|
Push–pull Amplifier
Push–pull may refer to: In electronic technology * Push–pull output, type of electronic circuit * Push–pull converter, in electronics, is a type of DC to DC converter that uses a transformer *Push–pull connector, an electronic cable connector * Push technology / Pull technology, in network communications In transport technology *Push–pull configuration, on aircraft * Push–pull train, a train able to be operated by a driver at either end *Push-to-pull compression fittings, a type of compression fitting that allows air line to be attached without the use of tools In other technology * Push processing, and its counterpart "pull processing" in photography *Push-and-pull enteroscopy, an endoscopic technique for visualization of the small bowel *Push–pull olefin, in organic chemistry * Push–pull perfusion, an ''in vivo'' sampling method * Push–pull technology, in agricultural pest management In the arts * ''Push Pull'' (Hoobastank album), 2018 *"(Do The) Push and Pu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Push–pull Output
A push–pull amplifier is a type of electronic circuit that uses a pair of active devices that alternately supply current to, or absorb current from, a connected load. This kind of amplifier can enhance both the load capacity and switching speed. Push–pull outputs are present in TTL and CMOS digital logic circuits and in some types of amplifiers, and are usually realized by a complementary pair of transistors, one dissipating or ''sinking'' current from the load to ground or a negative power supply, and the other supplying or ''sourcing'' current to the load from a positive power supply. A push–pull amplifier is more efficient than a single-ended "class-A" amplifier. The output power that can be achieved is higher than the continuous dissipation rating of either transistor or tube used alone and increases the power available for a given supply voltage. Symmetrical construction of the two sides of the amplifier means that even-order harmonics are cancelled, which can ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Push–pull Perfusion
Push–pull perfusion is an in vivo sampling method most commonly used for measuring neurotransmitters in the brain. Developed by J.H. Gaddum in 1960, this technique replaced the cortical cup technique for observing neurotransmitters. The advent of concentric microdialysis probes in the 1980s resulted in push-pull sampling falling out of favor, as such probes require less monitoring, and are less invasive than the higher flow rate push-pull probes (>10 microliter/min), which could result in lesions if flow is unbalanced. With the advent of microfluidics and miniaturized probes, low-flow push–pull sampling was developed in 2002. By using flow rates of ~50 nL/min, this technique minimizes tissue damage while providing finer spatial resolution than microdialysis Microdialysis is a minimally-invasive sampling technique that is used for continuous measurement of free, unbound analyte concentrations in the extracellular fluid of virtually any tissue. Analytes may include endog ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
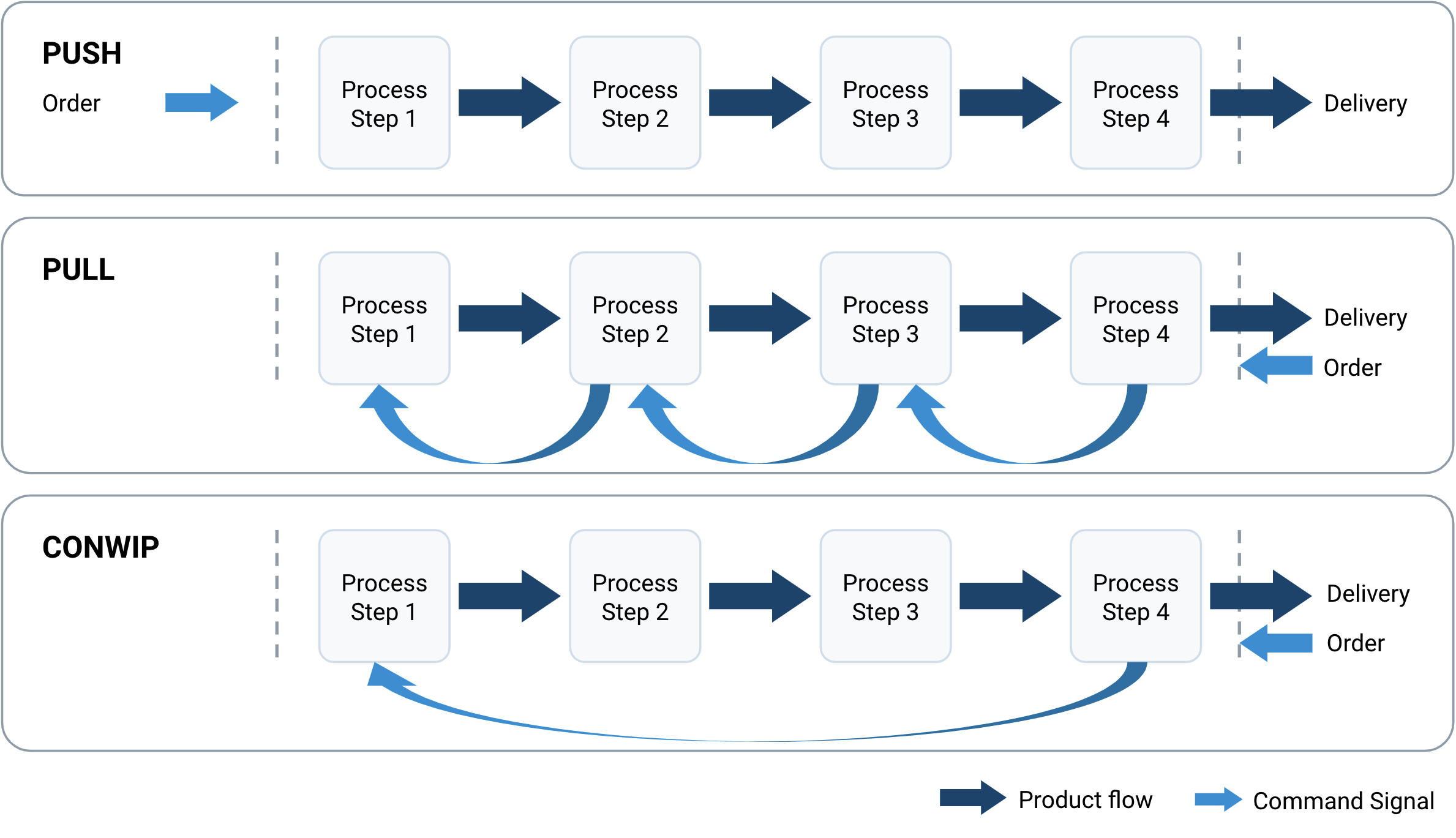
Push–pull Strategy
The business terms ''push'' and ''pull'' originated in logistics and supply chain management, but are also widely used in marketing and in the hotel distribution business. Walmart is an example of a company that uses the push vs. pull strategy. Supply-chain management Complete definition There are several definitions on the distinction between push and pull strategies. Liberopoulos (2013) identifies three such definitions: # A pull system initiates production as a reaction to present demand, while a push system initiates production in anticipation of future demand. # In a pull system, production is triggered by actual demands for finished products, while in a push system, production is initiated independently of demands. # A pull system is one that explicitly limits the amount of WIP that can be in the system, while a push system has no explicit limit on the amount of WIP that can be in the system. Other definitions are: * ''Push'': As stated by Bonney et al. (1999) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Push–pull Agricultural Pest Management
Push–pull technology is an intercropping strategy for controlling agricultural pests by using repellent "push" plants and trap "pull" plants. For example, cereal crops like maize or sorghum are often infested by stem borers. Grasses planted around the perimeter of the crop attract and trap the pests, whereas other plants, like ''Desmodium'', planted between the rows of maize, repel the pests and control the parasitic plant ''Striga''. Push–pull technology was developed at the International Centre of Insect Physiology and Ecology (ICIPE) in Kenya in collaboration with Rothamsted Research, UK. and national partners. This technology has been taught to smallholder farmers through collaborations with universities, NGOs and national research organizations. How push–pull works Push–pull technology involves use of behaviour-modifying stimuli to manipulate the distribution and abundance of stemborers and beneficial insects for management of stemborer pests. It is based on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pushmi-pullyu
This is a list of characters from the '' Doctor Dolittle'' series of children's books by Hugh Lofting and movies based on them. Most of the characters were introduced in the first book, the 1920 novel '' The Story of Doctor Dolittle''. Humans Doctor Dolittle ;Portrayed by: * Rex Harrison ( 1967) * Eddie Murphy (1998, 2001) * Robert Downey Jr. (2020) Doctor John Dolittle is an English physician who became a doctor for animals after his parrot, Polynesia, taught him to speak animal languages. He lives in the fictional town of Puddleby-on-the-Marsh in England's West Country, along with his many animal friends. He has very few human friends and spends most of his time treating animals, travelling the world with his animals and conducting research into new animals and new forms of animal languages. He is portrayed by Rex Harrison in the 1967 film '' Doctor Dolittle'', Eddie Murphy in '' Dr. Dolittle'' (1998) and '' Dr. Dolittle 2'' (2001), and by Robert Downey Jr. in '' Dolittle'' ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hans Hofmann
Hans Hofmann (March 21, 1880 – February 17, 1966) was a German-born American painter, renowned as both an artist and teacher. His career spanned two generations and two continents, and is considered to have both preceded and influenced Abstract Expressionism.de la Croix, Horst and Richard G. Tansey. ''Gardner's Art Through the Ages'', 7th Ed., New York: Harcourt Brace Jovanovich, 1980, p. 857-8. Born and educated near Munich, he was active in the early twentieth-century European avant-garde and brought a deep understanding and synthesis of Symbolism, Neo-impressionism, Fauvism, and Cubism when he emigrated to the United States in 1932.Chipp, Herschel B. ''Theories of Modern Art'', Berkeley & Los Angeles: University of California Press, 1968, p. 511–2. Hofmann's painting is characterized by its rigorous concern with pictorial structure and unity, spatial illusionism, and use of bold color for expressive means.Seitz, William C. ''Hans Hofmann'', New York: Museum of Modern Art, 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
(Do The) Push And Pull
"(Do The) Push and Pull (Part 1)" is a 1970 single on Stax Records by singer Rufus Thomas. The song was written by Thomas, and the recording was arranged by Carl Hampton, and produced by Al Bell and Tom Nixon. This was the first and only number-one song for Thomas, who had first hit the R&B chart in 1953. The song was at the top of the ''Billboard'' Best Selling Soul Singles The Hot R&B/Hip-Hop Songs chart ranks the most popular R&B and hip hop songs in the United States and is published weekly by ''Billboard''. Rankings are based on a measure of radio airplay, sales data, and streaming activity. The chart had 100 p ... chart for two weeks in February 1971. The single also reached the Top 30 on the pop chart, peaking at number 25. Chart performance References 1970 singles Rufus Thomas songs 1970 songs Stax Records singles {{1970s-R&B-song-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Push Pull (Hoobastank Album)
''Push Pull'' is the sixth studio album by American rock band Hoobastank, released on May 25, 2018 via Napalm. The album features a more pop rock sound with funk rock influences, different from the characteristic post-grunge and alternative style of the band. The album peaked at number 35 on ''Billboard''s Independent Albums chart. Track listing Personnel Hoobastank * Doug Robb – lead vocals, rhythm guitar * Daniel Estrin – lead guitar * Chris Hesse – drums * Jesse Charland – bass, backing vocals Production * Matt Wallace – production * Paul David Hager – mixing * Chris Hesse – mixing * Emily Lazar Emily B. Lazar is an American mastering engineer. She is the founder, president, and chief mastering engineer of The Lodge, an audio mastering facility that has operated in New York City's Greenwich Village since 1997. She won a Grammy Award fo ... – mastering References 2018 albums Hoobastank albums Napalm Records albums {{2010s-rock-albu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Push–pull Technology
Push–pull may refer to: In electronic technology *Push–pull output, type of electronic circuit * Push–pull converter, in electronics, is a type of DC to DC converter that uses a transformer * Push–pull connector, an electronic cable connector *Push technology / Pull technology, in network communications In transport technology *Push–pull configuration, on aircraft *Push–pull train, a train able to be operated by a driver at either end *Push-to-pull compression fittings, a type of compression fitting that allows air line to be attached without the use of tools In other technology * Push processing, and its counterpart "pull processing" in photography * Push-and-pull enteroscopy, an endoscopic technique for visualization of the small bowel * Push–pull olefin, in organic chemistry * Push–pull perfusion, an ''in vivo'' sampling method * Push–pull technology, in agricultural pest management In the arts * ''Push Pull'' (Hoobastank album), 2018 *" (Do The) Push and Pu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Push–pull Olefin
A push-pull olefin is a type of olefin characterized by an electron-withdrawing substituent on one side of the double bond and an electron-donating substituent on the other side. This makes the pi bond very polarized. The rotational barrier for a push-pull olefin is lower than that of an ordinary olefin and this makes it an interesting candidate for a molecular switch, for instance azobenzenes. A push-pull configuration also helps to stabilize the double bond because the carbon-carbon bond has considerably less double bond character. For instance, cyclobutadiene is a very unstable molecule but with both olefinic bonds in push-pull configuration (two ester substituents and two tertiary amine substituents) the molecule is stable indeed. References * ''Ethyl (2-cyano-3-ethoxyacryloyl)carbamate: irreversible thermal isomerization of a push-pull olefin'' Kuangsen Sung, Ming-Chi Lin, Pin-Mei Huang, Bo-Ren Zhuang, Robert Sung,Ru-Rong Wu Arkivoc 2005 p. 13 open access (publishing), ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
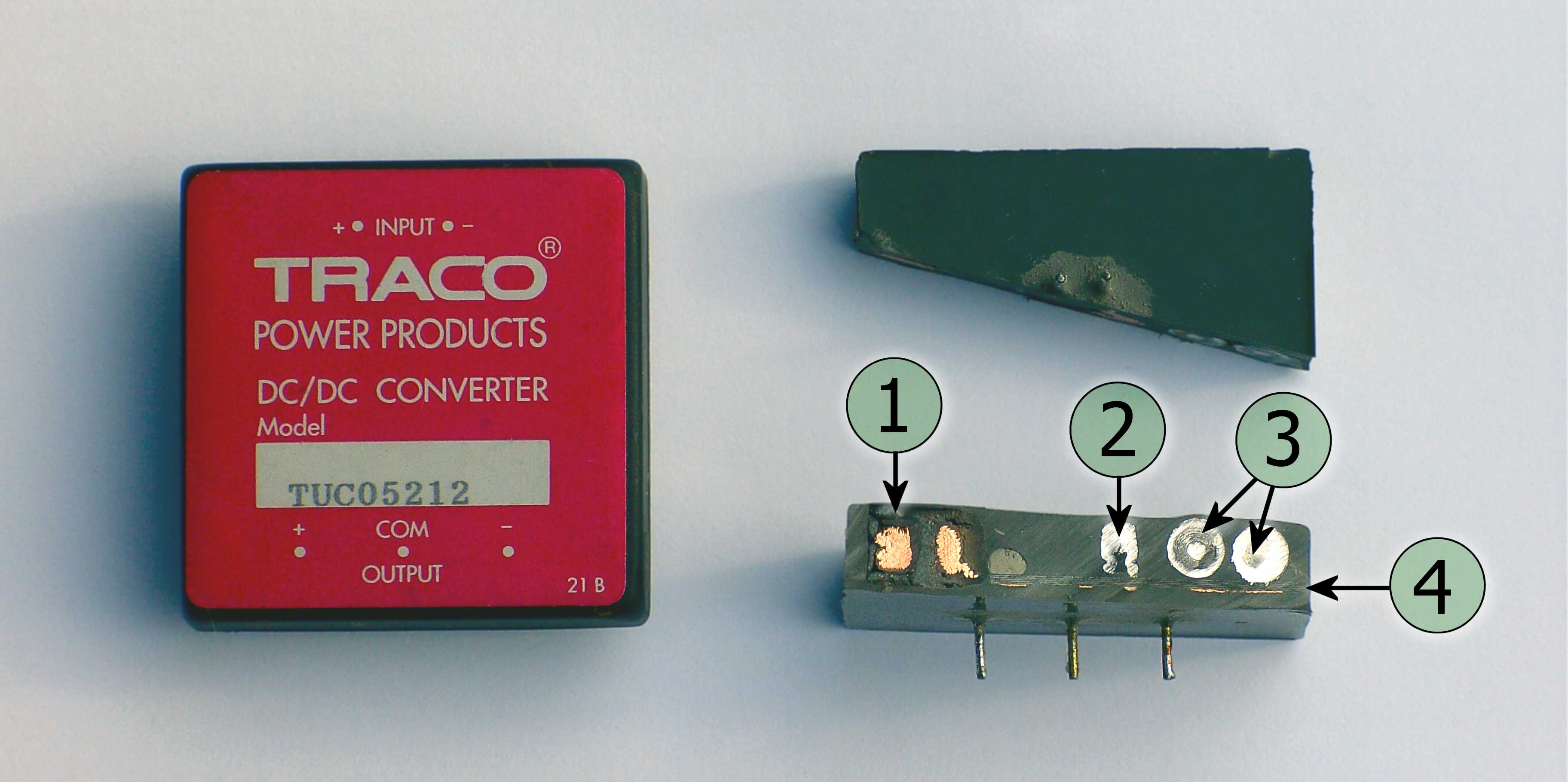
Push–pull Converter
A push–pull converter is a type of DC-to-DC converter, a switching converter that uses a transformer to change the voltage of a DC power supply. The distinguishing feature of a push-pull converter is that the transformer primary is supplied with current from the input line by pairs of transistors in a symmetrical push-pull circuit. The transistors are alternately switched on and off, periodically reversing the current in the transformer. Therefore, current is drawn from the line during both halves of the switching cycle. This contrasts with buck-boost converters, in which the input current is supplied by a single transistor which is switched on and off, so current is only drawn from the line during half the switching cycle. During the other half the output power is supplied by energy stored in inductors or capacitors in the power supply. Push–pull converters have steadier input current, create less noise on the input line, and are more efficient in higher power appl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
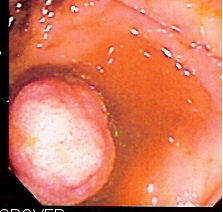
Push-and-pull Enteroscopy
Double-balloon enteroscopy, also known as push-and-pull enteroscopy, is an endoscopic technique for visualization of the small bowel. It was developed by Hironori Yamamoto in 2001. It is novel in the field of diagnostic gastroenterology as it is the first endoscopic technique that allows for the entire gastrointestinal tract to be visualized in real time. Technique The technique involves the use of a balloon at the end of a special enteroscope camera and an overtube, which is a tube that fits over the endoscope, and which is also fitted with a balloon. The procedure is usually done under general anesthesia, but may be done with the use of conscious sedation. The enteroscope and overtube are inserted through the mouth and passed in conventional fashion (that is, as with gastroscopy) into the small bowel. Following this, the endoscope is advanced a small distance in front of the overtube and the balloon at the end is inflated. Using the assistance of friction at the interface ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.png)