|
Penumbra (medicine)
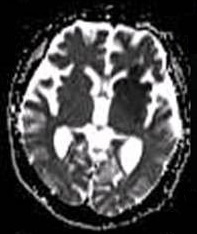
In pathology and anatomy the penumbra is the area surrounding an ischemic event such as thrombotic or embolic stroke. Immediately following the event, blood flow and therefore oxygen transport is reduced locally, leading to hypoxia of the cells near the location of the original insult. This can lead to hypoxic cell death (infarction) and amplify the original damage from the ischemia; however, the penumbra area may remain viable for several hours after an ischemic event due to the collateral arteries that supply the penumbral zone. As time elapses after the onset of stroke, the extent of the penumbra tends to decrease; therefore, in the emergency department a major concern is to protect the penumbra by increasing oxygen transport and delivery to cells in the danger zone, thereby limiting cell death. The existence of a penumbra implies that salvage of the cells is possible. There is a high correlation between the extent of spontaneous neurological recovery and the volume of penum ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pathology
Pathology is the study of the causes and effects of disease or injury. The word ''pathology'' also refers to the study of disease in general, incorporating a wide range of biology research fields and medical practices. However, when used in the context of modern medical treatment, the term is often used in a narrower fashion to refer to processes and tests that fall within the contemporary medical field of "general pathology", an area which includes a number of distinct but inter-related medical specialties that diagnose disease, mostly through analysis of tissue, cell, and body fluid samples. Idiomatically, "a pathology" may also refer to the predicted or actual progression of particular diseases (as in the statement "the many different forms of cancer have diverse pathologies", in which case a more proper choice of word would be " pathophysiologies"), and the affix ''pathy'' is sometimes used to indicate a state of disease in cases of both physical ailment (as in cardiomy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ion Pumps
An ion pump (also referred to as a sputter ion pump) is a type of vacuum pump which operates by sputtering a metal getter. Under ideal conditions, ion pumps are capable of reaching pressures as low as 10−11 mbar. An ion pump first ionizes gas within the vessel it is attached to and employs a strong electrical potential, typically 3–7 kV, which accelerates the ions into a solid electrode. Small bits of the electrode are sputtered into the chamber. Gasses are trapped by a combination of chemical reactions with the surface of the highly-reactive sputtered material, and being physically trapped underneath that material. History The first evidence for pumping from electrical discharge was found 1858 by Julius Plücker, who did early experiments on electrical discharge in vacuum tubes. In 1937, Frans Michel Penning observed some evidence of pumping in the operation of his cold cathode gauge. These early effects were comparatively slow to pump, and were therefore not commerc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tissue Remodeling
Tissue remodeling is the reorganization or renovation of existing tissues. Tissue remodeling can be either physiological or pathological. The process can either change the characteristics of a tissue such as in blood vessel remodeling, or result in the dynamic equilibrium of a tissue such as in bone remodeling. Macrophages repair wounds and remodel tissue by producing extracellular matrix and proteases to modify that specific matrix. A myocardial infarction induces tissue remodeling of the heart in a three-phase process: inflammation, proliferation, and maturation. Inflammation is characterized by massive necrosis in the infarcted area. Inflammatory cells clear the dead cells. In the proliferation phase, inflammatory cells die by apoptosis, being replaced by myofibroblasts which produce large amounts of collagen. In the maturation phase, myofibroblast numbers are reduced by apoptosis, allowing for infiltration by endothelial cells (for blood vessels) and cardiomyocytes (heart tissu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thrombectomy
Mechanical thrombectomy, or simply thrombectomy, is the interventional procedure of removing a blood clot (thrombus) from a blood vessel. It is commonly performed in the cerebral arteries (interventional neuroradiology). The effectiveness of thrombectomy was confirmed in several randomised clinical trials conducted at various medical centers throughout the United States. Notable physicians involved in the approval of thrombectomy include Jeffrey L. Saver, Mayank Goyal, Tudor G. Jovin, Adnan H. Siddiqui, Elad Levy , and Reza Jahan. Applications in brain Ischemic stroke represents the fifth most common cause of death in the western world and the number one cause of long-term disability. Until recent times, systemic intravenous fibrinolysis was the only evidence-based therapy for patients with acute onset of stroke due to large vessel occlusion. In 2015, the results of five trials from different countries were published in the ''New England Journal of Medicine'', demonstrating t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thrombolysis
Thrombolysis, also called fibrinolytic therapy, is the breakdown (lysis) of blood clots formed in blood vessels, using medication. It is used in ST elevation myocardial infarction, stroke, and in cases of severe venous thromboembolism (massive pulmonary embolism or extensive deep vein thrombosis). The main complication is bleeding (which can be dangerous), and in some situations thrombolysis may therefore be unsuitable. Thrombolysis can also play an important part in reperfusion therapy that deals specifically with blocked arteries. Medical uses Diseases where thrombolysis is used: * ST elevation myocardial infarction: Large trials have shown that mortality can be reduced using thrombolysis (particularly fibrinolysis) in treating heart attacks. It works by stimulating secondary fibrinolysis by plasmin through infusion of analogs of tissue plasminogen activator (tPA), the protein that normally activates plasmin. * Stroke: Thrombolysis reduces major disability or death when given ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cerebral Infarction
A cerebral infarction is the pathologic process that results in an area of necrotic tissue in the brain (cerebral infarct). It is caused by disrupted blood supply ( ischemia) and restricted oxygen supply ( hypoxia), most commonly due to thromboembolism, and manifests clinically as ischemic stroke. In response to ischemia, the brain degenerates by the process of liquefactive necrosis. Classification There are various classification systems for a cerebral infarction, some of which are described below. * The Oxford Community Stroke Project classification (OCSP, also known as the Bamford or Oxford classification) relies primarily on the initial symptoms. Based on the extent of the symptoms, the stroke episode is classified as total anterior circulation infarct (TACI), partial anterior circulation infarct (PACI), lacunar infarct (LACI) or posterior circulation infarct (POCI). These four entities predict the extent of the stroke, the area of the brain affected, the underlying cause, an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Perfusion
Perfusion is the passage of fluid through the circulatory system or lymphatic system to an organ or a tissue, usually referring to the delivery of blood to a capillary bed in tissue. Perfusion is measured as the rate at which blood is delivered to tissue, or volume of blood per unit time (blood flow) per unit tissue mass. The SI unit is m3/(s·kg), although for human organs perfusion is typically reported in ml/min/g. The word is derived from the French verb "perfuser" meaning to "pour over or through". All animal tissues require an adequate blood supply for health and life. Poor perfusion (malperfusion), that is, ischemia, causes health problems, as seen in cardiovascular disease, including coronary artery disease, cerebrovascular disease, peripheral artery disease, and many other conditions. Tests verifying that adequate perfusion exists are a part of a patient's assessment process that are performed by medical or emergency personnel. The most common methods include evalua ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ischemia
Ischemia or ischaemia is a restriction in blood supply to any tissue, muscle group, or organ of the body, causing a shortage of oxygen that is needed for cellular metabolism (to keep tissue alive). Ischemia is generally caused by problems with blood vessels, with resultant damage to or dysfunction of tissue i.e. hypoxia and microvascular dysfunction. It also implies local hypoxia in a part of a body resulting from constriction (such as vasoconstriction, thrombosis, or embolism). Ischemia causes not only insufficiency of oxygen, but also reduced availability of nutrients and inadequate removal of metabolic wastes. Ischemia can be partial (poor perfusion) or total blockage. The inadequate delivery of oxygenated blood to the organs must be resolved either by treating the cause of the inadequate delivery or reducing the oxygen demand of the system that needs it. For example, patients with myocardial ischemia have a decreased blood flow to the heart and are prescribed with medi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diffusion Weighted Imaging
Diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging (DWI or DW-MRI) is the use of specific MRI sequences as well as software that generates images from the resulting data that uses the diffusion of water molecules to generate contrast in MR images. It allows the mapping of the diffusion process of molecules, mainly water, in biological tissues, in vivo and non-invasively. Molecular diffusion in tissues is not random, but reflects interactions with many obstacles, such as macromolecules, fibers, and membranes. Water molecule diffusion patterns can therefore reveal microscopic details about tissue architecture, either normal or in a diseased state. A special kind of DWI, diffusion tensor imaging (DTI), has been used extensively to map white matter tractography in the brain. Introduction In diffusion weighted imaging (DWI), the intensity of each image element ( voxel) reflects the best estimate of the rate of water diffusion at that location. Because the mobility of water is driven by t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Perfusion Weighted Imaging
Perfusion MRI or perfusion-weighted imaging (PWI) is perfusion scanning by the use of a particular MRI sequence. The acquired data are then post-processed to obtain perfusion maps with different parameters, such as BV (blood volume), BF (blood flow), MTT (mean transit time) and TTP (time to peak). Clinical use In cerebral infarction, the penumbra has decreased perfusion. Another MRI sequence, diffusion weighted MRI, estimates the amount of tissue that is already necrotic, and the combination of those sequences can therefore be used to estimate the amount of brain tissue that is salvageable by thrombolysis and/or thrombectomy. Sequences There are 3 main techniques for perfusion MRI: * Dynamic susceptibility contrast (DSC): Gadolinium contrast is injected, and rapid repeated imaging (generally gradient-echo echo-planar T2 weighted) quantifies susceptibility-induced signal loss. * Dynamic contrast enhanced (DCE): Measuring shortening of the spin–lattice relaxation (T1) induced by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MRI Sequences
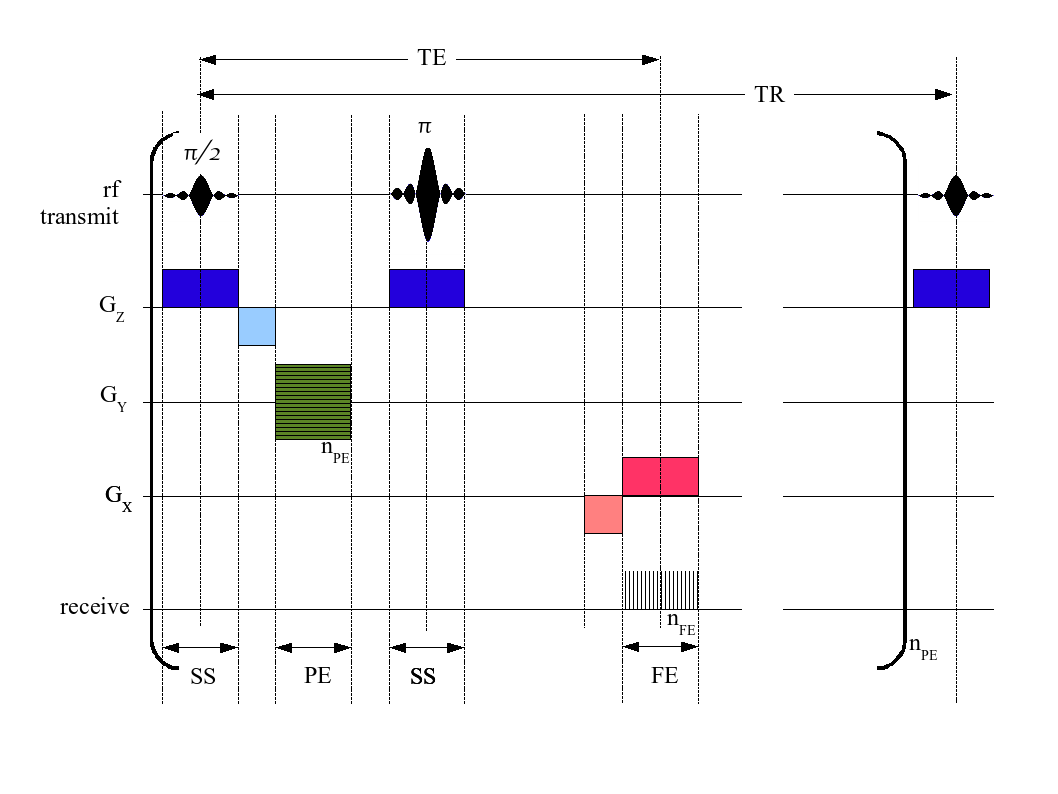
An MRI sequence in magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a particular setting of pulse sequences and pulsed field gradients, resulting in a particular image appearance. A multiparametric MRI is a combination of two or more sequences, and/or including Magnetic resonance imaging#Other specialized configurations, other specialized MRI configurations such as In vivo magnetic resonance spectroscopy, spectroscopy. Spin echo T1 and T2 Each tissue returns to its equilibrium state after excitation by the independent relaxation processes of T1 (Spin–lattice relaxation, spin-lattice; that is, magnetization in the same direction as the static magnetic field) and T2 (Spin-spin relaxation time, spin-spin; transverse to the static magnetic field). To create a T1-weighted image, magnetization is allowed to recover before measuring the MR signal by changing the repetition time (TR). This image weighting is useful for assessing the cerebral cortex, identifying fatty tissue, characterizing foc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magnetic Resonance Imaging
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a medical imaging technique used in radiology to form pictures of the anatomy and the physiological processes of the body. MRI scanners use strong magnetic fields, magnetic field gradients, and radio waves to generate images of the organs in the body. MRI does not involve X-rays or the use of ionizing radiation, which distinguishes it from CT and PET scans. MRI is a medical application of nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) which can also be used for imaging in other NMR applications, such as NMR spectroscopy. MRI is widely used in hospitals and clinics for medical diagnosis, staging and follow-up of disease. Compared to CT, MRI provides better contrast in images of soft-tissues, e.g. in the brain or abdomen. However, it may be perceived as less comfortable by patients, due to the usually longer and louder measurements with the subject in a long, confining tube, though "Open" MRI designs mostly relieve this. Additionally, implants and oth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)