|
Package Manager
A package manager or package-management system is a collection of software tools that automates the process of installing, upgrading, configuring, and removing computer programs for a computer in a consistent manner. A package manager deals with ''packages'', distributions of software and data in archive files. Packages contain metadata, such as the software's name, description of its purpose, version number, vendor, checksum (preferably a cryptographic hash function), and a list of dependencies necessary for the software to run properly. Upon installation, metadata is stored in a local package database. Package managers typically maintain a database of software dependencies and version information to prevent software mismatches and missing prerequisites. They work closely with software repositories, binary repository managers, and app stores. Package managers are designed to eliminate the need for manual installs and updates. This can be particularly useful for large ent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
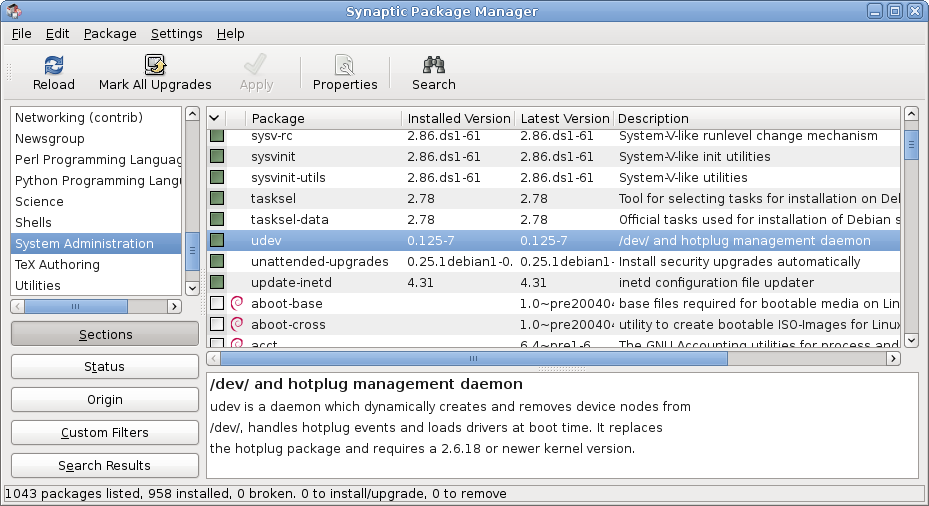
Synaptic Screenshot
Synaptic may refer to: * Synapse, part of the nervous system * Synaptic (software), a Linux graphical package management program * Synaptics, a semiconductor manufacturer * ''Synaptics'' (Mouse on Mars EP), 2017 See also * Synapse (other) A synapse is a neural junction used for communication between neurons Synapse may also refer to: Computing and information systems * Apache Synapse, open source enterprise service bus (ESB) and mediation engine * Azure Synapse, a fully managed ... * Synapsis, the pairing of two homologous chromosomes {{disambig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Static Library
In computer science, a static library or statically-linked library is a set of routines, external functions and variables which are resolved in a caller at compile-time and copied into a target application by a compiler, linker, or binder, producing an object file and a stand-alone executable. This executable and the process of compiling it are both known as a static build of the program. Historically, libraries could only be ''static''. Static libraries are either merged with other static libraries and object files during building/linking to form a single executable or loaded at run-time into the address space of their corresponding executable at a static memory offset determined at compile-time/link-time. Advantages and disadvantages There are several advantages to statically linking libraries with an executable instead of dynamically linking them. The most significant advantage is that the application can be certain that all its libraries are present and that they are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gentoo Linux
Gentoo Linux (pronounced ) is a Linux distribution built using the Portage package management system. Unlike a binary software distribution, the source code is compiled locally according to the user's preferences and is often optimized for the specific type of computer. Precompiled binaries are available for some larger packages or those with no available source code. Gentoo Linux was named after the gentoo penguin, the fastest swimming species of penguin. The name was chosen to reflect the potential speed improvements of machine-specific optimization, which is a major feature of Gentoo. Gentoo package management is designed to be modular, portable, easy to maintain, and flexible. Gentoo describes itself as a meta-distribution because of its adaptability, in that the majority of users have configurations and sets of installed programs which are unique to the system and the applications they use. History Gentoo Linux was initially created by Daniel Robbins as the ''Enoch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CheckInstall
CheckInstall is a computer program for Unix-like operating systems which eases the installation and uninstallation of software compiled from source by making use of package management systems. After software compilation it can automatically generate a Slackware-, RPM-, or Debian-compatible package that can later be cleanly uninstalled through the appropriate package manager. CheckInstall monitors the installation phase of a normal software build process and notes the files that are added to the system. It then builds a package that contains these files, using additional information gathered from the user. Finally, the files installed by the original run are removed and the package is installed using the system package tools, so the package will be properly registered in the local installed packages database. The primary benefits provided by CheckInstall versus simply running make install are the ability to remove the package from the system using the system packaging too ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
RPM Package Manager
RPM Package Manager (RPM) (originally Red Hat Package Manager, now a recursive acronym) is a free and open-source package management system. The name RPM refers to the file format and the package manager program itself. RPM was intended primarily for Linux distributions; the file format is the baseline package format of the Linux Standard Base. Although it was created for use in Red Hat Linux, RPM is now used in many Linux distributions such as PCLinuxOS, Fedora, AlmaLinux, CentOS, openSUSE, OpenMandriva and Oracle Linux. It has also been ported to some other operating systems, such as Novell NetWare (as of version 6.5 SP3), IBM's AIX (as of version 4), IBM i, and ArcaOS. An RPM package can contain an arbitrary set of files. Most RPM files are “binary RPMs” (or BRPMs) containing the compiled version of some software. There are also “source RPMs” (or SRPMs) containing the source code used to build a binary package. These have an appropriate tag in the file he ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Database
In computing, a database is an organized collection of data stored and accessed electronically. Small databases can be stored on a file system, while large databases are hosted on computer clusters or cloud storage. The design of databases spans formal techniques and practical considerations, including data modeling, efficient data representation and storage, query languages, security and privacy of sensitive data, and distributed computing issues, including supporting concurrent access and fault tolerance. A database management system (DBMS) is the software that interacts with end users, applications, and the database itself to capture and analyze the data. The DBMS software additionally encompasses the core facilities provided to administer the database. The sum total of the database, the DBMS and the associated applications can be referred to as a database system. Often the term "database" is also used loosely to refer to any of the DBMS, the database system or an appli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Synchronization (computer Science)
In computer science Computer science is the study of computation, automation, and information. Computer science spans theoretical disciplines (such as algorithms, theory of computation, information theory, and automation) to practical disciplines (includin ..., synchronization refers to one of two distinct but related concepts: synchronization of Process (computer science), processes, and synchronization of Dataset, data. ''Process synchronization'' refers to the idea that multiple processes are to join up or Handshake (computing), handshake at a certain point, in order to reach an agreement or commit to a certain sequence of action. ''Data synchronization'' refers to the idea of keeping multiple copies of a dataset in coherence with one another, or to maintain data integrity. Process synchronization primitives are commonly used to implement data synchronization. The need for synchronization The need for synchronization does not arise merely in multi-processor systems ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Download
In computer networks, download means to ''receive'' data from a remote system, typically a server such as a web server, an FTP server, an email server, or other similar system. This contrasts with uploading, where data is ''sent to'' a remote server. A ''download'' is a file offered for downloading or that has been downloaded, or the process of receiving such a file. Definition Downloading generally transfers entire files for local storage and later use, as contrasted with streaming, where the data is used nearly immediately, while the transmission is still in progress, and which may not be stored long-term. Websites that offer streaming media or media displayed in-browser, such as YouTube, increasingly place restrictions on the ability of users to save these materials to their computers after they have been received. Downloading is not the same as data transfer; moving or copying data between two storage devices would be data transfer, but ''receiving'' data from the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
System Administrator
A system administrator, or sysadmin, or admin is a person who is responsible for the upkeep, configuration, and reliable operation of computer systems, especially multi-user computers, such as servers. The system administrator seeks to ensure that the uptime, performance, resources, and security of the computers they manage meet the needs of the users, without exceeding a set budget when doing so. To meet these needs, a system administrator may acquire, install, or upgrade computer components and software; provide routine automation; maintain security policies; troubleshoot; train or supervise staff; or offer technical support for projects. Related fields Many organizations staff offer jobs related to system administration. In a larger company, these may all be separate positions within a computer support or Information Services (IS) department. In a smaller group they may be shared by a few sysadmins, or even a single person. * A database administrator (DBA) mai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Application Binary Interface
In computer software, an application binary interface (ABI) is an interface between two binary program modules. Often, one of these modules is a library or operating system facility, and the other is a program that is being run by a user. An ''ABI'' defines how data structures or computational routines are accessed in machine code, which is a low-level, hardware-dependent format. In contrast, an ''API'' defines this access in source code, which is a relatively high-level, hardware-independent, often human-readable format. A common aspect of an ABI is the calling convention, which determines how data is provided as input to, or read as output from, computational routines. Examples of this are the x86 calling conventions. Adhering to an ABI (which may or may not be officially standardized) is usually the job of a compiler, operating system, or library author. However, an application programmer may have to deal with an ABI directly when writing a program in a mix of programm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glasgow Haskell Compiler
The Glasgow Haskell Compiler (GHC) is an open-source native code compiler for the functional programming language Haskell. It provides a cross-platform environment for the writing and testing of Haskell code and it supports numerous extensions, libraries, and optimisations that streamline the process of generating and executing code. GHC is the most commonly used Haskell compiler. The lead developers are Simon Peyton Jones and Simon Marlow. History GHC originally started in 1989 as a prototype, written in LML (Lazy ML) by Kevin Hammond at the University of Glasgow. Later that year, the prototype was completely rewritten in Haskell, except for its parser, by Cordelia Hall, Will Partain, and Simon Peyton Jones. Its first beta release was on 1 April 1991 and subsequent releases added a strictness analyzer as well as language extensions such as monadic I/O, mutable arrays, unboxed data types, concurrent and parallel programming models (such as software transactional memory ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Portage (software)
Portage is a package management system originally created for and used by Gentoo Linux and also by ChromeOS, Calculate, Sabayon, and Funtoo Linux among others. Portage is based on the concept of ports collections. Gentoo is sometimes referred to as a ''meta-distribution'' due to the extreme flexibility of Portage, which makes it operating-system-independent. The Gentoo/Alt project was concerned with using Portage to manage other operating systems, such as BSDs, macOS and Solaris. The most notable of these implementations is the Gentoo/FreeBSD project. There is an ongoing effort called the Package Manager Specification project (PMS), which aims to standardise and document the behaviour of Portage, allowing the ebuild tree and Gentoo system packages to be used with alternative package managers such as Paludis and pkgcore. Its goal is to specify the exact set of features and behaviour of package managers and ebuilds, serving as an authoritative reference for Portage. Ove ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |