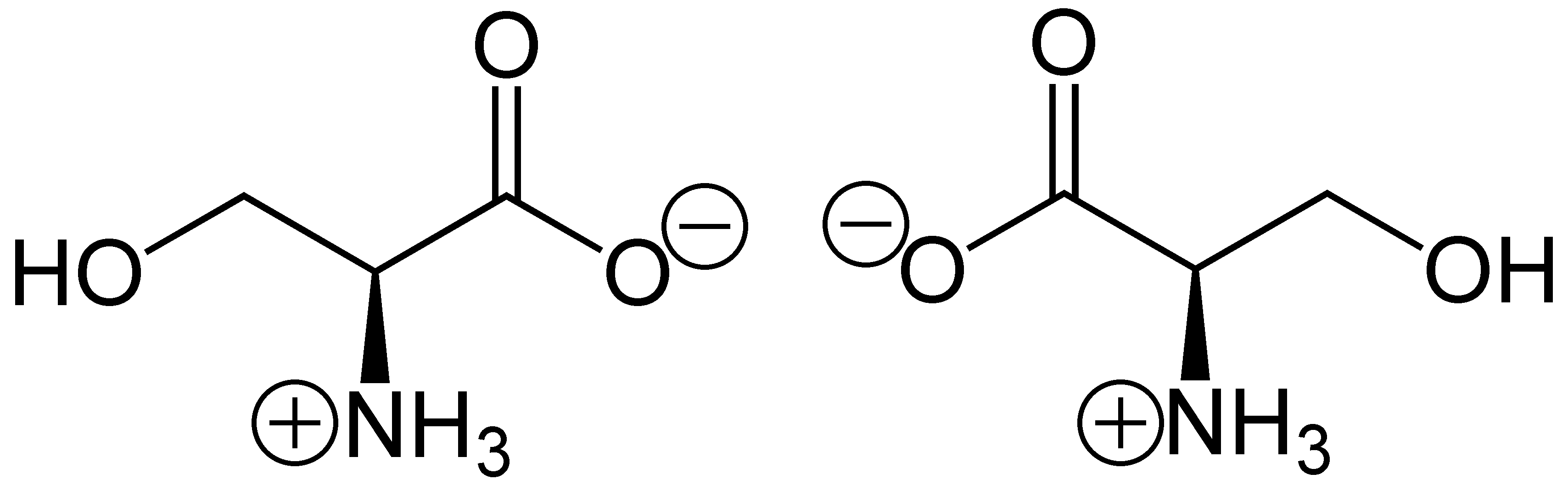|
Phosphomimetics
Phosphomimetics are amino acid substitutions that mimic a phosphorylated protein, thereby activating (or deactivating) the protein. Within cells, proteins are commonly modified at serine, tyrosine and threonine amino acids by adding a phosphate group. Phosphorylation is a common mode of activating or deactivating a protein as a form of regulation. However some non-phosphorylated amino acids appear chemically similar to phosphorylated amino acids. Therefore, by replacing an amino acid, the protein may maintain a higher level of activity. For example, aspartic acid is chemically similar to phospho-serine. Therefore, when an aspartic acid replaces a serine, it is a phosphomimetic of phospho-serine and can make the protein always in its phosphorylated form. Phosphonate-based compounds have been used as phosphotyrosine analogues, as they are less enzyme labile and are physiologically more stable. Applications This chemical similarity can be exploited in cancer, where a protein may ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phosphomimetics
Phosphomimetics are amino acid substitutions that mimic a phosphorylated protein, thereby activating (or deactivating) the protein. Within cells, proteins are commonly modified at serine, tyrosine and threonine amino acids by adding a phosphate group. Phosphorylation is a common mode of activating or deactivating a protein as a form of regulation. However some non-phosphorylated amino acids appear chemically similar to phosphorylated amino acids. Therefore, by replacing an amino acid, the protein may maintain a higher level of activity. For example, aspartic acid is chemically similar to phospho-serine. Therefore, when an aspartic acid replaces a serine, it is a phosphomimetic of phospho-serine and can make the protein always in its phosphorylated form. Phosphonate-based compounds have been used as phosphotyrosine analogues, as they are less enzyme labile and are physiologically more stable. Applications This chemical similarity can be exploited in cancer, where a protein may ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amino Acid
Amino acids are organic compounds that contain both amino and carboxylic acid functional groups. Although hundreds of amino acids exist in nature, by far the most important are the alpha-amino acids, which comprise proteins. Only 22 alpha amino acids appear in the genetic code. Amino acids can be classified according to the locations of the core structural functional groups, as Alpha and beta carbon, alpha- , beta- , gamma- or delta- amino acids; other categories relate to Chemical polarity, polarity, ionization, and side chain group type (aliphatic, Open-chain compound, acyclic, aromatic, containing hydroxyl or sulfur, etc.). In the form of proteins, amino acid '' residues'' form the second-largest component (water being the largest) of human muscles and other tissues. Beyond their role as residues in proteins, amino acids participate in a number of processes such as neurotransmitter transport and biosynthesis. It is thought that they played a key role in enabling life ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chemical Biology
Chemical biology is a scientific discipline spanning the fields of chemistry and biology. The discipline involves the application of chemical techniques, analysis, and often small molecules produced through synthetic chemistry, to the study and manipulation of biological systems. In contrast to biochemistry, which involves the study of the chemistry of biomolecules and regulation of biochemical pathways within and between cells, chemical biology deals with chemistry ''applied to'' biology (synthesis of biomolecules, the simulation of biological systems, etc.). Introduction Some forms of chemical biology attempt to answer biological questions by studying biological systems at the chemical level. In contrast to research using biochemistry, genetics, or molecular biology, where mutagenesis can provide a new version of the organism, cell, or biomolecule of interest, chemical biology probes systems ''in vitro'' and ''in vivo'' with small molecules that have been designed for a specific ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Serine
Serine (symbol Ser or S) is an α-amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins. It contains an α-amino group (which is in the protonated − form under biological conditions), a carboxyl group (which is in the deprotonated − form under biological conditions), and a side chain consisting of a hydroxymethyl group, classifying it as a polar amino acid. It can be synthesized in the human body under normal physiological circumstances, making it a nonessential amino acid. It is encoded by the codons UCU, UCC, UCA, UCG, AGU and AGC. Occurrence This compound is one of the naturally occurring proteinogenic amino acids. Only the L-stereoisomer appears naturally in proteins. It is not essential to the human diet, since it is synthesized in the body from other metabolites, including glycine. Serine was first obtained from silk protein, a particularly rich source, in 1865 by Emil Cramer. Its name is derived from the Latin for silk, ''sericum''. Serine's structure was estab ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tyrosine
-Tyrosine or tyrosine (symbol Tyr or Y) or 4-hydroxyphenylalanine is one of the 20 standard amino acids that are used by cells to synthesize proteins. It is a non-essential amino acid with a polar side group. The word "tyrosine" is from the Greek ''tyrós'', meaning ''cheese'', as it was first discovered in 1846 by German chemist Justus von Liebig in the protein casein from cheese. It is called tyrosyl when referred to as a functional group or side chain. While tyrosine is generally classified as a Hydrophobe, hydrophobic amino acid, it is more hydrophilic than phenylalanine. It is Genetic code, encoded by the Genetic code#Codons, codons UAC and UAU in messenger RNA. Functions Aside from being a proteinogenic amino acid, tyrosine has a special role by virtue of the phenol functionality. It occurs in proteins that are part of signal transduction processes and functions as a receiver of phosphate groups that are transferred by way of protein kinases. Phosphorylation of the hyd ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Threonine
Threonine (symbol Thr or T) is an amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins. It contains an α-amino group (which is in the protonated −NH form under biological conditions), a carboxyl group (which is in the deprotonated −COO− form under biological conditions), and a side chain containing a hydroxyl group, making it a polar, uncharged amino acid. It is essential in humans, meaning the body cannot synthesize it: it must be obtained from the diet. Threonine is synthesized from aspartate in bacteria such as ''E. coli''. It is encoded by all the codons starting AC (ACU, ACC, ACA, and ACG). Threonine sidechains are often hydrogen bonded; the most common small motifs formed are based on interactions with serine: ST turns, ST motifs (often at the beginning of alpha helices) and ST staples (usually at the middle of alpha helices). Modifications The threonine residue is susceptible to numerous posttranslational modifications. The hydroxyl side-chain can unde ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phosphate
In chemistry, a phosphate is an anion, salt, functional group or ester derived from a phosphoric acid. It most commonly means orthophosphate, a derivative of orthophosphoric acid . The phosphate or orthophosphate ion is derived from phosphoric acid by the removal of three protons . Removal of one or two protons gives the dihydrogen phosphate ion and the hydrogen phosphate ion ion, respectively. These names are also used for salts of those anions, such as ammonium dihydrogen phosphate and trisodium phosphate. File:3-phosphoric-acid-3D-balls.png, Phosphoricacid File:2-dihydrogenphosphate-3D-balls.png, Dihydrogenphosphate File:1-hydrogenphosphate-3D-balls.png, Hydrogenphosphate File:0-phosphate-3D-balls.png, Phosphate In organic chemistry, phosphate or orthophosphate is an organophosphate, an ester of orthophosphoric acid of the form where one or more hydrogen atoms are replaced by organic groups. An example is trimethyl phosphate, . The term also refers to the triv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phosphorylation
In chemistry, phosphorylation is the attachment of a phosphate group to a molecule or an ion. This process and its inverse, dephosphorylation, are common in biology and could be driven by natural selection. Text was copied from this source, which is available under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License. Protein phosphorylation often activates (or deactivates) many enzymes. Glucose Phosphorylation of sugars is often the first stage in their catabolism. Phosphorylation allows cells to accumulate sugars because the phosphate group prevents the molecules from diffusing back across their transporter. Phosphorylation of glucose is a key reaction in sugar metabolism. The chemical equation for the conversion of D-glucose to D-glucose-6-phosphate in the first step of glycolysis is given by :D-glucose + ATP → D-glucose-6-phosphate + ADP : ΔG° = −16.7 kJ/mol (° indicates measurement at standard condition) Hepatic cells are freely permeable to glucose, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aspartic Acid
Aspartic acid (symbol Asp or D; the ionic form is known as aspartate), is an α-amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins. Like all other amino acids, it contains an amino group and a carboxylic acid. Its α-amino group is in the protonated –NH form under physiological conditions, while its α-carboxylic acid group is deprotonated −COO− under physiological conditions. Aspartic acid has an acidic side chain (CH2COOH) which reacts with other amino acids, enzymes and proteins in the body. Under physiological conditions (pH 7.4) in proteins the side chain usually occurs as the negatively charged aspartate form, −COO−. It is a non-essential amino acid in humans, meaning the body can synthesize it as needed. It is encoded by the codons GAU and GAC. D-Aspartate is one of two D-amino acids commonly found in mammals. .html" ;"title="/sup>">/sup> In proteins aspartate sidechains are often hydrogen bonded to form asx turns or asx motifs, which frequently occur at ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
IRF3
Interferon regulatory factor 3, also known as IRF3, is an interferon regulatory factor. Function IRF3 is a member of the interferon regulatory transcription factor (IRF) family. IRF3 was originally discovered as a homolog of IRF1 and IRF2. IRF3 has been further characterized and shown to contain several functional domains including a nuclear export signal, a DNA-binding domain, a C-terminal IRF association domain and several regulatory phosphorylation sites. IRF3 is found in an inactive cytoplasmic form that upon serine/threonine phosphorylation forms a complex with CREBBP. The complex translocates into the nucleus for the transcriptional activation of interferons alpha and beta, and further interferon-induced genes. IRF3 plays an important role in the innate immune system's response to viral infection. Aggregated MAVS have been found to activate IRF3 dimerization. A 2015 study shows phosphorylation of innate immune adaptor proteins MAVS, STING and TRIF at a conserved pLxIS ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Interferon
Interferons (IFNs, ) are a group of signaling proteins made and released by host cells in response to the presence of several viruses. In a typical scenario, a virus-infected cell will release interferons causing nearby cells to heighten their anti-viral defenses. IFNs belong to the large class of proteins known as cytokines, molecules used for communication between cells to trigger the protective defenses of the immune system that help eradicate pathogens. Interferons are named for their ability to "interfere" with viral replication by protecting cells from virus infections. However, virus-encoded genetic elements have the ability to antagonize the IFN response contributing to viral pathogenesis and viral diseases. IFNs also have various other functions: they activate immune cells, such as natural killer cells and macrophages, and they increase host defenses by up-regulating antigen presentation by virtue of increasing the expression of major histocompatibility complex (M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genetic Engineering
Genetic engineering, also called genetic modification or genetic manipulation, is the modification and manipulation of an organism's genes using technology. It is a set of technologies used to change the genetic makeup of cells, including the transfer of genes within and across species boundaries to produce improved or novel organisms. New DNA is obtained by either isolating and copying the genetic material of interest using recombinant DNA methods or by artificially synthesising the DNA. A construct is usually created and used to insert this DNA into the host organism. The first recombinant DNA molecule was made by Paul Berg in 1972 by combining DNA from the monkey virus SV40 with the lambda virus. As well as inserting genes, the process can be used to remove, or "knock out", genes. The new DNA can be inserted randomly, or targeted to a specific part of the genome. An organism that is generated through genetic engineering is considered to be genetically modified (GM) an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |