|
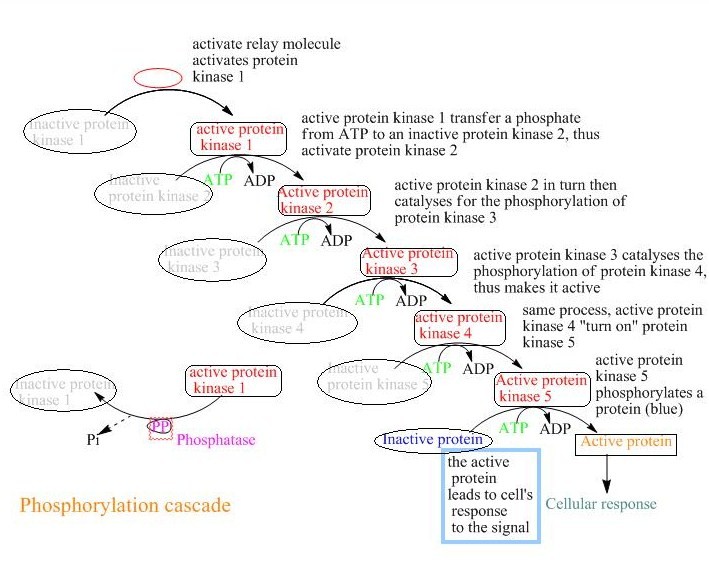
Phosphorylation Cascade
A phosphorylation cascade is a sequence of signaling pathway events where one enzyme phosphorylates another, causing a chain reaction leading to the phosphorylation of thousands of proteins. This can be seen in signal transduction of hormone messages. A signaling pathway begins at the cell surface where a hormone or protein binds to a receptor at the Extracellular matrix. The interactions between the molecule and receptor cause a Conformational change at the receptor, which activates multiple enzymes or proteins. These enzymes activate secondary messengers, which leads to the phosphorylation In chemistry, phosphorylation is the attachment of a phosphate group to a molecule or an ion. This process and its inverse, dephosphorylation, are common in biology and could be driven by natural selection. Text was copied from this source, wh ... of thousands of proteins. The end product of a Phosphorylation cascade is the changes occurring inside the cell. One best example that explains ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phosphorylation
In chemistry, phosphorylation is the attachment of a phosphate group to a molecule or an ion. This process and its inverse, dephosphorylation, are common in biology and could be driven by natural selection. Text was copied from this source, which is available under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License. Protein phosphorylation often activates (or deactivates) many enzymes. Glucose Phosphorylation of sugars is often the first stage in their catabolism. Phosphorylation allows cells to accumulate sugars because the phosphate group prevents the molecules from diffusing back across their transporter. Phosphorylation of glucose is a key reaction in sugar metabolism. The chemical equation for the conversion of D-glucose to D-glucose-6-phosphate in the first step of glycolysis is given by :D-glucose + ATP → D-glucose-6-phosphate + ADP : ΔG° = −16.7 kJ/mol (° indicates measurement at standard condition) Hepatic cells are freely permeable to glucose, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Signal Transduction
Signal transduction is the process by which a chemical or physical signal is transmitted through a cell as a series of molecular events, most commonly protein phosphorylation catalyzed by protein kinases, which ultimately results in a cellular response. Proteins responsible for detecting stimuli are generally termed receptors, although in some cases the term sensor is used. The changes elicited by ligand binding (or signal sensing) in a receptor give rise to a biochemical cascade, which is a chain of biochemical events known as a signaling pathway. When signaling pathways interact with one another they form networks, which allow cellular responses to be coordinated, often by combinatorial signaling events. At the molecular level, such responses include changes in the transcription or translation of genes, and post-translational and conformational changes in proteins, as well as changes in their location. These molecular events are the basic mechanisms controlling cell growth, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phosphorylation Cascade
A phosphorylation cascade is a sequence of signaling pathway events where one enzyme phosphorylates another, causing a chain reaction leading to the phosphorylation of thousands of proteins. This can be seen in signal transduction of hormone messages. A signaling pathway begins at the cell surface where a hormone or protein binds to a receptor at the Extracellular matrix. The interactions between the molecule and receptor cause a Conformational change at the receptor, which activates multiple enzymes or proteins. These enzymes activate secondary messengers, which leads to the phosphorylation In chemistry, phosphorylation is the attachment of a phosphate group to a molecule or an ion. This process and its inverse, dephosphorylation, are common in biology and could be driven by natural selection. Text was copied from this source, wh ... of thousands of proteins. The end product of a Phosphorylation cascade is the changes occurring inside the cell. One best example that explains ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Extracellular Matrix
In biology, the extracellular matrix (ECM), also called intercellular matrix, is a three-dimensional network consisting of extracellular macromolecules and minerals, such as collagen, enzymes, glycoproteins and hydroxyapatite that provide structural and biochemical support to surrounding cells. Because multicellularity evolved independently in different multicellular lineages, the composition of ECM varies between multicellular structures; however, cell adhesion, cell-to-cell communication and differentiation are common functions of the ECM. The animal extracellular matrix includes the interstitial matrix and the basement membrane. Interstitial matrix is present between various animal cells (i.e., in the intercellular spaces). Gels of polysaccharides and fibrous proteins fill the Interstitial fluid, interstitial space and act as a compression buffer against the stress placed on the ECM. Basement membranes are sheet-like depositions of ECM on which various epithelial cells rest ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Conformational Change
In biochemistry, a conformational change is a change in the shape of a macromolecule, often induced by environmental factors. A macromolecule is usually flexible and dynamic. Its shape can change in response to changes in its environment or other factors; each possible shape is called a conformation, and a transition between them is called a ''conformational change''. Factors that may induce such changes include temperature, pH, voltage, light in chromophores, concentration of ions, phosphorylation, or the binding of a ligand. Transitions between these states occur on a variety of length scales (tenths of Å to nm) and time scales (ns to s), and have been linked to functionally relevant phenomena such as allosteric signaling and enzyme catalysis. Laboratory analysis Many biophysical techniques such as crystallography, NMR, electron paramagnetic resonance (EPR) using spin label techniques, circular dichroism (CD), hydrogen exchange, and FRET can be used to study macrom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mitogen-activated Protein Kinase
A mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK or MAP kinase) is a type of protein kinase that is specific to the amino acids serine and threonine (i.e., a serine/threonine-specific protein kinase). MAPKs are involved in directing cellular responses to a diverse array of stimuli, such as mitogens, osmotic stress, heat shock and proinflammatory cytokines. They regulate cell functions including proliferation, gene expression, differentiation, mitosis, cell survival, and apoptosis. MAP kinases are found in eukaryotes only, but they are fairly diverse and encountered in all animals, fungi and plants, and even in an array of unicellular eukaryotes. MAPKs belong to the CMGC (CDK/MAPK/GSK3/CLK) kinase group. The closest relatives of MAPKs are the cyclin-dependent kinases (CDKs). Discovery The first mitogen-activated protein kinase to be discovered was ERK1 (MAPK3) in mammals. Since ERK1 and its close relative ERK2 (MAPK1) are both involved in growth factor signaling, the family was term ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |