|
Persistence Length
The persistence length is a basic mechanical property quantifying the bending stiffness of a polymer. The molecule behaves like a flexible elastic rod/beam (beam theory). Informally, for pieces of the polymer that are shorter than the persistence length, the molecule behaves like a rigid rod, while for pieces of the polymer that are much longer than the persistence length, the properties can only be described statistically, like a three-dimensional random walk. Formally, the persistence length, ''P'', is defined as the length over which correlations in the direction of the tangent are lost. In a more chemical based manner it can also be defined as the average sum of the projections of all bonds j ≥ i on bond i in an infinitely long chain. Let us define the angle ''θ'' between a vector that is tangent to the polymer at position 0 (zero) and a tangent vector at a distance ''L'' away from position 0, along the contour of the chain. It can be shown that the expectation value o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bending Stiffness
The bending stiffness (K) is the resistance of a member against bending deformation. It is a function of the Young's modulus E, the second moment of area I of the beam cross-section about the axis of interest, length of the beam and beam boundary condition. Bending stiffness of a beam can analytically be derived from the equation of beam deflection when it is applied by a force. :K = \frac where \mathrm is the applied force and \mathrm is the deflection. According to elementary beam theory, the relationship between the applied bending moment M and the resulting curvature \kappa of the beam is: :M = E I \kappa = E I \frac{\mathrm{d} x^2} where w is the deflection of the beam and x is the distance along the beam. Double integration of the above equation leads to computing the deflection of the beam, and in turn, the bending stiffness of the beam. Bending stiffness in beams is also known as Flexural rigidity. See also * Applied mechanics * Beam theory * Bending In applied ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Förster Resonance Energy Transfer
Förster resonance energy transfer (FRET), fluorescence resonance energy transfer, resonance energy transfer (RET) or electronic energy transfer (EET) is a mechanism describing energy transfer between two light-sensitive molecules (chromophores). A donor chromophore, initially in its electronic excited state, may transfer energy to an acceptor chromophore through nonradiative dipole–dipole coupling. The efficiency of this energy transfer is inversely proportional to the sixth power of the distance between donor and acceptor, making FRET extremely sensitive to small changes in distance. Measurements of FRET efficiency can be used to determine if two fluorophores are within a certain distance of each other. Such measurements are used as a research tool in fields including biology and chemistry. FRET is analogous to near-field communication, in that the radius of interaction is much smaller than the wavelength of light emitted. In the near-field region, the excited chromophore em ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paul Flory
Paul John Flory (June 19, 1910 – September 9, 1985) was an American chemist and Nobel laureate who was known for his work in the field of polymers, or macromolecules. He was a leading pioneer in understanding the behavior of polymers in solution, and won the Nobel Prize in Chemistry in 1974 "for his fundamental achievements, both theoretical and experimental, in the physical chemistry of macromolecules". Biography Personal life Flory was born in Sterling, Illinois, on June 19, 1910. He was raised by Ezra Flory and Nee Martha Brumbaugh. His father worked as a clergyman-educator, and his mother was a school teacher. He first gained his interest in science from Carl W Holl, who was a professor in chemistry. Holl was employed in Indiana at Manchester College as a chemistry professor. In 1936, he married Emily Catherine Tabor. He and Emily had three children together; Susan Springer, Melinda Groom and Paul John Flory jr. They also had five grandchildren. All of his children pu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Worm-like Chain
The worm-like chain (WLC) model in polymer physics is used to describe the behavior of polymers that are semi-flexible: fairly stiff with successive segments pointing in roughly the same direction, and with persistence length within a few orders of magnitude of the polymer length. The WLC model is the continuous version of the Kratky– Porod model. Model elements The WLC model envisions a continuously flexible isotropic rod. This is in contrast to the freely-jointed chain model, which is only flexible between discrete freely hinged segments. The model is particularly suited for describing stiffer polymers, with successive segments displaying a sort of cooperativity: nearby segments are roughly aligned. At room temperature, the polymer adopts a smoothly curved conformation; at T = 0 K, the polymer adopts a rigid rod conformation. For a polymer of maximum length L_0, parametrize the path of the polymer as s \in(0,L_0). Allow \hat t(s) to be the unit tangent vector to the chain ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polymer
A polymer (; Greek '' poly-'', "many" + ''-mer'', "part") is a substance or material consisting of very large molecules called macromolecules, composed of many repeating subunits. Due to their broad spectrum of properties, both synthetic and natural polymers play essential and ubiquitous roles in everyday life. Polymers range from familiar synthetic plastics such as polystyrene to natural biopolymers such as DNA and proteins that are fundamental to biological structure and function. Polymers, both natural and synthetic, are created via polymerization of many small molecules, known as monomers. Their consequently large molecular mass, relative to small molecule compounds, produces unique physical properties including toughness, high elasticity, viscoelasticity, and a tendency to form amorphous and semicrystalline structures rather than crystals. The term "polymer" derives from the Greek word πολύς (''polus'', meaning "many, much") and μέρος (''meros'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stokes–Einstein Equation
In physics (specifically, the kinetic theory of gases), the Einstein relation is a previously unexpected connection revealed independently by William Sutherland in 1904, Albert Einstein in 1905, and by Marian Smoluchowski in 1906 in their works on Brownian motion. The more general form of the equation is D = \mu \, k_\text T, where * is the diffusion coefficient; * is the "mobility", or the ratio of the particle's terminal drift velocity to an applied force, ; * is the Boltzmann constant; * is the absolute temperature. This equation is an early example of a fluctuation-dissipation relation. Two frequently used important special forms of the relation are: * Einstein–Smoluchowski equation, for diffusion of charged particles: D = \frac * Stokes–Einstein equation, for diffusion of spherical particles through a liquid with low Reynolds number: D = \frac Here * is the electrical charge of a particle; * is the electrical mobility of the charged particle; * is the dynam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
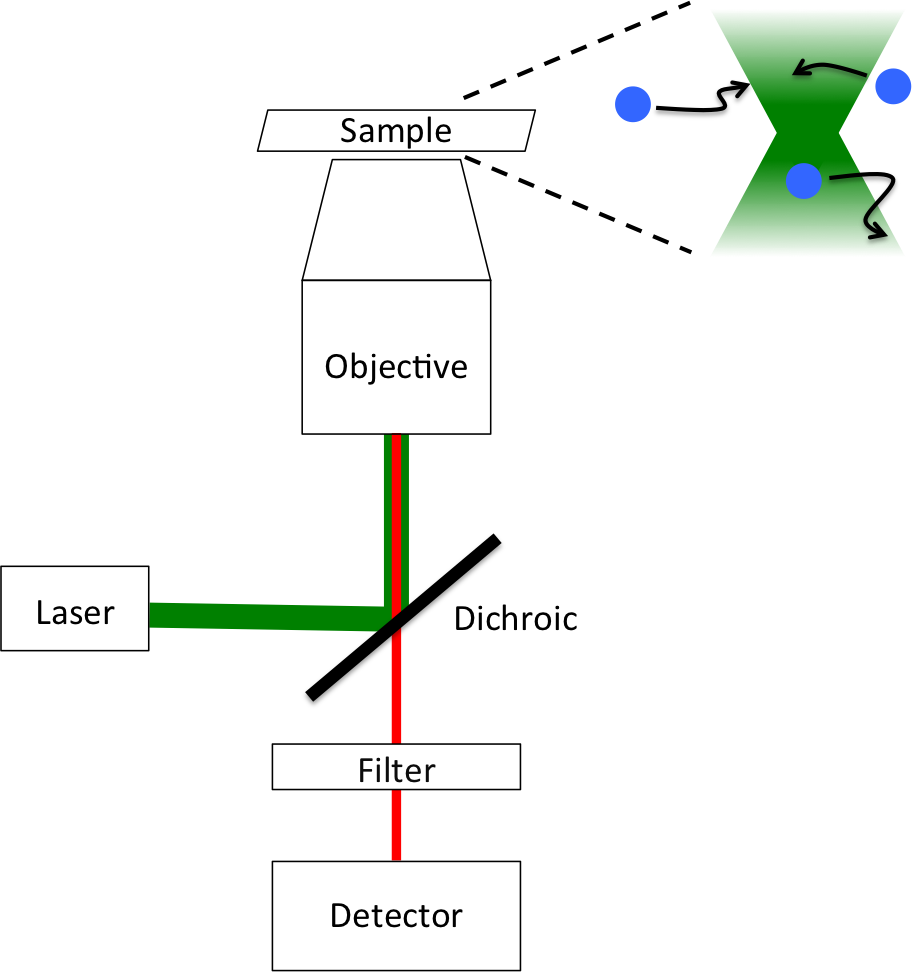
Fluorescence Correlation Spectroscopy
Fluorescence correlation spectroscopy (FCS) is a statistical analysis, via time correlation, of stationary fluctuations of the fluorescence intensity. Its theoretical underpinning originated from L. Onsager's regression hypothesis. The analysis provides kinetic parameters of the physical processes underlying the fluctuations. One of the interesting applications of this is an analysis of the concentration fluctuations of fluorescent particles (molecules) in solution. In this application, the fluorescence emitted from a very tiny space in solution containing a small number of fluorescent particles (molecules) is observed. The fluorescence intensity is fluctuating due to Brownian motion of the particles. In other words, the number of the particles in the sub-space defined by the optical system is randomly changing around the average number. The analysis gives the average number of fluorescent particles and average diffusion time, when the particle is passing through the space. Eventua ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Worm-like Chain
The worm-like chain (WLC) model in polymer physics is used to describe the behavior of polymers that are semi-flexible: fairly stiff with successive segments pointing in roughly the same direction, and with persistence length within a few orders of magnitude of the polymer length. The WLC model is the continuous version of the Kratky– Porod model. Model elements The WLC model envisions a continuously flexible isotropic rod. This is in contrast to the freely-jointed chain model, which is only flexible between discrete freely hinged segments. The model is particularly suited for describing stiffer polymers, with successive segments displaying a sort of cooperativity: nearby segments are roughly aligned. At room temperature, the polymer adopts a smoothly curved conformation; at T = 0 K, the polymer adopts a rigid rod conformation. For a polymer of maximum length L_0, parametrize the path of the polymer as s \in(0,L_0). Allow \hat t(s) to be the unit tangent vector to the chain ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polymer
A polymer (; Greek '' poly-'', "many" + ''-mer'', "part") is a substance or material consisting of very large molecules called macromolecules, composed of many repeating subunits. Due to their broad spectrum of properties, both synthetic and natural polymers play essential and ubiquitous roles in everyday life. Polymers range from familiar synthetic plastics such as polystyrene to natural biopolymers such as DNA and proteins that are fundamental to biological structure and function. Polymers, both natural and synthetic, are created via polymerization of many small molecules, known as monomers. Their consequently large molecular mass, relative to small molecule compounds, produces unique physical properties including toughness, high elasticity, viscoelasticity, and a tendency to form amorphous and semicrystalline structures rather than crystals. The term "polymer" derives from the Greek word πολύς (''polus'', meaning "many, much") and μέρος (''meros'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ångström
The angstromEntry "angstrom" in the Oxford online dictionary. Retrieved on 2019-03-02 from https://en.oxforddictionaries.com/definition/angstrom.Entry "angstrom" in the Merriam-Webster online dictionary. Retrieved on 2019-03-02 from https://www.merriam-webster.com/dictionary/angstrom. (, ; , ) or ångström is a metric unit of length equal to m; that is, one ten-billionth ( US) of a metre, a hundred-millionth of a centimetre,Entry "angstrom" in the Oxford English Dictionary, 2nd edition (1986). Retrieved on 2021-11-22 from https://www.oed.com/oed2/00008552. 0.1 nanometre, or 100 picometres. Its symbol is Å, a letter of the Swedish alphabet. The unit is named after the Swedish physicist Anders Jonas Ångström (1814–1874). The angstrom is often used in the natural sciences and technology to express sizes of atoms, molecules, microscopic biological structures, and lengths of chemical bonds, arrangement of atoms in crystals,Arturas Vailionis (2015):Geometry of Crystals Le ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spaghetti
Spaghetti () is a long, thin, solid, cylindrical pasta.spaghetti Dictionary.com. Dictionary.com Unabridged (v 1.1). Random House, Inc. (accessed: 3 June 2008). It is a of traditional . Like other pasta, spaghetti is made of milled and and sometimes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |