|
Pterobranch
Pterobranchia is a Class (biology), class of small worm-shaped animals. They belong to the Hemichordata, and live in secretion, secreted tubes on the ocean floor. Pterobranchia feed by filtering plankton out of the water with the help of cilia attached to tentacles. There are about 25 known living pterobranch species in three genera, which are ''Rhabdopleura'', ''Cephalodiscus'', and ''Atubaria''. On the other hand, there are several hundred extinct genera, some of which date from the Cambrian Period. The class Pterobranchia was established by Ray Lankester in 1877. It contained, at that time, the single genus ''Rhabdopleura''. ''Rhabdopleura'' was at first regarded as an aberrant polyzoon, but when the Challenger expedition, ''Challenger'' report on ''Cephalodiscus'' was published in 1887, it became clear that ''Cephalodiscus'', the second genus now included in the Order (biology), order, had affinities with the Enteropneusta. Electron microscope studies have suggested that pte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dendroidea
Graptolites are a group of Colony (biology)#Modular organisms, colonial animals, members of the subclass Graptolithina within the class (biology), class Pterobranchia. These Filter feeder, filter-feeding organisms are known chiefly from fossils found from the Middle Cambrian (Miaolingian, Wuliuan) through the Lower Carboniferous (Mississippian (geology), Mississippian). A possible early graptolite, ''Chaunograptus'', is known from the Middle Cambrian. Recent analyses have favored the idea that the living pterobranch ''Rhabdopleura'' represents an extant graptolite which diverged from the rest of the group in the Cambrian. Fossil graptolites and ''Rhabdopleura'' share a colony structure of interconnected zooids housed in organic tubes (theca) which have a basic structure of stacked half-rings (fuselli). Most extinct graptolites belong to two major orders: the bush-like Sessility (motility), sessile Dendroidea and the Plankton, planktonic, free-floating Graptoloidea. These orders mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
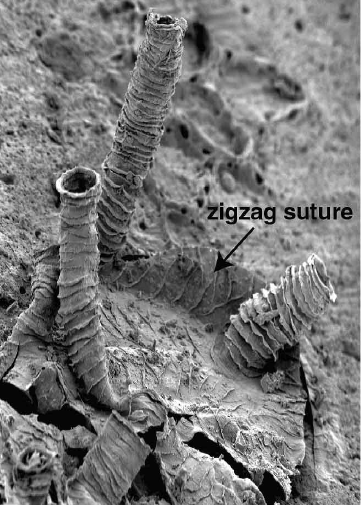
Graptolite
Graptolites are a group of colonial animals, members of the subclass Graptolithina within the class Pterobranchia. These filter-feeding Filter feeders are a sub-group of suspension feeding animals that feed by straining suspended matter and food particles from water, typically by passing the water over a specialized filtering structure. Some animals that use this method of feedin ... organisms are known chiefly from fossils found from the Middle Cambrian (Miaolingian, Wuliuan) through the Lower Carboniferous (Mississippian (geology), Mississippian). A possible early graptolite, ''Chaunograptus'', is known from the Middle Cambrian. Recent analyses have favored the idea that the living pterobranch ''Rhabdopleura'' represents an extant graptolite which diverged from the rest of the group in the Cambrian. Fossil graptolites and ''Rhabdopleura'' share a colony structure of interconnected zooids housed in organic tubes (theca) which have a basic structure of stacked half-rings (fuse ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Graptoloidea
Graptolites are a group of colonial animals, members of the subclass Graptolithina within the class Pterobranchia. These filter-feeding organisms are known chiefly from fossils found from the Middle Cambrian (Miaolingian, Wuliuan) through the Lower Carboniferous ( Mississippian). A possible early graptolite, ''Chaunograptus'', is known from the Middle Cambrian. Recent analyses have favored the idea that the living pterobranch ''Rhabdopleura'' represents an extant graptolite which diverged from the rest of the group in the Cambrian. Fossil graptolites and ''Rhabdopleura'' share a colony structure of interconnected zooids housed in organic tubes (theca) which have a basic structure of stacked half-rings (fuselli). Most extinct graptolites belong to two major orders: the bush-like sessile Dendroidea and the planktonic, free-floating Graptoloidea. These orders most likely evolved from encrusting pterobranchs similar to ''Rhabdopleura''. Due to their widespread abundance, plantkonic l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rhabdopleurida
Rhabdopleurida is one of three orders in the class Pterobranchia, which are small, worm-shaped animals, are the only surviving graptolites. Members belong to the hemichordates. Species in this order are sessile, colonial, connected with a stolon, living in clear water and secrete tubes called tubarium. They have a single gonad, the gill slits are absent and the collar has two tentaculated arms. ''Rhabdopleura'' is the best studied pterobranch in developmental biology. ''Rhabdopleura'' is the only extant graptolite. Taxonomy This small order is monotypic. It has only a single extant genus, containing four to six living species. Order Rhabdopleurida Fowler 1892 * Family Rhabdopleuridae Harmer 1905 ** Genus ''Rhabdopleura'' Allman 1869 *** ''Rhabdopleura annulata'' Norman 1921 — Indo-Pacific region *** '' Rhabdopleura compacta'' Hincks 1880 — Atlantic *** ''Rhabdopleura normani'' Allmann, 1869 — Atlantic and parts of the Pacific *** ''Rhabdopleura recondita'' Beli, Cameron ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rhabdopleura
''Rhabdopleura'' is a genus of colonial sessile hemichordates belonging to the Pterobranchia class. As one of the oldest living genera with a fossil record dating back to the Middle Cambrian, it is also considered to be the only living genus of graptolites. ''Rhabdopleura'' is the best studied pterobranch in developmental biology. Research in the 2010s by Jörg Maletz and other paleontologists and biologists have demonstrated that ''Rhabdopleura'' is an extant graptolite. Species List of species from Maletz (2014): ;Living species The genus ''Rhabdopleura'' contains at least five living species. * ''Rhabdopleura annulata'' Norman 1921 — Indo-Pacific region * '' Rhabdopleura compacta'' Hincks 1880 — Atlantic * ''Rhabdopleura normani'' Allmann, 1869 — Atlantic and parts of the Pacific * ''Rhabdopleura recondita'' Beli, Cameron and Piraino, 2018 — Mediterranean * ''Rhabdopleura striata'' Schepotieff 1909 — Pacific (Sri Lanka) ;''Nomen dubium'' (doubtful) * ''Rhabdopleu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atubaria
''Atubaria heterolopha'' is a species of hemichordates in the monotypic genus ''Atubaria'' and in the monotypic family Atubaridae. This taxon belongs to the pterobranchian order Cephalodiscida. It was described by Tadao Sato in 1936 from specimens found feeding on a colony of the hydrozoan '' Dycoryne conferta'' in Sagami Bay, Japan. Description The characteristics of this pterobranch species include a 1–5 mm long zooid, a collar with four pairs of tentaculated arms, a single pair of pharyngeal slits, and a solitary and sedentary behaviour. It closely resembles ''Cephalodiscus ''Cephalodiscus'' is a genus of hemichordates in the monotypic family Cephalodiscidae of the order Cephalodiscida. Description Unlike ''Rhabdopleura'', ''Cephalodiscus'' species do not form large colonies and are only pseudocolonial. ''Cephalod ...'' members. References {{taxonbar, from=Q3827927 Pterobranchia Animals described in 1936 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polyzoon
Bryozoa (also known as the Polyzoa, Ectoprocta or commonly as moss animals) are a phylum of simple, aquatic invertebrate animals, nearly all living in sedentary colonies. Typically about long, they have a special feeding structure called a lophophore, a "crown" of tentacles used for filter feeding. Most marine bryozoans live in tropical waters, but a few are found in oceanic trenches and polar waters. The bryozoans are classified as the marine bryozoans (Stenolaemata), freshwater bryozoans (Phylactolaemata), and mostly-marine bryozoans (Gymnolaemata), a few members of which prefer brackish water. 5,869living species are known. At least two genera are solitary (''Aethozooides'' and ''Monobryozoon''); the rest are colonial. The terms Polyzoa and Bryozoa were introduced in 1830 and 1831, respectively. Soon after it was named, another group of animals was discovered whose filtering mechanism looked similar, so it was included in Bryozoa until 1869, when the two groups were not ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cephalodiscus Dodecalophus
''Cephalodiscus dodecalophus'' is a sessile hemichordate belonging to the order Cephalodiscida. It has erect tubaria ''Tubaria'' is a genus of fungi in the family Tubariaceae. The genus is widely distributed, especially in temperate regions. ''Tubaria'' was originally named as a subgenus of ''Agaricus'' by Worthington George Smith in 1870. Claude Casimir Gill .... References dodecalophus {{hemichordate-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cephalodiscus
''Cephalodiscus'' is a genus of hemichordates in the monotypic family Cephalodiscidae of the order Cephalodiscida. Description Unlike ''Rhabdopleura'', ''Cephalodiscus'' species do not form large colonies and are only pseudocolonial. ''Cephalodiscus'' zooids are also more mobile than their ''Rhabdopleura'' counterparts, and are able to move around within tubarium, tubaria. ''Cephalodiscus'' zooids can be produced via asexual budding. There are a few pairs of tentacled arms, whereas ''Rhabdopleura'' has only one pair of arms. Species 19 living species of ''Cephalodiscus'' have been described: * ''Cephalodiscus agglutinans'' Harmer & Ridewood, 1914 * ''Cephalodiscus atlanticus'' Bayer, 1962 * ''Cephalodiscus australiensis'' Johnston & Muirhead, 1951 * ''Cephalodiscus calciformis'' Emig, 1977 * ''Cephalodiscus densus'' Andersson 1907 [''Cephalodiscus rarus'' Andersson, 1907; ''Cephalodiscus anderssoni'' Gravier 1912] * ''Cephalodiscus dodecalophus'' McIntosh 1882 * ''Cephalodisc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enteropneusta
The acorn worms or Enteropneusta are a hemichordate class of invertebrates consisting of one order of the same name. The closest non-hemichordate relatives of the Enteropneusta are the echinoderms. There are 111 known species of acorn worm in the world, the main species for research being '' Saccoglossus kowalevskii''. Two families—Harrimaniidae and Ptychoderidae—separated at least 370 million years ago. Until recently, it was thought that all species lived in the sediment on the seabed, subsisting as deposit feeders or suspension feeders. However, the early 21st century has seen the description of a new family, the Torquaratoridae, evidently limited to the deep sea, in which most of the species crawl on the surface of the ocean bottom and alternatively rise into the water column, evidently to drift to new foraging sites. It is assumed that the ancestors of acorn worms used to live in tubes like their relatives Pterobranchia, but that they eventually started to live a safer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electron Microscope
An electron microscope is a microscope that uses a beam of accelerated electrons as a source of illumination. As the wavelength of an electron can be up to 100,000 times shorter than that of visible light photons, electron microscopes have a higher resolving power than light microscopes and can reveal the structure of smaller objects. A scanning transmission electron microscope has achieved better than 50 pm resolution in annular dark-field imaging mode and magnifications of up to about 10,000,000× whereas most light microscopes are limited by diffraction to about 200 nm resolution and useful magnifications below 2000×. Electron microscopes use shaped magnetic fields to form electron optical lens systems that are analogous to the glass lenses of an optical light microscope. Electron microscopes are used to investigate the ultrastructure of a wide range of biological and inorganic specimens including microorganisms, cells, large molecules, biopsy samples, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Order (biology)
Order ( la, wikt:ordo#Latin, ordo) is one of the eight major hierarchical taxonomic ranks in Linnaean taxonomy. It is classified between Family_(biology), family and Class_(biology), class. In biological classification, the order is a taxonomic rank used in the classification of organisms and recognized by the nomenclature codes. An immediately higher rank, superorder, is sometimes added directly above order, with suborder directly beneath order. An order can also be defined as a group of related families. What does and does not belong to each order is determined by a taxonomist, as is whether a particular order should be recognized at all. Often there is no exact agreement, with different taxonomists each taking a different position. There are no hard rules that a taxonomist needs to follow in describing or recognizing an order. Some taxa are accepted almost universally, while others are recognized only rarely. The name of an order is usually written with a capital letter. Fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)

