|
Pit Brow Women
Pit brow women or pit brow lasses were female surface labourers at British collieries. They worked at the coal screens on the pit bank (or brow) at the shaft top until the 1960s. Their job was to pick stones from the coal after it was hauled to the surface. More women were employed in this capacity on the Lancashire Coalfield than in any other area. Background In the early coal industry women and girls worked underground alongside men and boys in small coal pits. It was common practice in Lancashire and Cumberland, Yorkshire, the East of Scotland and South Wales. The death of Elizabeth Higginson working underground was recorded in the register of Wigan Parish Church in 1641. An article in the ''Gentleman's Magazine'' in 1795 described Betty Hodson aged nine who worked underground with her brother, aged seven, dragging baskets of coals for their father. From the 1600s in Lancashire it was common for whole families to be employed in the pits. Colliers relied on their wives, sons and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wigan Pit Brow Lass
Wigan ( ) is a large town in Greater Manchester, England, on the River Douglas, Lancashire, River Douglas. The town is midway between the two cities of Manchester, to the south-east, and Liverpool, to the south-west. Bolton lies to the north-east and Warrington to the south. It is the largest settlement in the Metropolitan Borough of Wigan and is its administrative centre. The town has a population of 107,732 and the wider borough of 330,713. Wigan was formerly within the Historic counties of England, historic county of Lancashire. Wigan was in the territory of the Brigantes, an ancient Celtic tribe that ruled much of what is now northern England. The Brigantes were subjugated in the Roman conquest of Britain and the Roman settlement of ''Coccium'' was established where Wigan lies. Wigan was incorporated as a Borough status in the United Kingdom, borough in 1246, following the issue of a charter by Henry III of England, King Henry III of England. At the end of the Middle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carte De Visite
The ''carte de visite'' (, visiting card), abbreviated CdV, was a type of small photograph which was patented in Paris by photographer André Adolphe Eugène Disdéri in 1854, although first used by Louis Dodero. Each photograph was the size of a visiting card, and such photograph cards were commonly traded among friends and visitors in the 1860s. Albums for the collection and display of cards became a common fixture in Victorian parlors. The immense popularity of these card photographs led to the publication and collection of photographs of prominent persons. History and format The ''carte de visite'' was usually made of an albumen print, which was a thin paper photograph mounted on a thicker paper card. The size of a ''carte de visite'' is × mounted on a card sized × . In 1854, Disdéri had also patented a method of taking eight separate negatives on a single plate, which reduced production costs. The ''carte de visite'' was slow to gain widespread use until 1859, when ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mining In Lancashire
Mining is the extraction of valuable minerals or other geological materials from the Earth, usually from an ore body, lode, vein, seam, reef, or placer deposit. The exploitation of these deposits for raw material is based on the economic viability of investing in the equipment, labor, and energy required to extract, refine and transport the materials found at the mine to manufacturers who can use the material. Ores recovered by mining include metals, coal, oil shale, gemstones, limestone, chalk, dimension stone, rock salt, potash, gravel, and clay. Mining is required to obtain most materials that cannot be grown through agricultural processes, or feasibly created artificially in a laboratory or factory. Mining in a wider sense includes extraction of any non-renewable resource such as petroleum, natural gas, or even water. Modern mining processes involve prospecting for ore bodies, analysis of the profit potential of a proposed mine, extraction of the desired materials ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coal Mining In England
Coal is a combustible black or brownish-black sedimentary rock, formed as rock strata called coal seams. Coal is mostly carbon with variable amounts of other elements, chiefly hydrogen, sulfur, oxygen, and nitrogen. Coal is formed when dead plant matter decays into peat and is converted into coal by the heat and pressure of deep burial over millions of years. Vast deposits of coal originate in former wetlands called coal forests that covered much of the Earth's tropical land areas during the late Carboniferous ( Pennsylvanian) and Permian times. Many significant coal deposits are younger than this and originate from the Mesozoic and Cenozoic eras. Coal is used primarily as a fuel. While coal has been known and used for thousands of years, its usage was limited until the Industrial Revolution. With the invention of the steam engine, coal consumption increased. In 2020, coal supplied about a quarter of the world's primary energy and over a third of its electricity. Some iron ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Victorian Dress Reform
Victorian dress reform was an objective of the Victorian dress reform movement (also known as the rational dress movement) of the middle and late Victorian era, led by various reformers who proposed, designed, and wore clothing considered more practical and comfortable than the fashions of the time. Dress reformists were largely middle-class women involved in the first wave of feminism in the Western World, from the 1850s through the 1890s. The movement emerged in the Progressive Era along with calls for temperance, women's education, suffrage and moral purity. Dress reform called for emancipation from the "dictates of fashion", expressed a desire to "cover the limbs as well as the torso adequately," and promoted "rational dress". The movement had its greatest success in the reform of women's undergarments, which could be modified without exposing the wearer to social ridicule. Dress reformers were also influential in persuading women to adopt simplified garments for athletic ac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bal Maiden
A bal maiden, from the Cornish language , a mine, and the English "maiden", a young or unmarried woman, was a female manual labourer working in the mining industries of Cornwall and western Devon, at the south-western extremity of Great Britain. The term has been in use since at least the early 18th century. At least 55,000 women and girls worked as bal maidens, and the actual number is likely to have been much higher. While women worked in coal mines elsewhere in Britain, either on the surface or underground, bal maidens worked only on the surface. It is likely that Cornish women had worked in metal mining since antiquity, but the first records of female mine workers date from the 13th century. After the Black Death in the 14th century, mining declined, and no records of female workers have been found from then until the late 17th century. Industrial improvements, the end of Crown control of metal mines, and rising demand for raw materials caused a boom in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Victorian Morality
Victorian morality is a distillation of the moral views of the middle class in 19th-century Britain, the Victorian era. Victorian values emerged in all classes and reached all facets of Victorian living. The values of the period—which can be classed as religion, morality, Evangelicalism, industrial work ethic, and personal improvement—took root in Victorian morality. Current plays and all literature—including old classics like Shakespeare—were cleansed of content considered to be inappropriate for children, or "bowdlerized". Contemporary historians have generally come to regard the Victorian era as a time of many conflicts, such as the widespread cultivation of an outward appearance of dignity and restraint, together with serious debates about exactly how the new morality should be implemented. The international slave trade was abolished, and this ban was enforced by the Royal Navy. Slavery was ended in all the British colonies, child labour was ended in British facto ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Working-class
The working class (or labouring class) comprises those engaged in manual-labour occupations or industrial work, who are remunerated via waged or salaried contracts. Working-class occupations (see also " Designation of workers by collar colour") include blue-collar jobs, and most pink-collar jobs. Members of the working class rely exclusively upon earnings from wage labour; thus, according to more inclusive definitions, the category can include almost all of the working population of industrialized economies, as well as those employed in the urban areas (cities, towns, villages) of non-industrialized economies or in the rural workforce. Definitions As with many terms describing social class, ''working class'' is defined and used in many different ways. The most general definition, used by many socialists, is that the working class includes all those who have nothing to sell but their labour. These people used to be referred to as the proletariat, but that term has gone out of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arthur Munby
Arthur Joseph Munby (19 August 1828 – 29 January 1910) was a British diarist, poet, portrait photographer, barrister and solicitor. He is also known by his initials, A. J. Munby. Munby in Victorian Society The Victorian Era (1837-1901) was a period of great social change. Historian Leonore Davidoff writes that "The nineteenth century was the time when traditional social boundaries were being eclipsed by the rapid development of a market economy and the creation of a 'class' society". Social norms and boundaries were being redefined by the emerging Middle (Upper) class, which had the resources and time to formulate and propagate new social norms and rituals, and determine what was acceptable behavior and what was taboo. Victorian norms around sexuality insisted on the physical separation of male and female bodily functions and sexual acts from the public sphere. As class divisions were exacerbated by the growth of capitalism and industrialization, class designations began to ta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cabinet Card
The cabinet card was a style of photograph which was widely used for photographic portraiture after 1870. It consisted of a thin photograph mounted on a card typically measuring 108 by 165 mm ( by inches). History The '' carte de visite'' was displaced by the larger cabinet card in the 1880s. In the early 1860s, both types of photographs were essentially the same in process and design. Both were most often albumen prints, the primary difference being the cabinet card was larger and usually included extensive logos and information on the reverse side of the card to advertise the photographer’s services. However, later into its popularity, other types of papers began to replace the albumen process. Despite the similarity, the cabinet card format was initially used for landscape views before it was adopted for portraiture. Some cabinet card images from the 1890s have the appearance of a black-and-white photograph in contrast to the distinctive sepia toning notable in t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The National Archives (United Kingdom)
, type = Non-ministerial department , seal = , nativename = , logo = Logo_of_The_National_Archives_of_the_United_Kingdom.svg , logo_width = 150px , logo_caption = , formed = , preceding1 = , dissolved = , superseding = , jurisdiction = England and Wales, HM Government , headquarters = Kew, Richmond, Greater London TW9 4DU , region_code = GB , coordinates = , employees = 679 , budget = £43.9 million (2009–2010) , minister1_name = Michelle Donelan , minister1_pfo = Secretary of State for Digital, Culture, Media and Sport , minister2_name = TBC , minister2_pfo = Parliamentary Under Secretary of State , chief1_name = Jeff James , chief1_position = Chief Executive and Keeper of the Public Records , chief2_name = , chief2_position = , chief3_name = , chief3_position = , chief4_name = , chief4_position = , chief5_name = , chief5_position = , agency_type = , chief6_name = , chief6_position = , chief7_name = , chief7_position = ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
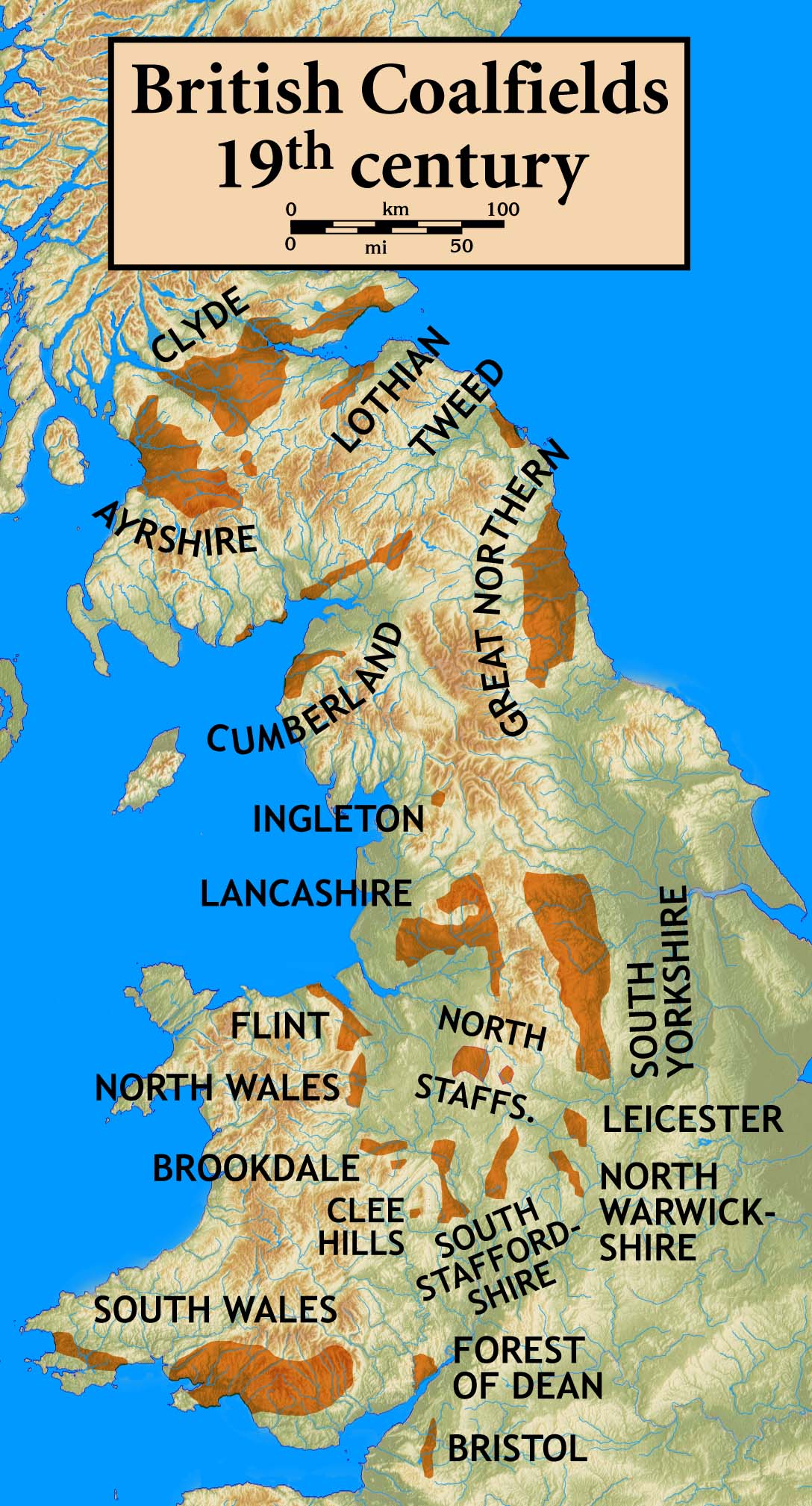
Lancashire Coalfield
The Lancashire Coalfield in North West England was an important British coalfield. Its coal seams were formed from the vegetation of tropical swampy forests in the Carboniferous period over 300 million years ago. The Romans may have been the first to use coal in Lancashire and its shallow seams and outcrops were exploited on a small scale from the Middle Ages and extensively after the start of the Industrial Revolution. The coalfield was at the forefront of innovation in coal mining, prompting the country's first canals, use of steam engines and creating conditions favourable for rapid industrialisation. The pits on the coalfield were at their most productive in 1907 when more than 26 million tons of coal were produced. By 1967 just 21 collieries remained. Parkside Colliery in Newton-le-Willows, St. Helens area, the last deep mine to be sunk on the coalfield, was closed in 1993. Geology The geology of the coalfield consists of the coal seams of the Upper, Middle and Lower Coal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)