|
Pharmacodynamics
Pharmacodynamics (PD) is the study of the biochemical and physiologic effects of drugs (especially pharmaceutical drugs). The effects can include those manifested within animals (including humans), microorganisms, or combinations of organisms (for example, infection). Pharmacodynamics and pharmacokinetics are the main branches of pharmacology, being itself a topic of biology interested in the study of the interactions between both endogenous and exogenous chemical substances with living organisms. In particular, pharmacodynamics is the study of how a drug affects an organism, whereas pharmacokinetics is the study of how the organism affects the drug. Both together influence dosing, benefit, and adverse effects. Pharmacodynamics is sometimes abbreviated as PD and pharmacokinetics as PK, especially in combined reference (for example, when speaking of PK/PD models). Pharmacodynamics places particular emphasis on dose–response relationships, that is, the relationships betwee ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pharmacodynamics
Pharmacodynamics (PD) is the study of the biochemical and physiologic effects of drugs (especially pharmaceutical drugs). The effects can include those manifested within animals (including humans), microorganisms, or combinations of organisms (for example, infection). Pharmacodynamics and pharmacokinetics are the main branches of pharmacology, being itself a topic of biology interested in the study of the interactions between both endogenous and exogenous chemical substances with living organisms. In particular, pharmacodynamics is the study of how a drug affects an organism, whereas pharmacokinetics is the study of how the organism affects the drug. Both together influence dosing, benefit, and adverse effects. Pharmacodynamics is sometimes abbreviated as PD and pharmacokinetics as PK, especially in combined reference (for example, when speaking of PK/PD models). Pharmacodynamics places particular emphasis on dose–response relationships, that is, the relationships betwee ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pharmacology
Pharmacology is a branch of medicine, biology and pharmaceutical sciences concerned with drug or medication action, where a drug may be defined as any artificial, natural, or endogenous (from within the body) molecule which exerts a biochemical or physiological effect on the cell, tissue, organ, or organism (sometimes the word ''pharmacon'' is used as a term to encompass these endogenous and exogenous bioactive species). More specifically, it is the study of the interactions that occur between a living organism and chemicals that affect normal or abnormal biochemical function. If substances have medicinal properties, they are considered pharmaceuticals. The field encompasses drug composition and properties,functions,sources,synthesis and drug design, molecular and cellular mechanisms, organ/systems mechanisms, signal transduction/cellular communication, molecular diagnostics, interactions, chemical biology, therapy, and medical applications and antipathogenic capabili ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pharmacokinetics
Pharmacokinetics (from Ancient Greek ''pharmakon'' "drug" and ''kinetikos'' "moving, putting in motion"; see chemical kinetics), sometimes abbreviated as PK, is a branch of pharmacology dedicated to determining the fate of substances administered to a living organism. The substances of interest include any chemical xenobiotic such as: pharmaceutical drugs, pesticides, food additives, cosmetics, etc. It attempts to analyze chemical metabolism and to discover the fate of a chemical from the moment that it is administered up to the point at which it is completely eliminated from the body. Pharmacokinetics is the study of how an organism affects a drug, whereas pharmacodynamics (PD) is the study of how the drug affects the organism. Both together influence dosing, benefit, and adverse effects, as seen in PK/PD models. Overview Pharmacokinetics describes how the body affects a specific xenobiotic/chemical after administration through the mechanisms of absorption and distribut ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
PK/PD Models
PK/PD modeling (pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic modeling) (alternatively abbreviated as PKPD or PK-PD modeling) is a technique that combines the two classical pharmacologic disciplines of pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics. It integrates a pharmacokinetic and a pharmacodynamic model component into one set of mathematical expressions that allows the description of the time course of effect intensity in response to administration of a drug dose. PK/PD modeling is related to the field of pharmacometrics. Central to PK/PD models is the concentration-effect or exposure-response relationship. A variety of PK/PD modeling approaches exist to describe exposure-response relationships. PK/PD relationships can be described by simple equations such as linear model, Emax model or sigmoid Emax model. However, if a delay is observed between the drug administration and the drug effect, a temporal dissociation needs to be taken into account and more complex models exist: * Direct vs Indirect l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enzyme Modulator
An enzyme modulator is a type of drug which modulates enzymes. They include enzyme inhibitors and enzyme inducers. In an homogeneous assay, "an enzyme modulator ... is covalently linked to the ligand which competes with free ligand from the test sample for the available antibodies." See also * Channel modulator * Receptor modulator A receptor modulator, or receptor ligand, is a general term for a substance, endogenous or exogenous, that binds to and regulates the activity of chemical receptors. They are ligands that can act on different parts of receptors and regulate activit ... * Transporter modulator References Metabolism Enzyme inhibitors {{pharmacology-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neostigmine
Neostigmine, sold under the brand name Bloxiverz, among others, is a medication used to treat myasthenia gravis, Ogilvie syndrome, and urinary retention without the presence of a blockage. It is also used in anaesthesia to end the effects of non-depolarising neuromuscular blocking medication. It is given by injection either intravenous, into a vein, intramuscular, muscle, or subcutaneous injection, under the skin. After injection effects are generally greatest within 30 minutes and last up to 4 hours. Common side effects include nausea, increased saliva, crampy abdominal pain, and slow heart rate. More severe side effects include low blood pressure, weakness, and allergic reactions. It is unclear if use in pregnancy is safe for the baby. Neostigmine is in the cholinergic family of medications. It works by blocking the action of acetylcholinesterase and therefore increases the levels of acetylcholine. Neostigmine was patented in 1931. It is on the WHO Model List of Essential M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
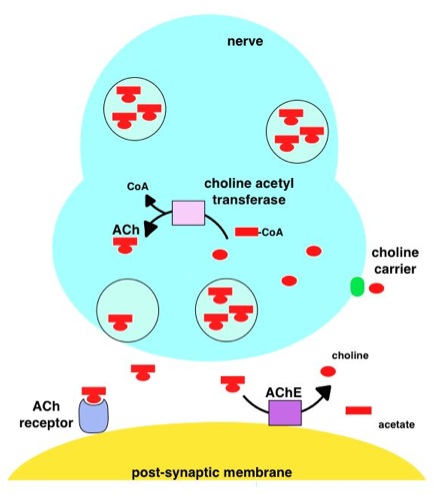
Acetylcholinesterase
Acetylcholinesterase (HGNC symbol ACHE; EC 3.1.1.7; systematic name acetylcholine acetylhydrolase), also known as AChE, AChase or acetylhydrolase, is the primary cholinesterase in the body. It is an enzyme that catalyzes the breakdown of acetylcholine and some other choline esters that function as neurotransmitters: : acetylcholine + H2O = choline + acetate It is found at mainly neuromuscular junctions and in chemical synapses of the cholinergic type, where its activity serves to terminate synaptic transmission. It belongs to the carboxylesterase family of enzymes. It is the primary target of inhibition by organophosphorus compounds such as nerve agents and pesticides. Enzyme structure and mechanism AChE is a hydrolase that hydrolyzes choline esters. It has a very high catalytic activity—each molecule of AChE degrades about 25,000 molecules of acetylcholine (ACh) per second, approaching the limit allowed by diffusion of the substrate. The active site of AChE comprises 2 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enzyme Inhibitor
An enzyme inhibitor is a molecule that binds to an enzyme and blocks its activity. Enzymes are proteins that speed up chemical reactions necessary for life, in which substrate molecules are converted into products. An enzyme facilitates a specific chemical reaction by binding the substrate to its active site, a specialized area on the enzyme that accelerates the most difficult step of the reaction. An enzyme inhibitor stops ("inhibits") this process, either by binding to the enzyme's active site (thus preventing the substrate itself from binding) or by binding to another site on the enzyme such that the enzyme's catalysis of the reaction is blocked. Enzyme inhibitors may bind reversibly or irreversibly. Irreversible inhibitors form a chemical bond with the enzyme such that the enzyme is inhibited until the chemical bond is broken. By contrast, reversible inhibitors bind non-covalently and may spontaneously leave the enzyme, allowing the enzyme to resume its function. Rev ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enzyme Inducer
An enzyme inducer is a type of drug that increases the metabolic activity of an enzyme either by binding to the enzyme and activating it, or by increasing the expression of the gene coding for the enzyme. It is the opposite of an enzyme repressor. See also * Enzyme activator * Enzyme inhibitor * Regulation of gene expression Regulation of gene expression, or gene regulation, includes a wide range of mechanisms that are used by cells to increase or decrease the production of specific gene products (protein or RNA). Sophisticated programs of gene expression are wid ... References External links Hepatic enzyme inducersHepatic enzyme inhibitors Medicinal chemistry Enzymes Metabolism {{medicinal-chem-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thermodynamic Free Energy
The thermodynamic free energy is a concept useful in the thermodynamics of chemical or thermal processes in engineering and science. The change in the free energy is the maximum amount of work that a thermodynamic system can perform in a process at constant temperature, and its sign indicates whether the process is thermodynamically favorable or forbidden. Since free energy usually contains potential energy, it is not absolute but depends on the choice of a zero point. Therefore, only relative free energy values, or changes in free energy, are physically meaningful. The free energy is a thermodynamic state function, like the internal energy, enthalpy, and entropy. The free energy is the portion of any first-law energy that is available to perform thermodynamic work at constant temperature, ''i.e.'', work mediated by thermal energy. Free energy is subject to irreversible loss in the course of such work. Since first-law energy is always conserved, it is evident that free energy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enzyme Activator
Enzyme activators are molecules that bind to enzymes and increase their activity. They are the opposite of enzyme inhibitors. These molecules are often involved in the allosteric regulation of enzymes in the control of metabolism. An example of an enzyme activator working in this way is fructose 2,6-bisphosphate, which activates phosphofructokinase 1 and increases the rate of glycolysis in response to the hormone glucagon. In some cases, when a substrate binds to one catalytic subunit of an enzyme, this can trigger an increase in the substrate affinity as well as catalytic activity in the enzyme's other subunits, and thus the substrate acts as an activator. Examples Hexokinase-I Hexokinase-I (HK-I) is an enzyme activator because it draws glucose into the glycolysis pathway. Its function is to phosphorylate glucose releasing glucose-6-phosphate (G6P) as the product. HK-I not only signals the activation of glucose into glycolysis but also maintains a low glucose concentra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |