|
Paramacellodid
Paramacellodidae is an extinct family of lizards that first appeared in the Middle Jurassic around 170 million years ago (Ma) and became extinct at the end of the Cretaceous around 66 Ma. It was one of the earliest groups of lizards to have undergone an evolutionary radiation, with members found across the supercontinent Laurasia. The phylogenetic relationships and constituent species of Paramacellodidae are uncertain. Many studies regard them to be scincomorphs, a large group that includes skinks and their closest extinct relatives, and possibly also to Cordyoidea, a group that includes spinytail lizards and relatives. Like modern skinks, paramacelloidids had rectangular bony plates called osteoderms covering most of their bodies, including their backs, undersides, and tails. They also had short and robust limbs. Paramacellodids are distinguished from other lizards by the combination two traits in their dentition, the teeth are labiolingually expanded at their bases, and the t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sharovisaurus
''Sharovisaurus'' is an extinct genus of scincomorph lizard from the Late Jurassic of Kazakhstan. It belongs to an extinct family of Mesozoic lizards called Paramacellodidae, which existed across most of Laurasia during the Late Jurassic and Early Cretaceous. The type and only species is ''Sharovisaurus karatauensis'', named in 1984 on the basis of a nearly complete articulated skeleton from the Oxfordian-aged Karabastau Formation. The back and tail of the skeleton are covered in rectangular-shaped bony plates called osteoderms, which have a similar arrangement to those of modern skink Skinks are lizards belonging to the family Scincidae, a family in the infraorder Scincomorpha. With more than 1,500 described species across 100 different taxonomic genera, the family Scincidae is one of the most diverse families of lizards. Ski ...s. At in length from the tip of its snout to the base of its tail, ''Sharovisaurus'' was one of the largest paramacellodids. Like other paramacello ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atokasaurus
''Atokasaurus'' is an extinct genus of scincomorph lizard from the Early Cretaceous of Oklahoma. The type and only species is ''Atokasaurus metarsiodon'', named in 2002 on the basis of a single isolated lower jaw bone found within the Antlers Formation in Atoka County. It is similar in appearance to extinct lizards in the family Paramacellodidae and may itself be a paramacellodid, although the phylogenetic In biology, phylogenetics (; from Greek φυλή/ φῦλον [] "tribe, clan, race", and wikt:γενετικός, γενετικός [] "origin, source, birth") is the study of the evolutionary history and relationships among or within groups o ... relationships of the group are uncertain. ''Atokasaurus'' differs from other paramacellodids in having teeth in the lower jaw with enlarged bases and an S-shaped profile when viewed edge-on. References Early Cretaceous reptiles of North America Cretaceous lizards Fossil taxa described in 2002 {{paleo-lizard-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Family (biology)
Family ( la, familia, plural ') is one of the eight major hierarchical taxonomic ranks in Linnaean taxonomy. It is classified between order and genus. A family may be divided into subfamilies, which are intermediate ranks between the ranks of family and genus. The official family names are Latin in origin; however, popular names are often used: for example, walnut trees and hickory trees belong to the family Juglandaceae, but that family is commonly referred to as the "walnut family". What belongs to a family—or if a described family should be recognized at all—are proposed and determined by practicing taxonomists. There are no hard rules for describing or recognizing a family, but in plants, they can be characterized on the basis of both vegetative and reproductive features of plant species. Taxonomists often take different positions about descriptions, and there may be no broad consensus across the scientific community for some time. The publishing of new data and opini ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gondwana
Gondwana () was a large landmass, often referred to as a supercontinent, that formed during the late Neoproterozoic (about 550 million years ago) and began to break up during the Jurassic period (about 180 million years ago). The final stages of break-up, involving the separation of Antarctica from South America (forming the Drake Passage) and Australia, occurred during the Paleogene. Gondwana was not considered a supercontinent by the earliest definition, since the landmasses of Baltica, Laurentia, and Siberia were separated from it. To differentiate it from the Indian region of the same name (see ), it is also commonly called Gondwanaland. Gondwana was formed by the accretion of several cratons. Eventually, Gondwana became the largest piece of continental crust of the Palaeozoic Era, covering an area of about , about one-fifth of the Earth's surface. During the Carboniferous Period, it merged with Laurasia to form a larger supercontinent called Pangaea. Gondwana (and Pan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
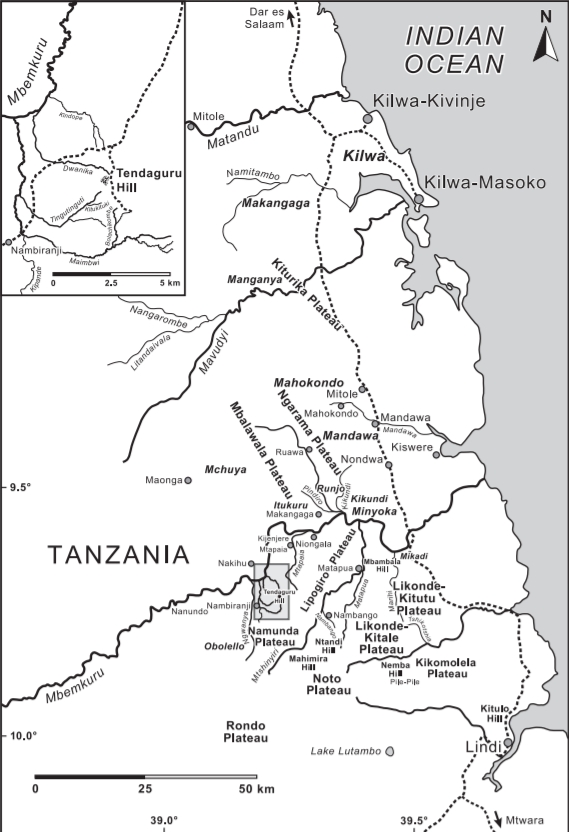
Tendaguru Formation
The Tendaguru Formation, or Tendaguru Beds are a highly fossiliferous formation and Lagerstätte located in the Lindi Region of southeastern Tanzania. The formation represents the oldest sedimentary unit of the Mandawa Basin, overlying Neoproterozoic basement, separating by a long hiatus and unconformity. The formation reaches a total sedimentary thickness of more than . The formation ranges in age from the late Middle Jurassic to the Early Cretaceous, Oxfordian to Hauterivian stages, with the base of the formation possibly extending into the Callovian. The Tendaguru Formation is subdivided into six members; from oldest to youngest Lower Dinosaur Member, the ''Nerinella'' Member, the Middle Dinosaur Member, ''Indotrigonia africana'' Member, the Upper Dinosaur Member, and the ''Rutitrigonia bornhardti-schwarzi'' Member. The succession comprises a sequence of sandstones, shales, siltstones, conglomerates with minor oolitic limestones, deposited in an overall shallow marine to c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Morrison Formation
The Morrison Formation is a distinctive sequence of Late Jurassic, Upper Jurassic sedimentary rock found in the western United States which has been the most fertile source of dinosaur fossils in North America. It is composed of mudstone, sandstone, siltstone, and limestone and is light gray, greenish gray, or red. Most of the fossils occur in the green siltstone beds and lower sandstones, relics of the rivers and floodplains of the Jurassic period. It is centered in Wyoming and Colorado, with outcrops in Montana, North Dakota, South Dakota, Nebraska, Kansas, the panhandles of Oklahoma and Texas, New Mexico, Arizona, Utah, and Idaho. Equivalent rocks under different names are found in Canada. It covers an area of 1.5 million square kilometers (600,000 square miles), although only a tiny fraction is exposed and accessible to geologists and Paleontology, paleontologists. Over 75% is still buried under the prairie to the east, and much of its western paleogeographic extent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Late Jurassic
The Late Jurassic is the third epoch of the Jurassic Period, and it spans the geologic time from 163.5 ± 1.0 to 145.0 ± 0.8 million years ago (Ma), which is preserved in Upper Jurassic strata.Owen 1987. In European lithostratigraphy, the name "Malm" indicates rocks of Late Jurassic age. In the past, ''Malm'' was also used to indicate the unit of geological time, but this usage is now discouraged to make a clear distinction between lithostratigraphic and geochronologic/chronostratigraphic units. Subdivisions The Late Jurassic is divided into three ages, which correspond with the three (faunal) stages of Upper Jurassic rock: Paleogeography During the Late Jurassic Epoch, Pangaea broke up into two supercontinents, Laurasia to the north, and Gondwana to the south. The result of this break-up was the spawning of the Atlantic Ocean. However, at this time, the Atlantic Ocean was relatively narrow. Life forms of the epoch This epoch is well known for many famous types of dinosau ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Osteoderm
Osteoderms are bony deposits forming scales, plates, or other structures based in the dermis. Osteoderms are found in many groups of extant and extinct reptiles and amphibians, including lizards, crocodilians, frogs, temnospondyls (extinct amphibians), various groups of dinosaurs (most notably ankylosaurs and stegosaurians), phytosaurs, aetosaurs, placodonts, and hupehsuchians (marine reptiles with possible ichthyosaur affinities). Osteoderms are uncommon in mammals, although they have occurred in many xenarthrans (armadillos and the extinct glyptodonts and mylodontid and scelidotheriid ground sloths). The heavy, bony osteoderms have evolved independently in many different lineages. The armadillo osteoderm is believed to develop in subcutaneous dermal tissues. These varied structures should be thought of as anatomical analogues, not homologues, and do not necessarily indicate monophyly. The structures are however derived from scutes, common to all classes of amniotes and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spinytail Lizard
The genus ''Cordylus'' (Sauria: Cordylidae) includes a wide variety of species of small to medium spiny lizards from Africa, collectively called girdle-tailed lizards or girdled lizards. All are diurnal and ovoviviparous (live-bearing, without shelled eggs). Most species are rupicolous (rock-dwelling), while a few species are arboreal or live in burrows. They defend themselves with osteoderms (flat bony plates in the skin) and by quickly retreating into rock crevices or burrows. Many species live in groups, and males defend territories. Cordylids are generally listed under CITES Appendix II. They are not necessarily threatened with extinction, but trade is controlled to prevent overexploitation. Some species of ''Cordylus'' have limited ranges and may be threatened with habitat destruction or over collecting for the pet trade. Classification Broadley (2006) recognized 47 species in the genus ''Cordylus'', including eight species originally placed in the genus '' Pseudocordylus'' ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Skink
Skinks are lizards belonging to the family Scincidae, a family in the infraorder Scincomorpha. With more than 1,500 described species across 100 different taxonomic genera, the family Scincidae is one of the most diverse families of lizards. Skinks are characterized by their smaller legs in comparison to typical lizards and are found in different habitats except arctic and subarctic regions. Description Skinks look like lizards of the family Lacertidae (sometimes called ''true lizards''), but most species of skinks have no pronounced neck and relatively small legs. Several genera (e.g., ''Typhlosaurus'') have no limbs at all. This is not true for all skinks, however, as some species such as the red-eyed crocodile skink have a head that is very distinguished from the body. These lizards also have legs that are relatively small proportional to their body size. Skinks' skulls are covered by substantial bony scales, usually matching up in shape and size, while overlapping. Other gen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scincomorpha
Scincomorpha is an infraorder and clade of lizards including skinks (Scincidae) and their close relatives. These include the living families Cordylidae (girdled lizards), Gerrhosauridae (plated lizards), and Xantusiidae (night lizards), as well as many extinct taxa. Other roughly equivalent terms include the suborder Scinciformata, or the superfamily Scincoidea, though different authors use these terms in a broader or more restricted usage relative to true skinks. They first appear in the fossil record about 170 million years ago, during the Jurassic period.Evans, S.E. and Jones, M.E.H. (2010). "The Origin, Early History and Diversification of Lepidosauromorph Reptiles," pp. 27-44 in Bandyopadhyay, S. (ed.), ''New Aspects of Mesozoic Biodiversity'', 27 Lecture Notes in Earth Sciences 132./ref> The phylogeny below follows that of Alifanov in 2016. Image:Polyglyphanadon sternbergi - IMG 0694.jpg, '' Polyglyphanodon, Polyglyphanodon sternbergi'' File:Bronze Grass Skink (Mabuya ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |





.jpg)