|
Psychobiotic
Psychobiotics is a term used in preliminary research to refer to live bacteria that, when ingested in appropriate amounts, might confer a mental health benefit by affecting microbiota of the host organism. Whether bacteria might play a role in the gut-brain axis is under research. A 2020 literature review suggests that the consumption of psychobiotics could be considered as a viable option to restore mental health although lacking randomized controlled trials on clear mental health outcomes in humans. Types In experimental probiotic psychobiotics, the bacteria most commonly used are gram-positive bacteria, such as ''Bifidobacterium'' and ''Lactobacillus'' families, as these do not contain lipopolysaccharide chains, reducing the likelihood of an immunological response. Prebiotics are substances, such as fructans and oligosaccharides, that induce the growth or activity of beneficial microorganisms, such as bacteria on being fermented in the gut. Multiple bacterial species cont ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Probiotic
Probiotics are live microorganisms promoted with claims that they provide health benefits when consumed, generally by improving or restoring the gut microbiota. Probiotics are considered generally safe to consume, but may cause bacteria- host interactions and unwanted side effects in rare cases. There is some evidence that probiotics are beneficial for some conditions, but there is little evidence for many of the health benefits claimed for them. The first discovered probiotic was a certain strain of bacillus in Bulgarian yoghurt, called '' Lactobacillus bulgaricus''. The discovery was made in 1905 by Bulgarian physician and microbiologist Stamen Grigorov. The modern-day theory is generally attributed to Russian Nobel laureate Élie Metchnikoff, who postulated around 1907 that yoghurt-consuming Bulgarian peasants lived longer. A growing probiotics market has led to the need for stricter requirements for scientific substantiation of putative benefits conferred by microorganisms ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prebiotic (nutrition)
Prebiotics are compounds in food that induce the growth or activity of beneficial microorganisms such as bacteria and fungi. The most common example is in the gastrointestinal tract, where prebiotics can alter the composition of organisms in the gut microbiome. Dietary prebiotics are typically nondigestible fiber compounds that pass undigested through the upper part of the gastrointestinal tract and stimulate the growth or activity of advantageous bacteria in the colon by acting as substrates for them. They were first identified and named by Marcel Roberfroid in 1995. Depending on the jurisdiction, they may have regulatory scrutiny as food additives for the health claims made for marketing purposes. Common prebiotics used in food manufacturing include beta-glucan from oats and inulin from chicory root. Definition The definition of prebiotics and the food ingredients that can fall under this classification, has evolved since its first definition in 1995. In its earliest definit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bifidobacterium Infantis
''Bifidobacterium longum'' is a Gram-positive, catalase-negative, rod-shaped bacterium present in the human gastrointestinal tract and one of the 32 species that belong to the genus ''Bifidobacterium''. It is a microaerotolerant anaerobe and considered to be one of the earliest colonizers of the gastrointestinal tract of infants. When grown on general anaerobic medium, ''B. longum'' forms white, glossy colonies with a convex shape. While ''B. longum'' is not significantly present in the adult gastrointestinal tract, it is considered part of the gut microbiota and its production of lactic acid is believed to prevent growth of pathogenic organisms. ''B. longum'' is non-pathogenic and is often added to food products. Classification In 2002, three previously distinct species of ''Bifidobacterium'', ''B. infantis'', ''B. longum'', and ''B. suis'', were unified into a single species named ''B. longum'' with the biotypes ''infantis, longum,'' and ''suis'', respectively. This occurred a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bifidobacterium Longum
''Bifidobacterium longum'' is a Gram-positive, catalase-negative, rod-shaped bacterium present in the human gastrointestinal tract and one of the 32 species that belong to the genus '' Bifidobacterium''. It is a microaerotolerant anaerobe and considered to be one of the earliest colonizers of the gastrointestinal tract of infants. When grown on general anaerobic medium, ''B. longum'' forms white, glossy colonies with a convex shape. While ''B. longum'' is not significantly present in the adult gastrointestinal tract, it is considered part of the gut microbiota and its production of lactic acid is believed to prevent growth of pathogenic organisms. ''B. longum'' is non-pathogenic and is often added to food products. Classification In 2002, three previously distinct species of ''Bifidobacterium'', ''B. infantis'', ''B. longum'', and ''B. suis'', were unified into a single species named ''B. longum'' with the biotypes ''infantis, longum,'' and ''suis'', respectively. This occurre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Probiotics
Probiotics are live microorganisms promoted with claims that they provide health benefits when consumed, generally by improving or restoring the gut microbiota. Probiotics are considered generally safe to consume, but may cause bacteria-host interactions and unwanted side effects in rare cases. There is some evidence that probiotics are beneficial for some conditions, but there is little evidence for many of the health benefits claimed for them. The first discovered probiotic was a certain strain of bacillus in Bulgarian yoghurt, called ''Lactobacillus bulgaricus''. The discovery was made in 1905 by Bulgarian physician and microbiologist Stamen Grigorov. The modern-day theory is generally attributed to Russian Nobel laureate Élie Metchnikoff, who postulated around 1907 that yoghurt-consuming Bulgarian peasants lived longer. A growing probiotics market has led to the need for stricter requirements for scientific substantiation of putative benefits conferred by microorganisms ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
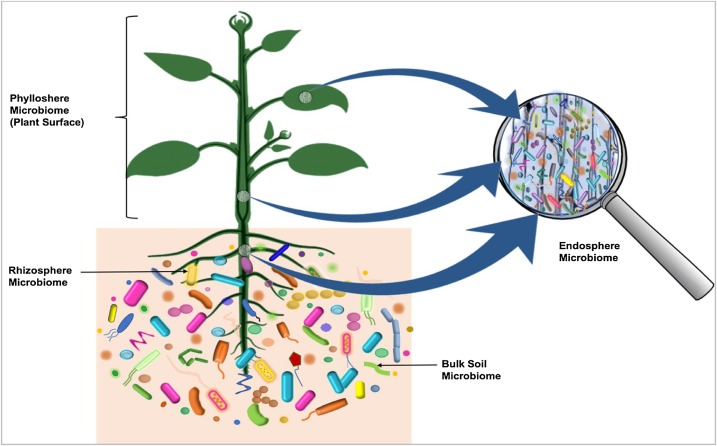
Microbiota
Microbiota are the range of microorganisms that may be commensal, symbiotic, or pathogenic found in and on all multicellular organisms, including plants. Microbiota include bacteria, archaea, protists, fungi, and viruses, and have been found to be crucial for immunologic, hormonal, and metabolic homeostasis of their host. The term ''microbiome'' describes either the collective genomes of the microbes that reside in an ecological niche or within the microbes themselves. The microbiome and host emerged during evolution as a synergistic unit from epigenetics and genetic characteristics, sometimes collectively referred to as a holobiont. The presence of microbiota in human and other metazoan guts has been critical for understanding the co-evolution between metazoans and bacteria. Microbiota play key roles in the intestinal immune and metabolic responses via their fermentation product ( short-chain fatty acid), acetate. Introduction All plants and animals, from simple l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fructans
A fructan is a polymer of fructose molecules. Fructans with a short chain length are known as fructooligosaccharides. Fructans can be found in over 12% of the angiosperms including both monocots and dicots such as agave, artichokes, asparagus, leeks, garlic, onions (including spring onions), yacón, jícama, barley and wheat. Fructans also appear in grass, with dietary implications for horses and other grazing animals (Equidae). Types Fructans are built up of fructose residues, normally with a sucrose unit (i.e. a glucose–fructose disaccharide) at what would otherwise be the reducing terminus. The linkage position of the fructose residues determine the type of the fructan. There are five types of fructans. Linkage normally occurs at one of the two primary hydroxyls (OH-1 or OH-6), and there are two basic types of simple fructan: * 1-linked: in inulin, the fructosyl residues are linked by β-2,1-linkages * 6-linked: in levan and phlein, the fructosyl residues are linked ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lactobacillus Casei
''Lacticaseibacillus casei ''is an organism that belongs to the largest genus in the family '' Lactobacillaceae'', a lactic acid bacteria (LAB), that was previously classified as ''Lactobacillus casei-01''. This bacteria has been identified as facultatively anaerobic or microaerophilic, acid-tolerant, non-spore-forming bacteria. The taxonomy of this group has been debated for several years because researchers struggled to differentiate between the strains of ''L. casei'' and ''L. paracasei''. It has recently been accepted as a single species with five subspecies: ''L. casei'' subsp. ''rhamnosus'', ''L. casei'' subsp. ''alactosus'', ''L. casei'' subsp. ''casei'', ''L. casei'' subsp. ''tolerans'', and ''L. casei'' subsp. ''pseudoplantarum''. The taxonomy of this genus was determined according to the phenotypic, physiological, and biochemical similarities. This species is a non-sporing, rod-shaped, gram positive microorganism that can be found within the reproductive and digestive t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
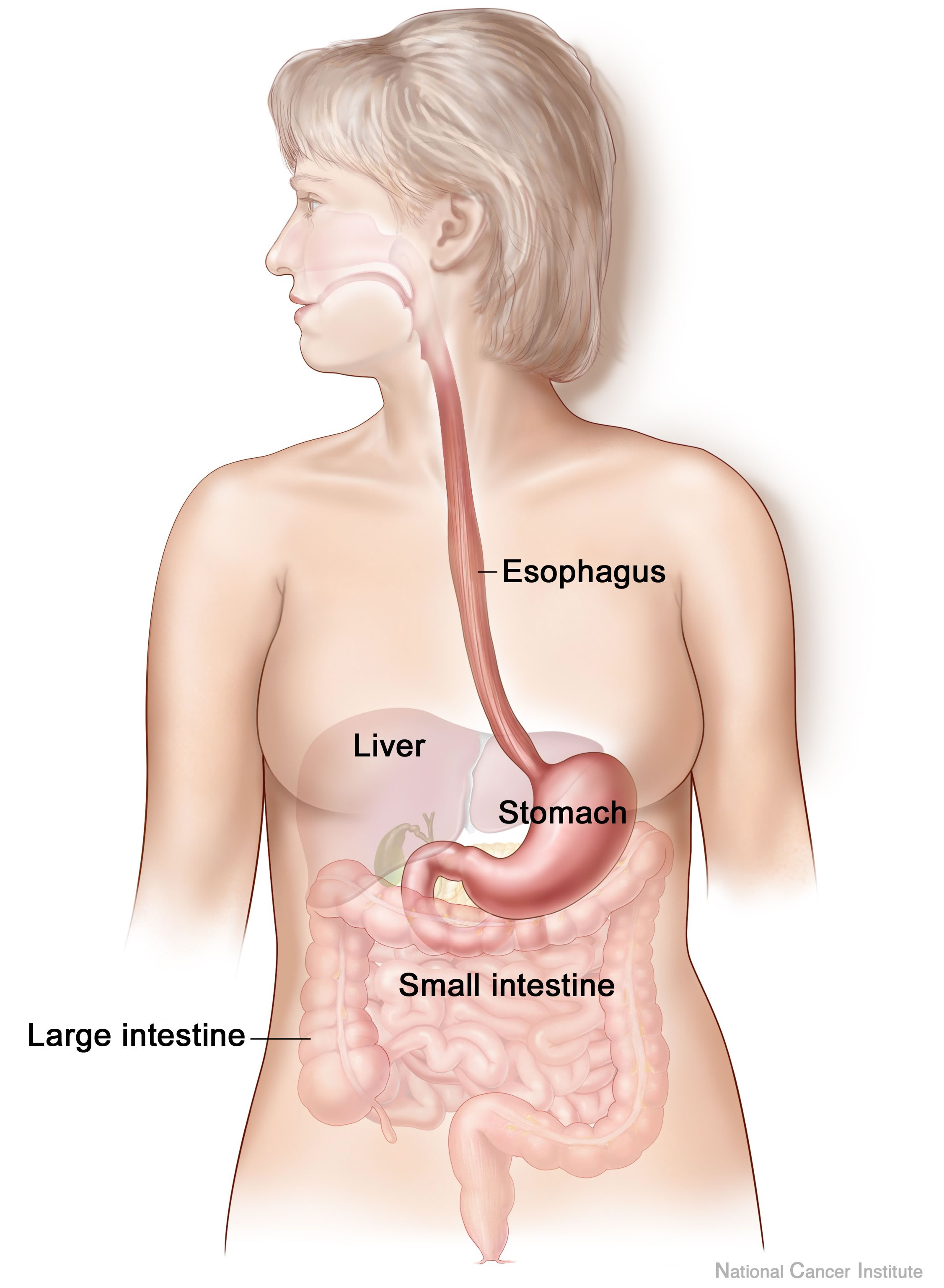
Digestive System
The human digestive system consists of the gastrointestinal tract plus the accessory organs of digestion (the tongue, salivary glands, pancreas, liver, and gallbladder). Digestion involves the breakdown of food into smaller and smaller components, until they can be absorbed and assimilated into the body. The process of digestion has three stages: the cephalic phase, the gastric phase, and the intestinal phase. The first stage, the cephalic phase of digestion, begins with secretions from gastric glands in response to the sight and smell of food. This stage includes the mechanical breakdown of food by chewing, and the chemical breakdown by digestive enzymes, that takes place in the mouth. Saliva contains the digestive enzymes amylase, and lingual lipase, secreted by the salivary and serous glands on the tongue. Chewing, in which the food is mixed with saliva, begins the mechanical process of digestion. This produces a bolus which is swallowed down the esophagus to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bacteriology
Bacteriology is the branch and specialty of biology that studies the morphology, ecology, genetics and biochemistry of bacteria as well as many other aspects related to them. This subdivision of microbiology involves the identification, classification, and characterization of bacterial species. Because of the similarity of thinking and working with microorganisms other than bacteria, such as protozoa, fungi, and viruses, there has been a tendency for the field of bacteriology to extend as microbiology. The terms were formerly often used interchangeably. However, bacteriology can be classified as a distinct science. Overview Definition Bacteriology is the study of bacteria and their relation to medicine. Bacteriology evolved from physicians needing to apply the germ theory to address the concerns relating to disease spreading in hospitals the 19th century. Identification and characterizing of bacteria being associated to diseases led to advances in pathogenic bacteriology. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lactobacillus Gasseri
''Lactobacillus gasseri'' is a species in the genus ''Lactobacillus'' identified in 1980 by François Gasser and his associates. It is part of the vaginal flora. Its genome has been sequenced. ''L. gasseri'' is a normal inhabitant of the lower reproductive tract in healthy women. It also produces Lactocillin. ''Lactobacillus gasseri'' produces gassericin A, a bacteriocin Bacteriocins are proteinaceous or peptidic toxins produced by bacteria to inhibit the growth of similar or closely related bacterial strain(s). They are similar to yeast and paramecium killing factors, and are structurally, functionally, and .... References Further reading * * * * *External links *[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lactobacillus Rhamnosus
''Lacticaseibacillus rhamnosus'' (previously ''Lactobacillus rhamnosus'') is a bacterium that originally was considered to be a subspecies of ''L. casei'', but genetic research found it to be a separate species in the ''L. casei'' clade, which also includes ''L. paracasei'' and ''L. zeae''. It is a short Gram-positive homofermentative facultative anaerobic non-spore-forming rod that often appears in chains. Some strains of ''L. rhamnosus'' bacteria are being used as probiotics, and are particularly useful in treating infections of the female urogenital tract, most particularly very difficult to treat cases of bacterial vaginosis (or "BV"). The species ''Lacticaseibacillus rhamnosus'' and ''Limosilactobacillus reuteri'' are commonly found in the healthy female genito-urinary tract and are helpful to regain control of dysbiotic bacterial overgrowth during an active infection. ''L. rhamnosus'' sometimes is used in dairy products such as fermented milk and as non-starter-lactic ac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |