|
Psammon
Psammon (from Greek "psammos", "sand") is a group of organisms inhabiting coastal sand moist — biota buried in sediments. Psammon is a part of water fauna, along with periphyton, plankton, nekton, and benthos Benthos (), also known as benthon, is the community of organisms that live on, in, or near the bottom of a sea, river, lake, or stream, also known as the benthic zone. Psammon is also sometimes considered a part of benthos due to its near-bottom distribution. Psammon term is commonly used to refer to freshwater reservoirs such as lakes. References {{Authority control Marine animals Biology termino ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Greek Language
Greek ( el, label= Modern Greek, Ελληνικά, Elliniká, ; grc, Ἑλληνική, Hellēnikḗ) is an independent branch of the Indo-European family of languages, native to Greece, Cyprus, southern Italy (Calabria and Salento), southern Albania, and other regions of the Balkans, the Black Sea coast, Asia Minor, and the Eastern Mediterranean. It has the longest documented history of any Indo-European language, spanning at least 3,400 years of written records. Its writing system is the Greek alphabet, which has been used for approximately 2,800 years; previously, Greek was recorded in writing systems such as Linear B and the Cypriot syllabary. The alphabet arose from the Phoenician script and was in turn the basis of the Latin, Cyrillic, Armenian, Coptic, Gothic, and many other writing systems. The Greek language holds a very important place in the history of the Western world. Beginning with the epics of Homer, ancient Greek literature includes many works of l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Periphyton
Periphyton is a complex mixture of algae, cyanobacteria, heterotrophic microbes, and detritus that is attached to submerged surfaces in most aquatic ecosystems. The related term Aufwuchs (German "surface growth" or "overgrowth") refers to the collection of small animals and plants that adhere to open surfaces in aquatic environments, such as parts of rooted plants. Periphyton serves as an important food source for invertebrates, tadpoles, and some fish. It can also absorb contaminants, removing them from the water column and limiting their movement through the environment. The periphyton is also an important indicator of water quality; responses of this community to pollutants can be measured at a variety of scales representing physiological to community-level changes. Periphyton has often been used as an experimental system in, e.g., pollution-induced community tolerance studies. Composition In both marine and freshwater environments, algae – particularly green algae and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
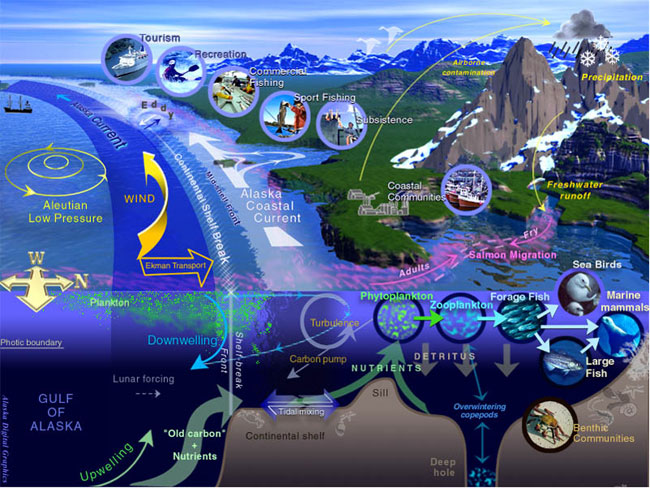
Plankton
Plankton are the diverse collection of organisms found in water (or air) that are unable to propel themselves against a current (or wind). The individual organisms constituting plankton are called plankters. In the ocean, they provide a crucial source of food to many small and large aquatic organisms, such as bivalves, fish and whales. Marine plankton include bacteria, archaea, algae, protozoa and drifting or floating animals that inhabit the saltwater of oceans and the brackish waters of estuaries. Freshwater plankton are similar to marine plankton, but are found in the freshwaters of lakes and rivers. Plankton are usually thought of as inhabiting water, but there are also airborne versions, the aeroplankton, that live part of their lives drifting in the atmosphere. These include plant spores, pollen and wind-scattered seeds, as well as microorganisms swept into the air from terrestrial dust storms and oceanic plankton swept into the air by sea spray. Though m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nekton
Nekton or necton (from the ) refers to the actively swimming aquatic organisms in a body of water. The term was proposed by German biologist Ernst Haeckel to differentiate between the active swimmers in a body of water, and the passive organisms that were carried along by the current, the plankton. As a guideline, nektonic organisms have a high Reynolds number (greater than 1000) and planktonic organisms a low one (less than 10). However, some organisms can begin life as plankton and transition to nekton later on in life, sometimes making distinction difficult when attempting to classify certain plankton-to-nekton species as one or the other. For this reason, some biologists choose not to use this term. History The term was first proposed and used by the German biologist Ernst Haeckel in 1891 in his article ''Plankton-Studien'' where he contrasted it with plankton, the aggregate of passively floating, drifting, or somewhat motile organisms present in a body of water, primarily t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Benthos
Benthos (), also known as benthon, is the community of organisms that live on, in, or near the bottom of a sea, river, lake, or stream, also known as the benthic zone.Benthos from the Census of Antarctic Marine Life website This community lives in or near marine or freshwater sedimentary environments, from tidal pools along the , out to the continental shelf, and then down to the [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Encyclopædia Britannica
The ( Latin for "British Encyclopædia") is a general knowledge English-language encyclopaedia. It is published by Encyclopædia Britannica, Inc.; the company has existed since the 18th century, although it has changed ownership various times through the centuries. The encyclopaedia is maintained by about 100 full-time editors and more than 4,000 contributors. The 2010 version of the 15th edition, which spans 32 volumes and 32,640 pages, was the last printed edition. Since 2016, it has been published exclusively as an online encyclopaedia. Printed for 244 years, the ''Britannica'' was the longest running in-print encyclopaedia in the English language. It was first published between 1768 and 1771 in the Scottish capital of Edinburgh, as three volumes. The encyclopaedia grew in size: the second edition was 10 volumes, and by its fourth edition (1801–1810) it had expanded to 20 volumes. Its rising stature as a scholarly work helped recruit eminent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of Salzburg
The University of Salzburg (german: Universität Salzburg), also known as the Paris Lodron University of Salzburg (''Paris-Lodron-Universität Salzburg'', PLUS), is an Austrian public university in Salzburg municipality, Salzburg state, named after its founder, Prince-Archbishop Paris Lodron. Established in 1622, the university was closed in 1810 and re-established in 1962. Nowadays, it has around 18,000 students and 2,800 employees; it is the largest educational institution in Salzburg state. It is divided into six faculties: Catholic Theology, Law and Economics, Cultural Sciences, Social Sciences, Natural Sciences, Analytical and Life Sciences. Benedictine University On 23 July 1622, Archbishop Paris Lodron appointed the scholar Albert Keuslin first rector of the Benedictine university. Keuslin, a graduate of the Jesuit University of Dillingen, had established the ''Akademisches Gymnasium'', a secondary school, at Salzburg five years earlier. By resolution of Emperor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marine Animals
Marine life, sea life, or ocean life is the plants, animals and other organisms that live in the salt water of seas or oceans, or the brackish water of coastal estuaries. At a fundamental level, marine life affects the nature of the planet. Marine organisms, mostly microorganisms, produce oxygen and sequester carbon. Marine life in part shape and protect shorelines, and some marine organisms even help create new land (e.g. coral building reefs). Most life forms evolved initially in marine habitats. By volume, oceans provide about 90% of the living space on the planet. The earliest vertebrates appeared in the form of fish, which live exclusively in water. Some of these evolved into amphibians, which spend portions of their lives in water and portions on land. One group of amphibians evolved into reptiles and mammals and a few subsets of each returned to the ocean as sea snakes, sea turtles, seals, manatees, and whales. Plant forms such as kelp and other algae grow in the wate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |