|
Pseudo Jahn–Teller Effect
The pseudo Jahn–Teller effect (PJTE), occasionally also known as second-order JTE, is a direct extension of the Jahn–Teller effect (JTE) where spontaneous symmetry breaking in polyatomic systems (molecules and solids) occurs even in nondegenerate electronic states under the influence of sufficiently low-lying excited states of appropriate symmetry. "The pseudo Jahn–Teller effect is the only source of instability and distortions of high-symmetry configurations of polyatomic systems in nondegenerate states, and it contributes significantly to the instability in degenerate states". History In their early 1957 paper on the (what is now called) pseudo Jahn–Teller effect (PJTE), Öpik and Pryce showed that a small splitting of the degenerate electronic term does not necessarily remove the instability and distortion of the polyatomic system induced by the Jahn–Teller effect (JTE), provided the splitting is sufficiently small (the two split states remain “pseudo degenerate” ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jahn–Teller Effect
The Jahn–Teller effect (JT effect or JTE) is an important mechanism of spontaneous symmetry breaking in molecular and solid-state systems which has far-reaching consequences in different fields, and is responsible for a variety of phenomena in spectroscopy, stereochemistry, crystal chemistry, molecular and solid-state physics, and materials science. The effect is named for Hermann Arthur Jahn and Edward Teller, who first reported studies about it in 1937.Bunker, Philip R.; Jensen, Per (1998) ''Molecular Symmetry and Spectroscopy'' (2nd ed.). NRC Research Press, Ottaw/ref> Simplified overview The Jahn–Teller effect, sometimes also referred to as Jahn–Teller distortion, describes the geometrical distortion of molecules and ions that result from certain electron configurations. The Jahn–Teller theorem essentially states that any non-linear molecule with a spatially degenerate electronic ground state will undergo a geometrical distortion that removes that degeneracy, because t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Condensed Matter Physics
Condensed matter physics is the field of physics that deals with the macroscopic and microscopic physical properties of matter, especially the solid and liquid phases which arise from electromagnetic forces between atoms. More generally, the subject deals with "condensed" phases of matter: systems of many constituents with strong interactions between them. More exotic condensed phases include the superconducting phase exhibited by certain materials at low temperature, the ferromagnetic and antiferromagnetic phases of spins on crystal lattices of atoms, and the Bose–Einstein condensate found in ultracold atomic systems. Condensed matter physicists seek to understand the behavior of these phases by experiments to measure various material properties, and by applying the physical laws of quantum mechanics, electromagnetism, statistical mechanics, and other theories to develop mathematical models. The diversity of systems and phenomena available for study makes condensed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flexoelectricity
Flexoelectricity is a property of a dielectric material whereby it exhibits a spontaneous electrical polarization induced by a strain gradient. Flexoelectricity is closely related to piezoelectricity, but while piezoelectricity refers to polarization due to uniform strain, flexoelectricity refers specifically to polarization due to strain that changes from point to point in the material. This nonuniform strain breaks centrosymmetry, meaning that unlike in piezoelectiricty, flexoelectric effects can occur in centrosymmetric crystal structures. Flexoelectricity is not the same as Ferroelasticity. Inverse flexoelectricity, quite intuitively can be defined as generation of strain gradient due to polarization. Similarly extending on that, Converse flexoelectricity would refer to the process where a polarization gradient induces strain in a material. The electric polarization due to mechanical stress in a dielectric is given by :P_i=e_\epsilon_+\mu_\frac where the first term correspo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electrostriction
Electrostriction (cf. magnetostriction) is a property of all electrical non-conductors, or dielectrics, that causes them to change their shape under the application of an electric field. Explanation Electrostriction is a property of all dielectric materials, and is caused by displacement of ions in the crystal lattice upon being exposed to an external electric field. Positive ions will be displaced in the direction of the field, while negative ions will be displaced in the opposite direction. This displacement will accumulate throughout the bulk material and result in an overall strain (elongation) in the direction of the field. The thickness will be reduced in the orthogonal directions characterized by Poisson's ratio. All insulating materials consisting of more than one type of atom will be ionic to some extent due to the difference of electronegativity of the atoms, and therefore exhibit electrostriction. The resulting strain (ratio of deformation to the original dimension) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Permittivity
In electromagnetism, the absolute permittivity, often simply called permittivity and denoted by the Greek letter ''ε'' ( epsilon), is a measure of the electric polarizability of a dielectric. A material with high permittivity polarizes more in response to an applied electric field than a material with low permittivity, thereby storing more energy in the material. In electrostatics, the permittivity plays an important role in determining the capacitance of a capacitor. In the simplest case, the electric displacement field D resulting from an applied electric field E is :\mathbf = \varepsilon \mathbf. More generally, the permittivity is a thermodynamic function of state. It can depend on the frequency, magnitude, and direction of the applied field. The SI unit for permittivity is farad per meter (F/m). The permittivity is often represented by the relative permittivity ''ε''r which is the ratio of the absolute permittivity ''ε'' and the vacuum permittivity ''ε''0 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Multiferroicity
Multiferroics are defined as materials that exhibit more than one of the primary ferroic properties in the same phase: * ferromagnetism – a magnetisation that is switchable by an applied magnetic field * ferroelectricity – an electric polarisation that is switchable by an applied electric field * ferroelasticity – a deformation that is switchable by an applied stress While ferroelectric ferroelastics and ferromagnetic ferroelastics are formally multiferroics, these days the term is usually used to describe the ''magnetoelectric multiferroics'' that are simultaneously ferromagnetic and ferroelectric. Sometimes the definition is expanded to include nonprimary order parameters, such as antiferromagnetism or ferrimagnetism. In addition, other types of primary order, such as ferroic arrangements of magnetoelectric multipoles of which ferrotoroidicity is an example, have also been recently proposed. Besides scientific interest in their physical properties, multiferroics have potent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
BaTiO3
Barium titanate (BTO) is an inorganic compound with chemical formula BaTiO3. Barium titanate appears white as a powder and is transparent when prepared as large crystals. It is a ferroelectric, pyroelectric, and piezoelectric ceramic material that exhibits the photorefractive effect. It is used in capacitors, electromechanical transducers and nonlinear optics. Structure The solid exists in one of four polymorphs depending on temperature. From high to low temperature, these crystal symmetries of the four polymorphs are cubic, tetragonal, orthorhombic and rhombohedral crystal structure. All of these phases exhibit the ferroelectric effect apart from the cubic phase. The high temperature cubic phase is easiest to describe, as it consists of regular corner-sharing octahedral TiO6 units that define a cube with O vertices and Ti-O-Ti edges. In the cubic phase, Ba2+ is located at the center of the cube, with a nominal coordination number of 12. Lower symmetry phases are stabili ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Graphene
Graphene () is an allotrope of carbon consisting of a Single-layer materials, single layer of atoms arranged in a hexagonal lattice nanostructure. "Carbon nanostructures for electromagnetic shielding applications", Mohammed Arif Poothanari, Sabu Thomas, et al., ''Industrial Applications of Nanomaterials'', 2019. "Carbon nanostructures include various low-dimensional allotropes of carbon including carbon black (CB), carbon fiber, carbon nanotubes (CNTs), fullerene, and graphene." The name is derived from "graphite" and the suffix -ene, reflecting the fact that the graphite allotrope of carbon contains numerous double bonds. Each atom in a graphene sheet is connected to its three nearest neighbors by a strong σ-bond, and contributes to a valence band one electron that extends over the whole sheet. This is the same type of b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
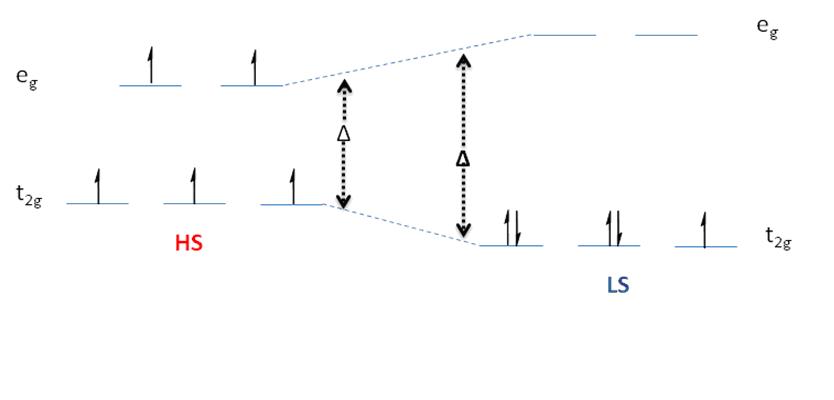
Spin Crossover
Spin crossover (SCO) is a phenomenon that occurs in some metal complexes wherein the spin state of the complex changes due to an external stimulus. The stimuli can include temperature or pressure. Spin crossover is sometimes referred to as spin transition or spin equilibrium behavior. The change in spin state usually involves interchange of low spin (LS) and high spin (HS) configuration. Spin crossover is commonly observed with first row transition metal complexes with a d4 through d7 electron configuration in an octahedral ligand geometry. Spin transition curves typically plot the high-spin molar fraction against temperature. Often a gradual spin transition is followed by an abrupt (ΔT = 10K) transition with hysteresis and a two-step transition. The abruptness with hysteresis indicates cooperativity, or “communication”, between neighboring metal complexes. In the latter case, the material is bistable and can exist in the two different spin states with a different range of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
-3D-balls.png)