 |
Phrygian Mode
The Phrygian mode (pronounced ) can refer to three different musical modes: the ancient Greek ''tonos'' or ''harmonia,'' sometimes called Phrygian, formed on a particular set of octave species or scales; the Medieval Phrygian mode, and the modern conception of the Phrygian mode as a diatonic scale, based on the latter. Ancient Greek Phrygian The octave species (scale) underlying the ancient-Greek Phrygian ''tonos'' (in its diatonic genus) corresponds to the medieval and modern Dorian mode. The terminology is based on the ''Elements'' by Aristoxenos (fl. c. 335 BC), a disciple of Aristotle. The Phrygian ''tonos'' or ''harmonia'' is named after the ancient kingdom of Phrygia in Anatolia. In Greek music theory, the ''harmonia'' given this name was based on a ''tonos'', in turn based on a scale or octave species built from a tetrachord which, in its diatonic genus, consisted of a series of rising intervals of a whole tone, followed by a semitone, followed by a whole tone. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
 |
Mode (music)
In music theory, the term mode or ''modus'' is used in a number of distinct senses, depending on context. Its most common use may be described as a type of musical scale coupled with a set of characteristic melodic and harmonic behaviors. It is applied to major and minor keys as well as the seven diatonic modes (including the former as Ionian and Aeolian) which are defined by their starting note or tonic. ( Olivier Messiaen's modes of limited transposition are strictly a scale type.) Related to the diatonic modes are the eight church modes or Gregorian modes, in which authentic and plagal forms of scales are distinguished by ambitus and tenor or reciting tone. Although both diatonic and gregorian modes borrow terminology from ancient Greece, the Greek ''tonoi'' do not otherwise resemble their mediaeval/modern counterparts. In the Middle Ages the term modus was used to describe both intervals and rhythm. Modal rhythm was an essential feature of the modal notation syste ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
Cleonides
Cleonides ( el, Κλεονείδης) is the author of a Greek treatise on music theory titled Εἰσαγωγὴ ἁρμονική ''Eisagōgē harmonikē'' (Introduction to Harmonics). The date of the treatise, based on internal evidence, can be established only to the broad period between the 3rd century BCE and the 4th century CE; however, treatises titled ''eisagōgē'' generally began to appear only in the 1st century BCE, which seems the most likely period for Cleonides' work.Jon Solomon, "Cleonides leoneidēs, ''The New Grove Dictionary of Music and Musicians'', second edition, edited by Stanley Sadie and John Tyrrell (London: Macmillan Publishers, 2001). The attribution of the ''Eisagōgē'' in some manuscripts to Euclid Euclid (; grc-gre, Εὐκλείδης; BC) was an ancient Greek mathematician active as a geometer and logician. Considered the "father of geometry", he is chiefly known for the ''Elements'' treatise, which established the foundations of ... o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
 |
Jazz
Jazz is a music genre that originated in the African-American communities of New Orleans, Louisiana in the late 19th and early 20th centuries, with its roots in blues and ragtime. Since the 1920s Jazz Age, it has been recognized as a major form of musical expression in traditional and popular music. Jazz is characterized by swing and blue notes, complex chords, call and response vocals, polyrhythms and improvisation. Jazz has roots in European harmony and African rhythmic rituals. As jazz spread around the world, it drew on national, regional, and local musical cultures, which gave rise to different styles. New Orleans jazz began in the early 1910s, combining earlier brass band marches, French quadrilles, biguine, ragtime and blues with collective polyphonic improvisation. But jazz did not begin as a single musical tradition in New Orleans or elsewhere. In the 1930s, arranged dance-oriented swing big bands, Kansas City jazz (a hard-swinging, bluesy, improvisationa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
 |
Natural Minor
In music theory, the minor scale is three scale patterns – the natural minor scale (or Aeolian mode), the harmonic minor scale, and the melodic minor scale (ascending or descending) – rather than just two as with the major scale, which also has a harmonic form but lacks a melodic form. In each of these scales, the first, third, and fifth scale degrees form a minor triad (rather than a major triad, as in a major scale). In some contexts, ''minor scale'' is used to refer to any heptatonic scale with this property (see Related modes below). Natural minor scale Relationship to relative major A natural minor scale (or Aeolian mode) is a diatonic scale that is built by starting on the sixth degree of its relative major scale. For instance, the A natural minor scale can be built by starting on the 6th degree of the C major scale: : Because of this, the key of A minor is called the ''relative minor'' of C major. Every major key has a relative minor, w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
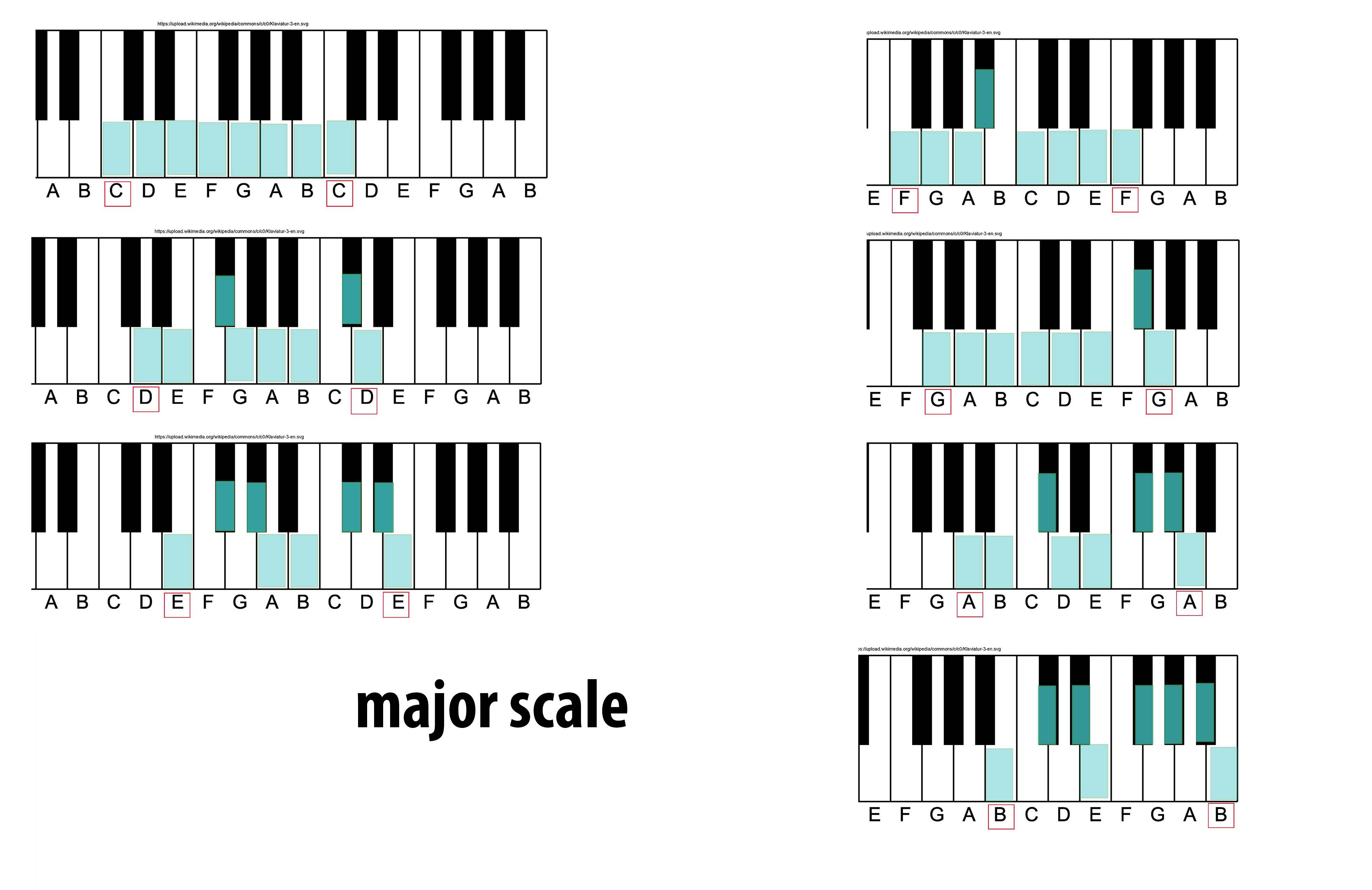 |
Major Mode
The major scale (or Ionian mode) is one of the most commonly used musical scales, especially in Western music. It is one of the diatonic scales. Like many musical scales, it is made up of seven notes: the eighth duplicates the first at double its frequency so that it is called a higher octave of the same note (from Latin "octavus", the eighth). The simplest major scale to write is C major, the only major scale not requiring sharps or flats: The major scale had a central importance in Western music, particularly in the common practice period and in popular music. In Carnatic music, it is known as ''Sankarabharanam''. In Hindustani classical music, it is known as ''Bilaval''. Structure A major scale is a diatonic scale. The sequence of intervals between the notes of a major scale is: : whole, whole, half, whole, whole, whole, half where "whole" stands for a whole tone (a red u-shaped curve in the figure), and "half" stands for a semitone (a red angled lin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
Scale Degrees
In music theory, the scale degree is the position of a particular note on a scale relative to the tonic, the first and main note of the scale from which each octave is assumed to begin. Degrees are useful for indicating the size of intervals and chords and whether an interval is major or minor. In the most general sense, the scale degree is the number given to each step of the scale, usually starting with 1 for tonic. Defining it like this implies that a tonic is specified. For instance, the 7-tone diatonic scale may become the major scale once the proper degree has been chosen as tonic (e.g. the C-major scale C–D–E–F–G–A–B, in which C is the tonic). If the scale has no tonic, the starting degree must be chosen arbitrarily. In set theory, for instance, the 12 degrees of the chromatic scale usually are numbered starting from C=0, the twelve pitch classes being numbered from 0 to 11. In a more specific sense, scale degrees are given names that indicate their p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
 |
Tonality
Tonality is the arrangement of pitches and/or chords of a musical work in a hierarchy of perceived relations, stabilities, attractions and directionality. In this hierarchy, the single pitch or triadic chord with the greatest stability is called the tonic. The root of the tonic chord forms the name given to the key, so in the key of C major, the note C is both the tonic of the scale and the root of the tonic chord (which is C–E–G). Simple folk music songs often start and end with the tonic note. The most common use of the term "is to designate the arrangement of musical phenomena around a referential tonic in European music from about 1600 to about 1910". Contemporary classical music from 1910 to the 2000s may practice or avoid any sort of tonality—but harmony in almost all Western popular music remains tonal. Harmony in jazz includes many but not all tonal characteristics of the European common practice period, usually known as "classical music". "All harmonic idi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
Aeolian Mode
The Aeolian mode is a musical mode or, in modern usage, a diatonic scale also called the natural minor scale. On the white piano keys, it is the scale that starts with A. Its ascending interval form consists of a ''key note, whole step, half step, whole step, whole step, half step, whole step, whole step.'' That means that, in A aeolian (or A minor), you would play A, move up a whole step (two piano keys) to B, move up a half step (one piano key) to C, then up a whole step to D, a whole step to E, a half step to F, a whole step to G, and a final whole step to a high A. : History The word ''Aeolian'', like the names for the other ancient Greek ''tonoi'' and ''harmoniai'', is an ethnic designation: in this case, for the inhabitants of Aeolis (Αἰολίς)—the Aeolian Islands and adjacent coastal district of Asia Minor. In the music theory of ancient Greece, it was an alternative name (used by some later writers, such as Cleonides) for what Aristoxenus called the Low Lyd ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Natural Minor Scale
In music theory, the minor scale is three scale patterns – the natural minor scale (or Aeolian mode), the harmonic minor scale, and the melodic minor scale (ascending or descending) – rather than just two as with the major scale, which also has a harmonic form but lacks a melodic form. In each of these scales, the first, third, and fifth scale degrees form a minor triad (rather than a major triad, as in a major scale). In some contexts, ''minor scale'' is used to refer to any heptatonic scale with this property (see Related modes below). Natural minor scale Relationship to relative major A natural minor scale (or Aeolian mode) is a diatonic scale that is built by starting on the sixth degree of its relative major scale. For instance, the A natural minor scale can be built by starting on the 6th degree of the C major scale: : Because of this, the key of A minor is called the ''relative minor'' of C major. Every major key has a relative minor, whi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
 |
Hypophrygian Mode
The Hypophrygian (deuterus plagalis) mode, literally meaning "below Phrygian (plagal second)", is a musical mode or diatonic scale in medieval chant theory, the fourth mode of church music. This mode is the plagal counterpart of the authentic third mode, which was called '' Phrygian''. In the Middle Ages and Renaissance this mode was described in two ways: the diatonic scale from B to B an octave above, divided at the mode final E (B–C–D–E + E–F–G–A–B); and as a mode with final E and ambitus from the A below to the C above. The note A above the final (the tenor of the corresponding fourth psalm tone) had an important melodic function. The melodic range of the ecclesiastical Hypophrygian mode therefore goes from the perfect fourth or fifth below the tonic to the perfect fifth or minor sixth above. The name Hypophrygian originates in an octave species of ancient Greek music theory. According to Aristoxenus, this octave species was originally described around ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
Ambitus (music)
Ambitus () is a Latin term literally meaning ''enclos r'', and in Medieval Latin means the "range" of a melodic line, most usually referring to the range of scale degrees attributed to a given mode, particularly in Gregorian chant. In Gregorian chant specifically, the ambitus is the range, or the distance between the highest and lowest note. Different chants vary widely in their ambitus. Even relatively florid chants like Alleluias may have a narrow ambitus. Earlier writers termed the modal ambitus "perfect" when it was a ninth or tenth (that is, an octave plus one or two notes, either at the top or bottom or both), but from the late fifteenth century onward "perfect ambitus" usually meant one octave, and the ambitus was called "imperfect" when it was less, and "pluperfect" when it was more than an octave. All of the church modes are distinguished in part by their ambitus. The plagal modes have the final in the middle of the ambitus, while the authentic modes generally go no m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
 |
Pentachord
A pentachord in music theory may be either of two things. In pitch-class set theory, a pentachord is defined as any five pitch classes, regarded as an unordered collection . In other contexts, a pentachord may be any consecutive five-note section of a diatonic scale . A pentad is a five-note chord . Under the latter definition, a diatonic scale comprises five non-transpositionally equivalent pentachords rather than seven because the Ionian and Mixolydian pentachords and the Dorian and Aeolian pentachords are intervallically identical (CDEFG=GABCD; DEFGA=ABCDE). The name "pentachord" was also given to a musical instrument, now in disuse, built to the specifications of Sir Edward Walpole. It was demonstrated by Karl Friedrich Abel at his first public concert in London, on 5 April 1759, when it was described as "newly invented" . In the dedication to Walpole of his cello sonatas op. 3, the cellist/composer James Cervetto James Cervetto (8 January 1748 – 5 February 1837) wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |