|
Perihepatic Packing
Perihepatic packing is a surgical procedure used in connection with trauma surgery to the liver. In this procedure the liver is packed to stop non arterial bleeding, most often caused by liver injury. During this surgery laparotomy pads are placed around the bleeding liver. The main purpose of hepatic packing is to prevent the bleeding so trauma triad of death can be avoided. Under- or over-packing of the liver can cause adverse outcomes, and if the bleeding cannot be controlled through this surgical method, the Pringle manoeuvre The Pringle manoeuvre is a surgical technique used in some abdominal operations and in liver trauma. The hepatoduodenal ligament is clamped either with a surgical tool called a haemostat, an umbilical tape or by hand. This limits blood inflow thr ... is an alternate technique that can be utilized temporally. References Surgical procedures and techniques {{surgery-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trauma Surgery
Trauma surgery is a surgery, surgical Specialty (medicine), specialty that utilizes both operative and non-operative management to treat traumatic injuries, typically in an acute setting. Trauma surgeons generally complete Residency (medicine), residency training in General surgery, general surgery and often fellowship training in trauma or surgical intensive-care medicine, critical care. The trauma surgeon is responsible for initially resuscitating and stabilizing and later evaluating and managing the patient. The attending trauma surgeon also leads the trauma team, which typically includes nurses and support staff as well as resident physicians in teaching hospitals. Training Most United States trauma surgeons practice in larger centers and complete a 1-2 year trauma surgery fellowship, which often includes a surgical critical care fellowship. They may therefore sit for the American Board of Surgery (ABS) certifying examination in Surgical Critical Care. National surgical ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Liver
The liver is a major Organ (anatomy), organ only found in vertebrates which performs many essential biological functions such as detoxification of the organism, and the Protein biosynthesis, synthesis of proteins and biochemicals necessary for digestion and growth. In humans, it is located in the quadrant (anatomy), right upper quadrant of the abdomen, below the thoracic diaphragm, diaphragm. Its other roles in metabolism include the regulation of Glycogen, glycogen storage, decomposition of red blood cells, and the production of hormones. The liver is an accessory digestive organ that produces bile, an alkaline fluid containing cholesterol and bile acids, which helps the fatty acid degradation, breakdown of fat. The gallbladder, a small pouch that sits just under the liver, stores bile produced by the liver which is later moved to the small intestine to complete digestion. The liver's highly specialized biological tissue, tissue, consisting mostly of hepatocytes, regulates a w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Artery
An artery (plural arteries) () is a blood vessel in humans and most animals that takes blood away from the heart to one or more parts of the body (tissues, lungs, brain etc.). Most arteries carry oxygenated blood; the two exceptions are the pulmonary and the umbilical arteries, which carry deoxygenated blood to the organs that oxygenate it (lungs and placenta, respectively). The effective arterial blood volume is that extracellular fluid which fills the arterial system. The arteries are part of the circulatory system, that is responsible for the delivery of oxygen and nutrients to all cells, as well as the removal of carbon dioxide and waste products, the maintenance of optimum blood pH, and the circulation of proteins and cells of the immune system. Arteries contrast with veins, which carry blood back towards the heart. Structure The anatomy of arteries can be separated into gross anatomy, at the macroscopic level, and microanatomy, which must be studied with a microscop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
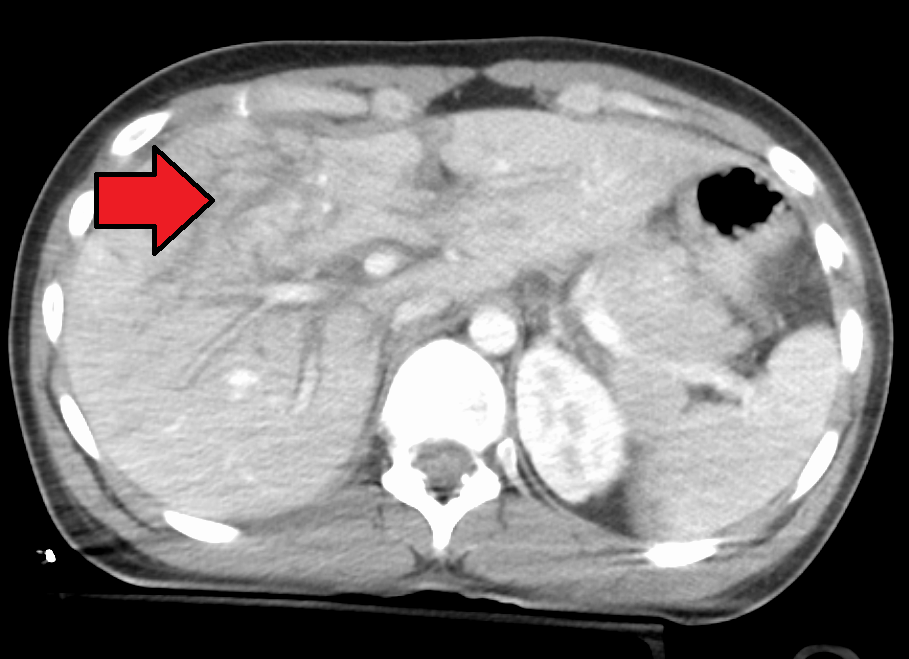
Liver Injury
A liver injury, also known as liver laceration, is some form of trauma sustained to the liver. This can occur through either a blunt force such as a car accident, or a penetrating foreign object such as a knife. Liver injuries constitute 5% of all traumas, making it the most common abdominal injury. Generally nonoperative management and observation is all that is required for a full recovery. Cause Given its anterior position in the abdominal cavity and its large size, the liver is prone to gun shot wounds and stab wounds. Its firm location under the diaphragm also makes it especially prone to shearing forces. Common causes of this type of injury are blunt force mechanisms such as motor vehicle accidents, falls, and sports injuries. Typically these blunt forces dissipate through and around the structure of the liver and causes irreparable damage to the internal microarchitecture of the tissue. With increasing velocity of the impact, the internal damage of the liver tissue als ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trauma Triad Of Death
The trauma triad of death is a medical term describing the combination of hypothermia, acidosis, and coagulopathy. This combination is commonly seen in patients who have sustained severe traumatic injuries and results in a significant rise in the mortality rate. Commonly, when someone presents with these signs, damage control surgery is employed to reverse the effects. The three conditions share a complex relationship; each factor can compound the others, resulting in high mortality if this positive feedback loop continues uninterrupted. Severe bleeding in trauma diminishes oxygen delivery, and may lead to hypothermia. This in turn can halt the coagulation cascade, preventing blood from clotting. In the absence of blood-bound oxygen and nutrients (hypoperfusion), the body's cells burn glucose anaerobically for energy, causing the release of lactic acid, ketone bodies, and other acidic compounds into the blood stream, which lower the blood's pH, leading to metabolic acido ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pringle Manoeuvre
The Pringle manoeuvre is a surgical technique used in some abdominal operations and in liver trauma. The hepatoduodenal ligament is clamped either with a surgical tool called a haemostat, an umbilical tape or by hand. This limits blood inflow through the hepatic artery and the portal vein, controlling bleeding from the liver. Uses The Pringle manoeuvre is used during liver surgery and in some cases of severe liver trauma to minimize blood loss. For short durations of use, it is very effective at reducing intraoperative blood loss. The Pringle manoeuvre is applied during closure of a vena cava injury when an atriocaval shunt is placed. Limits The Pringle manoeuvre is more effective in preventing blood loss during liver surgery if central venous pressure is maintained at 5 mmHg or lower. This is due to the fact that Pringle manoeuver technique aims at controlling the blood inflow into the liver, having no effect on the outflow. In case of using Pringle manoeuver during liver ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Surgical Clinics Of North America
''The'' () is a grammatical article in English, denoting persons or things that are already or about to be mentioned, under discussion, implied or otherwise presumed familiar to listeners, readers, or speakers. It is the definite article in English. ''The'' is the most frequently used word in the English language; studies and analyses of texts have found it to account for seven percent of all printed English-language words. It is derived from gendered articles in Old English which combined in Middle English and now has a single form used with nouns of any gender. The word can be used with both singular and plural nouns, and with a noun that starts with any letter. This is different from many other languages, which have different forms of the definite article for different genders or numbers. Pronunciation In most dialects, "the" is pronounced as (with the voiced dental fricative followed by a schwa) when followed by a consonant sound, and as (homophone of the archaic pron ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.png)