three genera have been found: the classical '' Trichoplax adhaerens'', '' Hoilungia hongkongensis'', and '' Polyplacotoma mediterranea'', where the last appears most basal. The last two have been found only since 2017. Although the Placozoa were first discovered in 1883 by the German zoologist Franz Eilhard Schulze (1840–1921) and since the 1970s more systematically analyzed by the German protozoologist Karl Gottlieb Grell (1912–1994), a common name does not yet exist for the taxon; the scientific name means "flat animals". Biology ''Trichoplax'' is a small, flattened, animal around across. An amorphous multi-celled body, analogous to a single-celled ''Amoeba'', it has no regular outline, although the lower surface is somewhat concave, and the upper surface is always flattened. The body consists of an outer layer of simple epithe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trichoplax Adhaerens
''Trichoplax adhaerens'' is one of the three named species in the phylum Placozoa. The others are '' Hoilungia hongkongensis'' and '' Polyplacotoma mediterranea''. The Placozoa is a basal group of multicellular animals (metazoa). ''Trichoplax'' are very flat organisms around a millimetre in diameter, lacking any organs or internal structures. They have two cellular layers: the top epitheloid layer is made of ciliated «cover cells» flattened toward the outside of the organism, and the bottom layer is made up of cylinder cells that possess cilia used in locomotion, and gland cells that lack cilia. Between these layers is the fibre syncytium, a liquid-filled cavity strutted open by star-like fibres. ''Trichoplax'' feed by absorbing food particles—mainly microbes—with their underside. They generally reproduce asexually, by dividing or budding, but can also reproduce sexually. Though ''Trichoplax'' has a small genome in comparison to other animals, nearly 87% of its 11,514 p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
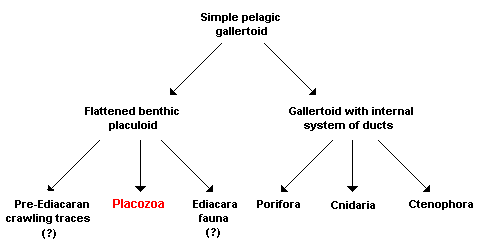
Placozoa
The Placozoa are a basal form of marine free-living (non-parasitic) multicellular organism. They are the simplest in structure of all animals. Three genera have been found: the classical ''Trichoplax adhaerens'', '' Hoilungia hongkongensis'', and '' Polyplacotoma mediterranea'', where the last appears most basal. The last two have been found only since 2017. Although the Placozoa were first discovered in 1883 by the German zoologist Franz Eilhard Schulze (1840–1921) and since the 1970s more systematically analyzed by the German protozoologist Karl Gottlieb Grell (1912–1994), a common name does not yet exist for the taxon; the scientific name means "flat animals". Biology ''Trichoplax'' is a small, flattened, animal around across. An amorphous multi-celled body, analogous to a single-celled ''Amoeba'', it has no regular outline, although the lower surface is somewhat concave, and the upper surface is always flattened. The body consists of an outer layer of simple epithel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Placozoan Anatomy
The Placozoa are a basal form of marine free-living (non-parasitic) multicellular organism. They are the simplest in structure of all animals. Three genera have been found: the classical ''Trichoplax adhaerens'', ''Hoilungia hongkongensis'', and ''Polyplacotoma mediterranea'', where the last appears most basal. The last two have been found only since 2017. Although the Placozoa were first discovered in 1883 by the German zoologist Franz Eilhard Schulze (1840–1921) and since the 1970s more systematically analyzed by the German protozoologist Karl Gottlieb Grell (1912–1994), a common name does not yet exist for the taxon; the scientific name means "flat animals". Biology ''Trichoplax'' is a small, flattened, animal around across. An amorphous multi-celled body, analogous to a single-celled ''Amoeba'', it has no regular outline, although the lower surface is somewhat concave, and the upper surface is always flattened. The body consists of an outer layer of simple epitheliu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trichoplacidae
''Trichoplax adhaerens'' is one of the three named species in the phylum Placozoa. The others are ''Hoilungia hongkongensis'' and ''Polyplacotoma mediterranea''. The Placozoa is a basal group of multicellular animals (metazoa). ''Trichoplax'' are very flat organisms around a millimetre in diameter, lacking any organs or internal structures. They have two cellular layers: the top epitheloid layer is made of ciliated «cover cells» flattened toward the outside of the organism, and the bottom layer is made up of cylinder cells that possess cilia used in locomotion, and gland cells that lack cilia. Between these layers is the fibre syncytium, a liquid-filled cavity strutted open by star-like fibres. ''Trichoplax'' feed by absorbing food particles—mainly microbes—with their underside. They generally reproduce asexually, by dividing or budding, but can also reproduce sexually. Though ''Trichoplax'' has a small genome in comparison to other animals, nearly 87% of its 11,514 pre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hoilungia Hongkongensis
''Hoilungia hongkongensis'' is a species in the phylum Placozoa. The organism appears superficially similar to ''Trichoplax adhaerens'', but genetic analysis of its mitochondrial DNA shows numerous differences. It was discovered in brackish water from mangrove swamps in Hong Kong. These organisms are generally found in the biofilm surfaces in tropical and subtropical environments. Phylogenetically, they are placed closest to cnidarians. They are diploblastic animals and are believed to have dorso-ventral polarity along top and bottom body layers. Their body is overtly similar to oral-aboral axis of cnidarians. They feed from lower tissue layer which has various peptidergic gland cells. They feed on algae, bacteria, yeast and other byproducts of biofilms. They reproduce asexually through binary fission and there is also some evidence of sexual reproduction. The ''Hoilungia hongkongensis'' genome adds support to the phylogenetic placement of the Placozoa in the animal tree of life N ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polyplacotoma Mediterranea
''Polyplacotoma mediterranea'' is a species in the phylum Placozoa The Placozoa are a basal form of marine free-living (non-parasitic) multicellular organism. They are the simplest in structure of all animals. Three genera have been found: the classical ''Trichoplax adhaerens'', ''Hoilungia hongkongensis'', an ..., only representative of the genus ''Polyplacotoma''. They differ greatly from other species of placozoans with regards to their morphology and genetic makeup. ''P. mediterranea'' has the smallest mitogenome, the lowest GC content, and the smallest intergenic spacer regions of all placozoans. Their bodily structure consists of elongated polytomous body branches, as well as a maximum size that is greater than 10 mm in length. The mitochondrial genome of ''Polyplacotoma mediterranea'' is also very compact and contains overlapping protein and tRNA gene codes.Miyazawa, H., Osigus, H., Rolfes, S., Kamm, K., Schierwater, B., & Nakano, H. (2020). Mitochondrial Genome Evolu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dickinsonia
''Dickinsonia'' is an extinct genus of basal animal that lived during the late Ediacaran period in what is now Australia, China, Russia and Ukraine. The individual ''Dickinsonia'' typically resembles a bilaterally symmetrical ribbed oval. Its affinities are presently unknown; its mode of growth is consistent with a stem-group bilaterian affinity, though some have suggested that it belongs to the fungi, or even an "extinct kingdom". It lived during the late Ediacaran (part of Precambrian). The discovery of cholesterol molecules in fossils of ''Dickinsonia'' lends support to the idea that ''Dickinsonia'' was an animal. Description ''Dickinsonia'' fossils are known only in the form of imprints and casts in sandstone beds. The specimens found range from a few millimetres to about in length, and from a fraction of a millimetre to a few millimetres thick. They are nearly bilaterally symmetric, segmented, round or oval in outline, slightly expanded to one end (i.e. egg-shaped ou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ediacaran Biota
The Ediacaran (; formerly Vendian) biota is a taxonomic period classification that consists of all life forms that were present on Earth during the Ediacaran Period (). These were composed of enigmatic tubular and frond-shaped, mostly sessile, organisms. Trace fossils of these organisms have been found worldwide, and represent the earliest known complex multicellular organisms. The Ediacaran biota may have undergone evolutionary radiation in a proposed event called the Avalon explosion, . This was after the Earth had thawed from the Cryogenian period's extensive glaciation. This biota largely disappeared with the rapid increase in biodiversity known as the Cambrian explosion. Most of the currently existing body plans of animals first appeared in the fossil record of the Cambrian rather than the Ediacaran. For macroorganisms, the Cambrian biota appears to have almost completely replaced the organisms that dominated the Ediacaran fossil record, although relationships ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genetic Recombination
Genetic recombination (also known as genetic reshuffling) is the exchange of genetic material between different organisms which leads to production of offspring with combinations of traits that differ from those found in either parent. In eukaryotes, genetic recombination during meiosis can lead to a novel set of genetic information that can be further passed on from parents to offspring. Most recombination occurs naturally and can be classified into two types: (1) ''interchromosomal'' recombination, occurring through independent assortment of alleles whose loci are on different but homologous chromosomes (random orientation of pairs of homologous chromosomes in meiosis I); & (2) ''intrachromosomal'' recombination, occurring through crossing over. During meiosis in eukaryotes, genetic recombination involves the pairing of homologous chromosomes. This may be followed by information transfer between the chromosomes. The information transfer may occur without physical exchange (a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Middle Triassic
In the geologic timescale, the Middle Triassic is the second of three epochs of the Triassic period or the middle of three series in which the Triassic system is divided in chronostratigraphy. The Middle Triassic spans the time between Ma and Ma (million years ago). It is preceded by the Early Triassic Epoch and followed by the Late Triassic Epoch. The Middle Triassic is divided into the Anisian and Ladinian ages or stages. Formerly the middle series in the Triassic was also known as Muschelkalk. This name is now only used for a specific unit of rock strata with approximately Middle Triassic age, found in western Europe. Middle Triassic fauna Following the Permian–Triassic extinction event, the most devastating of all mass-extinctions, life recovered slowly. In the Middle Triassic, many groups of organisms reached higher diversity again, such as the marine reptiles (e.g. ichthyosaurs, sauropterygians, thallatosaurs), ray-finned fish and many invertebrate gr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Muschelkalk
The Muschelkalk (German for "shell-bearing limestone"; french: calcaire coquillier) is a sequence of sedimentary rock strata (a lithostratigraphic unit) in the geology of central and western Europe. It has a Middle Triassic (240 to 230 million years) age and forms the middle part of the tripartite Germanic Trias, that give the Triassic its name, lying above the older Buntsandstein and below the younger Keuper. The Muschelkalk ("mussel chalk") consists of a sequence of limestone and dolomite beds. In the past, the time span in which the Muschelkalk was deposited could also be called "Muschelkalk". In modern stratigraphy, however, the name only applies to the stratigraphic unit. Occurrence The name ''Muschelkalk'' was first used by German geologist Georg Christian Füchsel (1722-1773). In 1834, Friedrich August von Alberti included it into the Triassic system. The name indicates a characteristic feature of the unit, namely the frequent occurrence of lenticular banks compos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Algivore
Algae eater or algivore is a common name for any bottom-dwelling or filter-feeding aquatic animal species that specialize in feeding on algae and phytoplanktons. Algae eaters are important for the fishkeeping hobby and many are commonly kept by aquarium hobbyists to improve water quality. They are also important primary consumers that relay the biomass and energy from photosynthetic autotrophes up into the food web, as well as protecting the aquatic ecosystem against algae blooms. Freshwater Fish Some of the common and most popular freshwater aquarium algae eaters include: * Many loricariid catfish of South America, such as genera '' Otocinclus'', '' Ancistrus'', and '' Plecostomus'', constantly graze algae and biofilm, although many species of "plecos", which attain an adult length of over 10 inches, eat much less frequently as they near adulthood. * The Siamese algae eater (''Crossocheilus oblongus'') is a more gregarious and tolerant cyprinid that ranges up to . It i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |