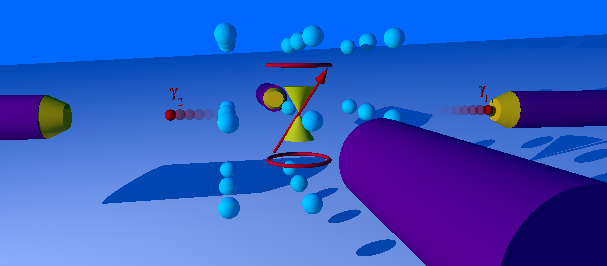|
Perturbed Angular Correlation
The perturbed γ-γ angular correlation, PAC for short or PAC-Spectroscopy, is a method of nuclear solid-state physics with which magnetic and electric fields in crystal structures can be measured. In doing so, electrical field gradients and the Larmor frequency in magnetic fields as well as dynamic effects are determined. With this very sensitive method, which requires only about 10-1000 billion atoms of a radioactive isotope per measurement, material properties in the local structure, phase transitions, magnetism and diffusion can be investigated. The PAC method is related to nuclear magnetic resonance and the Mössbauer effect, but shows no signal attenuation at very high temperatures. Today only the time-differential perturbed angular correlation (TDPAC) is used. History and development PAC goes back to a theoretical work by Donald R. Hamilton from 1940. The first successful experiment was carried out by Brady and Deutsch in 1947. Essentially spin and parity of nuclear spi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Perturbation Theory (quantum Mechanics)
In quantum mechanics, perturbation theory is a set of approximation schemes directly related to mathematical perturbation for describing a complicated quantum system in terms of a simpler one. The idea is to start with a simple system for which a mathematical solution is known, and add an additional "perturbing" Hamiltonian representing a weak disturbance to the system. If the disturbance is not too large, the various physical quantities associated with the perturbed system (e.g. its energy levels and eigenstates) can be expressed as "corrections" to those of the simple system. These corrections, being small compared to the size of the quantities themselves, can be calculated using approximate methods such as asymptotic series. The complicated system can therefore be studied based on knowledge of the simpler one. In effect, it is describing a complicated unsolved system using a simple, solvable system. Approximate Hamiltonians Perturbation theory is an important tool for de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Auger Effect
The Auger effect or Auger−Meitner effect is a physical phenomenon in which the filling of an inner-shell vacancy of an atom is accompanied by the emission of an electron from the same atom. When a core electron is removed, leaving a vacancy, an electron from a higher energy level may fall into the vacancy, resulting in a release of energy. Although most often this energy is released in the form of an emitted photon, the energy can also be transferred to another electron, which is ejected from the atom; this second ejected electron is called an Auger electron. Effect The effect was first discovered by Lise Meitner in 1922; Pierre Victor Auger independently discovered the effect shortly after and is credited with the discovery in most of the scientific community. Upon ejection, the kinetic energy of the Auger electron corresponds to the difference between the energy of the initial electronic transition into the vacancy and the ionization energy for the electron shell from which ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Planck Constant
The Planck constant, or Planck's constant, is a fundamental physical constant of foundational importance in quantum mechanics. The constant gives the relationship between the energy of a photon and its frequency, and by the mass-energy equivalence, the relationship between mass and frequency. Specifically, a photon's energy is equal to its frequency multiplied by the Planck constant. The constant is generally denoted by h. The reduced Planck constant, or Dirac constant, equal to the constant divided by 2 \pi, is denoted by \hbar. In metrology it is used, together with other constants, to define the kilogram, the SI unit of mass. The SI units are defined in such a way that, when the Planck constant is expressed in SI units, it has the exact value The constant was first postulated by Max Planck in 1900 as part of a solution to the ultraviolet catastrophe. At the end of the 19th century, accurate measurements of the spectrum of black body radiation existed, but the distribut ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Elementary Charge
The elementary charge, usually denoted by is the electric charge carried by a single proton or, equivalently, the magnitude of the negative electric charge carried by a single electron, which has charge −1 . This elementary charge is a fundamental physical constant. In the SI system of units, the value of the elementary charge is exactly defined as e = coulombs, or 160.2176634 zeptocoulombs (zC). Since the 2019 redefinition of SI base units, the seven SI base units are defined by seven fundamental physical constants, of which the elementary charge is one. In the centimetre–gram–second system of units (CGS), the corresponding quantity is . Robert A. Millikan and Harvey Fletcher's oil drop experiment first directly measured the magnitude of the elementary charge in 1909, differing from the modern accepted value by just 0.6%. Under assumptions of the then-disputed atomic theory, the elementary charge had also been indirectly inferred to ~3% accuracy from bla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Laplace Equation
In mathematics and physics, Laplace's equation is a second-order partial differential equation named after Pierre-Simon Laplace, who first studied its properties. This is often written as \nabla^2\! f = 0 or \Delta f = 0, where \Delta = \nabla \cdot \nabla = \nabla^2 is the Laplace operator,The delta symbol, Δ, is also commonly used to represent a finite change in some quantity, for example, \Delta x = x_1 - x_2. Its use to represent the Laplacian should not be confused with this use. \nabla \cdot is the divergence operator (also symbolized "div"), \nabla is the gradient operator (also symbolized "grad"), and f (x, y, z) is a twice-differentiable real-valued function. The Laplace operator therefore maps a scalar function to another scalar function. If the right-hand side is specified as a given function, h(x, y, z), we have \Delta f = h. This is called Poisson's equation, a generalization of Laplace's equation. Laplace's equation and Poisson's equation are the simplest exa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quadrupole Moment
A quadrupole or quadrapole is one of a sequence of configurations of things like electric charge or current, or gravitational mass that can exist in ideal form, but it is usually just part of a multipole expansion of a more complex structure reflecting various orders of complexity. Mathematical definition The quadrupole moment tensor ''Q'' is a rank-two tensor—3×3 matrix. There are several definitions, but it is normally stated in the traceless form (i.e. Q_ + Q_ + Q_ = 0). The quadrupole moment tensor has thus nine components, but because of transposition symmetry and zero-trace property, in this form only five of these are independent. For a discrete system of \ell point charges or masses in the case of a gravitational quadrupole, each with charge q_\ell, or mass m_\ell, and position \vec_\ell = \left(r_, r_, r_\right) relative to the coordinate system origin, the components of the ''Q'' matrix are defined by: : Q_ = \sum_\ell q_\ell\left(3r_ r_ - \left\, \vec_\ell \righ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nuclear Magneton
The nuclear magneton (symbol ''μ'') is a physical constant of magnetic moment, defined in SI units by: :\mu_\text = and in Gaussian CGS units by: :\mu_\text = where: :''e'' is the elementary charge, :''ħ'' is the reduced Planck constant, :''m'' is the proton rest mass, and :''c'' is the speed of light In SI units, its value is approximately: :''μ'' = In Gaussian CGS units, its value can be given in convenient units as :''μ'' = The nuclear magneton is the natural unit for expressing magnetic dipole moments of heavy particles such as nucleons and atomic nuclei. Due to the fact that neutrons and protons consist of quarks and thus are not really Dirac particles, their magnetic moments differ from ''μ'': :\mu_\text = 2793 \mu_\text :\mu_\text = -1913 \mu_\text The magnetic dipole moment of the electron, which is much larger as a consequence of much larger charge-to-mass ratio, is usually expressed in units of the ''Bohr magneton'', which is calculated in the same ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Landé G-factor
In physics, the Landé ''g''-factor is a particular example of a ''g''-factor, namely for an electron with both spin and orbital angular momenta. It is named after Alfred Landé, who first described it in 1921. In atomic physics, the Landé ''g''-factor is a multiplicative term appearing in the expression for the energy levels of an atom in a weak magnetic field. The quantum states of electrons in atomic orbitals are normally degenerate in energy, with these degenerate states all sharing the same angular momentum. When the atom is placed in a weak magnetic field, however, the degeneracy is lifted. Description The factor comes about during the calculation of the first-order perturbation in the energy of an atom when a weak uniform magnetic field (that is, weak in comparison to the system's internal magnetic field) is applied to the system. Formally we can write the factor as, :g_J= g_L\frac+g_S\frac. The orbital g_L is equal to 1, and under the approximation g_S = 2 , the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nuclear Spin
In atomic physics, the spin quantum number is a quantum number (designated ) which describes the intrinsic angular momentum (or spin angular momentum, or simply spin) of an electron or other particle. The phrase was originally used to describe the fourth of a set of quantum numbers (the principal quantum number , the azimuthal quantum number , the magnetic quantum number , and the spin quantum number ), which completely describe the quantum state of an electron in an atom. The name comes from a physical spinning of the electron about an axis, as proposed by Uhlenbeck and Goudsmit. The value of is the component of spin angular momentum parallel to a given direction (the –axis), which can be either +1/2 or –1/2 (in units of the reduced Planck constant). However this simplistic picture was quickly realized to be physically impossible because it would require the electrons to rotate faster than the speed of light. It was therefore replaced by a more abstract quantum-mechanical ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |