|
Phytyl
Phytane is the isoprenoid alkane formed when phytol, a constituent of chlorophyll, loses its hydroxyl group. When phytol loses one carbon atom, it yields pristane. Other sources of phytane and pristane have also been proposed than phytol. Pristane and phytane are common constituents in petroleum and have been used as proxies for depositional redox conditions, as well as for correlating oil and its source rock (i.e. elucidating where oil formed). In environmental studies, pristane and phytane are target compounds for investigating oil spills. Chemistry Phytane is a non-polar organic compound that is a clear and colorless liquid at room temperature. It is a head-to-tail linked regular isoprenoid with chemical formula C20H42. Phytane has many structural isomers. Among them, crocetane is a tail-to-tail linked isoprenoid and often co-elutes with phytane during gas chromatography (GC) due to its structural similarity. Phytane also has many stereoisomers because of its three ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chlorophyll
Chlorophyll (also chlorophyl) is any of several related green pigments found in cyanobacteria and in the chloroplasts of algae and plants. Its name is derived from the Greek words , ("pale green") and , ("leaf"). Chlorophyll allow plants to absorb energy from light. Chlorophylls absorb light most strongly in the blue portion of the electromagnetic spectrum as well as the red portion. Conversely, it is a poor absorber of green and near-green portions of the spectrum. Hence chlorophyll-containing tissues appear green because green light, diffusively reflected by structures like cell walls, is less absorbed. Two types of chlorophyll exist in the photosystems of green plants: chlorophyll ''a'' and ''b''. History Chlorophyll was first isolated and named by Joseph Bienaimé Caventou and Pierre Joseph Pelletier in 1817. The presence of magnesium in chlorophyll was discovered in 1906, and was that element's first detection in living tissue. After initial work done by German ch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pristane
Pristane is a natural saturated terpenoid alkane obtained primarily from shark liver oil, from which its name is derived (Latin ''pristis'', "shark"). It is also found in the stomach oil of birds in the order Procellariiformes and in mineral oil and some foods. Pristane and phytane are used in the fields of geology and environmental science as biomarkers to characterize origins and evolution of petroleum hydrocarbons and coal. It is a transparent oily liquid that is immiscible with water, but soluble in diethyl ether, benzene, chloroform and carbon tetrachloride. Pristane is known to induce autoimmune diseases in rodents. It is used in research to understand the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis and lupus. It is used as a lubricant, a transformer oil, an immunologic adjuvant, and an anti-corrosion agent, biological marker, plasmocytomas inducer and in production of monoclonal antibodies. Biosynthetically, pristane is derived from phytol and is used as a biomarker in petrole ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Terpenoid
The terpenoids, also known as isoprenoids, are a class of naturally occurring organic chemicals derived from the 5-carbon compound isoprene and its derivatives called terpenes, diterpenes, etc. While sometimes used interchangeably with "terpenes", terpenoids contain additional functional groups, usually containing oxygen. When combined with the hydrocarbon terpenes, terpenoids comprise about 80,000 compounds. They are the largest class of plant secondary metabolites, representing about 60% of known natural products. Many terpenoids have substantial pharmacological bioactivity and are therefore of interest to medicinal chemists. Plant terpenoids are used for their aromatic qualities and play a role in traditional herbal remedies. Terpenoids contribute to the scent of eucalyptus, the flavors of cinnamon, cloves, and ginger, the yellow color in sunflowers, and the red color in tomatoes. Well-known terpenoids include citral, menthol, camphor, salvinorin A in the plant ''Salvia div ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
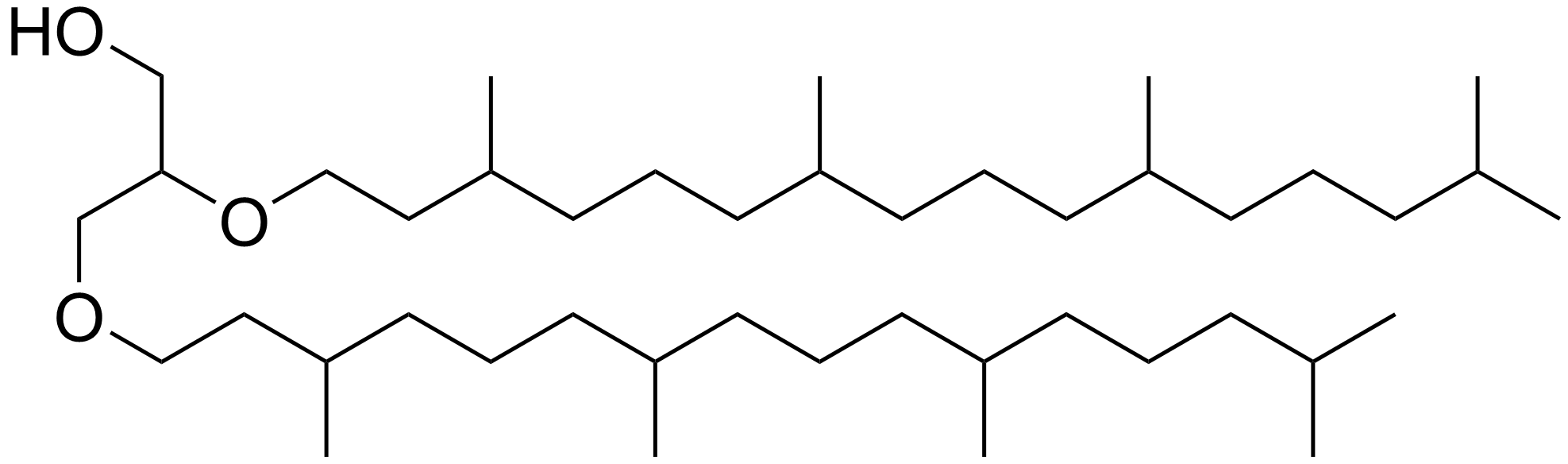
Archaeol
Archaeol is composed of two phytanyl chains linked to the sn-2 and sn-3 positions of glycerol. As its phosphate ester, it is a common component of the membranes of archaea. Structure and contrast with other lipids Archaeol is a diether. The 2,3-sn-glycerol structure and ether bond linkage are two key differences between lipids found in archaea vs those of bacteria and eukarya. The latter use 1,2-sn-glycerol, and mostly, ester bonds. Natural archaeol has 3R, 7R, 11R configurations for the three chiral centers in the isoprenoid chains. There are four structural variations, contributing to the complexity of the membrane lipids in function and properties. The two phytanyl chains can form a 36-member ring to yield macrocyclic archaeol. Hydroxylated archaeol has phytanyl chains hydroxylated at the first tertiary carbon atom, while sesterterpanyl archaeol have the phytanyl side chains with C25 sesterterpanyl chains, substituting at C2 of glycerol or at both carbons. Unsaturated a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Haloarchaea
Haloarchaea (halophilic archaea, halophilic archaebacteria, halobacteria) are a class of the Euryarchaeota, found in water saturated or nearly saturated with salt. Halobacteria are now recognized as archaea rather than bacteria and are one of the largest groups. The name 'halobacteria' was assigned to this group of organisms before the existence of the domain Archaea was realized, and while valid according to taxonomic rules, should be updated. Halophilic archaea are generally referred to as haloarchaea to distinguish them from halophilic bacteria. These microorganisms are among the halophile organisms, that they require high salt concentrations to grow, with most species requiring more than 2.0M NaCl for growth and survival. They are a distinct evolutionary branch of the Archaea distinguished by the possession of ether-linked lipids and the absence of murein in their cell walls. Haloarchaea can grow aerobically or anaerobically. Parts of the membranes of haloarchaea are pur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Methanogen
Methanogens are microorganisms that produce methane as a metabolic byproduct in hypoxic conditions. They are prokaryotic and belong to the domain Archaea. All known methanogens are members of the archaeal phylum Euryarchaeota. Methanogens are common in wetlands, where they are responsible for marsh gas, and in the digestive tracts of animals such as ruminants and many humans, where they are responsible for the methane content of belching in ruminants and flatulence in humans. In marine sediments, the biological production of methane, also termed methanogenesis, is generally confined to where sulfates are depleted, below the top layers. Moreover, methanogenic archaea populations play an indispensable role in anaerobic wastewater treatments. Others are extremophiles, found in environments such as hot springs and submarine hydrothermal vents as well as in the "solid" rock of Earth's crust, kilometers below the surface. Physical description Methanogens are coccoid (spherica ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Substituent
A substituent is one or a group of atoms that replaces (one or more) atoms, thereby becoming a moiety in the resultant (new) molecule. (In organic chemistry and biochemistry, the terms ''substituent'' and ''functional group'', as well as '' side chain'' and ''pendant group'', are used almost interchangeably to describe those branches from the parent structure, though certain distinctions are made in polymer chemistry. In polymers, side chains extend from the backbone structure. In proteins, side chains are attached to the alpha carbon atoms of the amino acid backbone.) The suffix ''-yl'' is used when naming organic compounds that contain a single bond replacing one hydrogen; ''-ylidene'' and ''-ylidyne'' are used with double bonds and triple bonds, respectively. In addition, when naming hydrocarbons that contain a substituent, positional numbers are used to indicate which carbon atom the substituent attaches to when such information is needed to distinguish between isomers. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archaeol
Archaeol is composed of two phytanyl chains linked to the sn-2 and sn-3 positions of glycerol. As its phosphate ester, it is a common component of the membranes of archaea. Structure and contrast with other lipids Archaeol is a diether. The 2,3-sn-glycerol structure and ether bond linkage are two key differences between lipids found in archaea vs those of bacteria and eukarya. The latter use 1,2-sn-glycerol, and mostly, ester bonds. Natural archaeol has 3R, 7R, 11R configurations for the three chiral centers in the isoprenoid chains. There are four structural variations, contributing to the complexity of the membrane lipids in function and properties. The two phytanyl chains can form a 36-member ring to yield macrocyclic archaeol. Hydroxylated archaeol has phytanyl chains hydroxylated at the first tertiary carbon atom, while sesterterpanyl archaeol have the phytanyl side chains with C25 sesterterpanyl chains, substituting at C2 of glycerol or at both carbons. Unsaturated a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stereocenter
In stereochemistry, a stereocenter of a molecule is an atom (center), axis or plane that is the focus of stereoisomerism; that is, when having at least three different groups bound to the stereocenter, interchanging any two different groups creates a new stereoisomer. Stereocenters are also referred to as stereogenic centers. A stereocenter is geometrically defined as a point (location) in a molecule; a stereocenter is usually but not always a specific atom, often carbon. Stereocenters can exist on chiral or achiral molecules; stereocenters can contain single bonds or double bonds. The number of hypothetical stereoisomers can be predicted by using 2''n'', with ''n'' being the number of tetrahedral stereocenters; however, exceptions such as meso compounds can reduce the prediction to below the expected 2''n''. Chirality centers are a type of stereocenter with four different substituent groups; chirality centers are a specific subset of stereocenters because they can only ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stereoisomerism
In stereochemistry, stereoisomerism, or spatial isomerism, is a form of isomerism in which molecules have the same molecular formula and sequence of bonded atoms (constitution), but differ in the three-dimensional orientations of their atoms in space. This contrasts with structural isomers, which share the same molecular formula, but the bond connections or their order differs. By definition, molecules that are stereoisomers of each other represent the same structural isomer. Enantiomers Enantiomers, also known as optical isomers, are two stereoisomers that are related to each other by a reflection: they are mirror images of each other that are non-superposable. Human hands are a macroscopic analog of this. Every stereogenic center in one has the opposite configuration in the other. Two compounds that are enantiomers of each other have the same physical properties, except for the direction in which they rotate polarized light and how they interact with different optical isomers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |